Question: What is the difference between a reversible and irreversible gas expansion? [26] How does a car battery store energy? [27] What are the common muzzle

![[26] How does a car battery store energy? [27] What are the](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667dd6645cb87_916667dd6642a5b9.jpg)


![range of their targets? [28] Michael Faraday was born very near to](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667dd665b7d70_917667dd6658ff22.jpg)










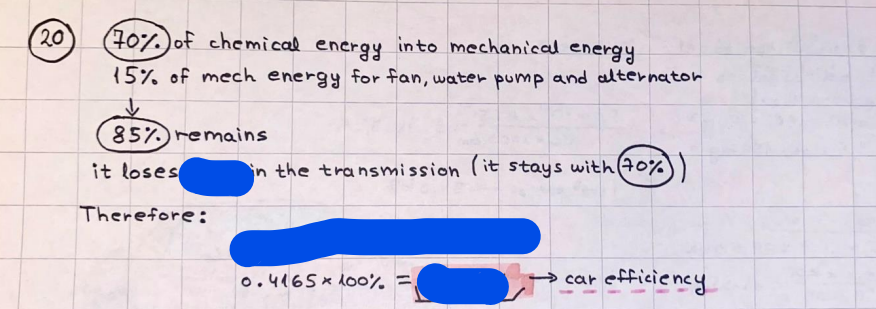







![CHY power = n x AHcomb [CH4]-+802 (exothermic) Power :Temp 4 *](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667dd6717b2ee_929667dd6715465f.jpg)








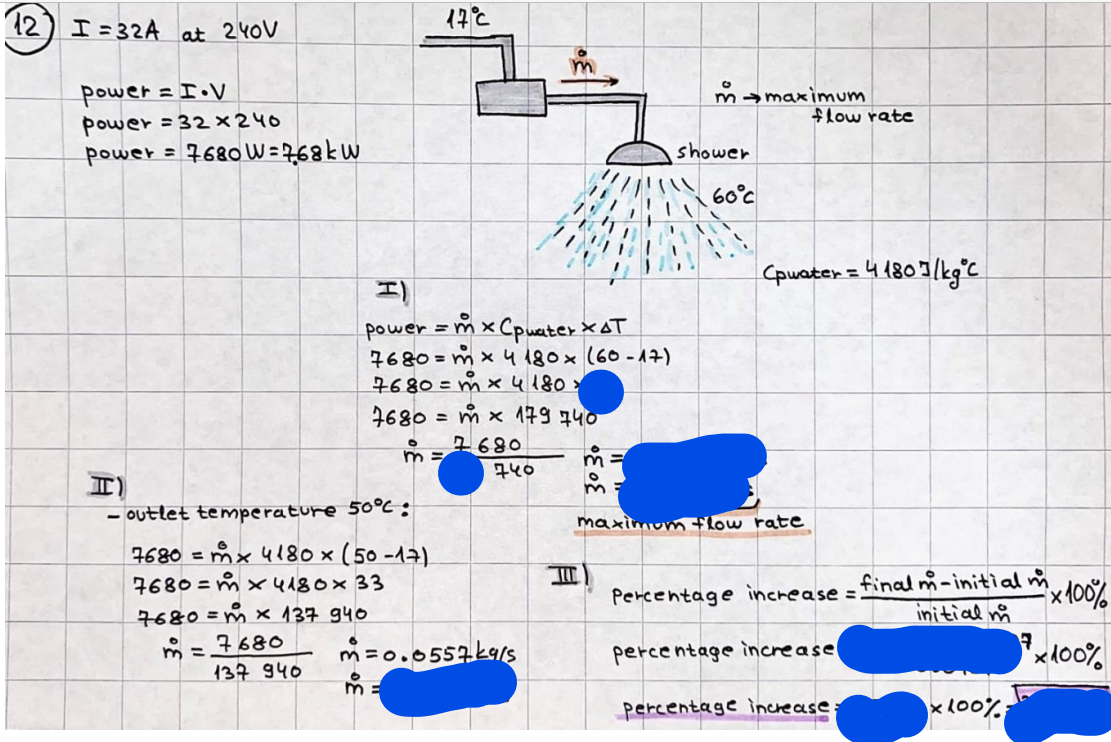
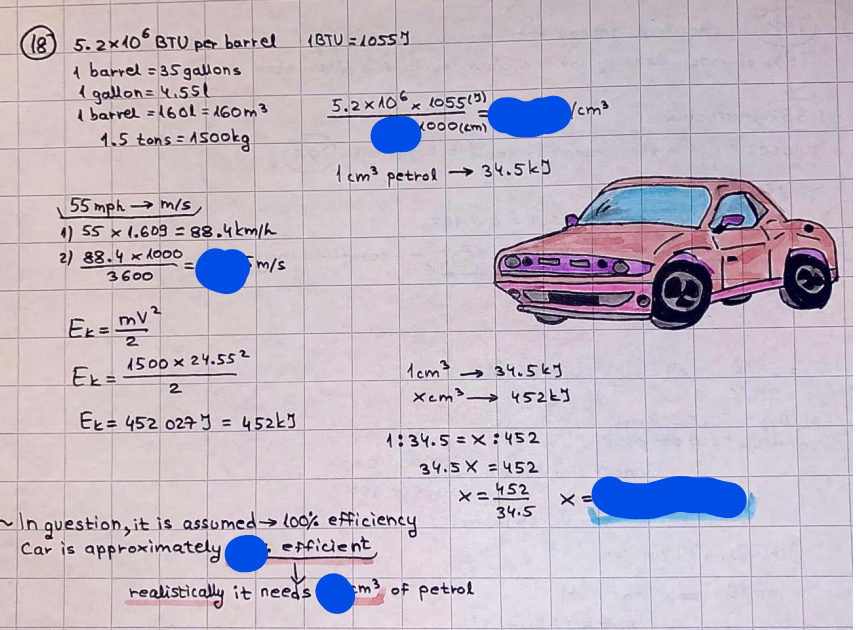

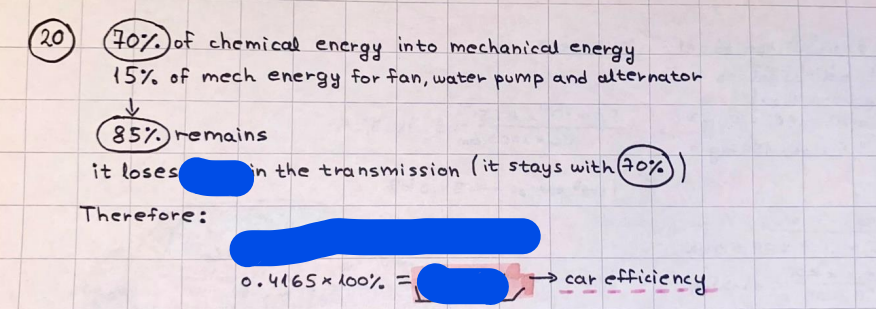
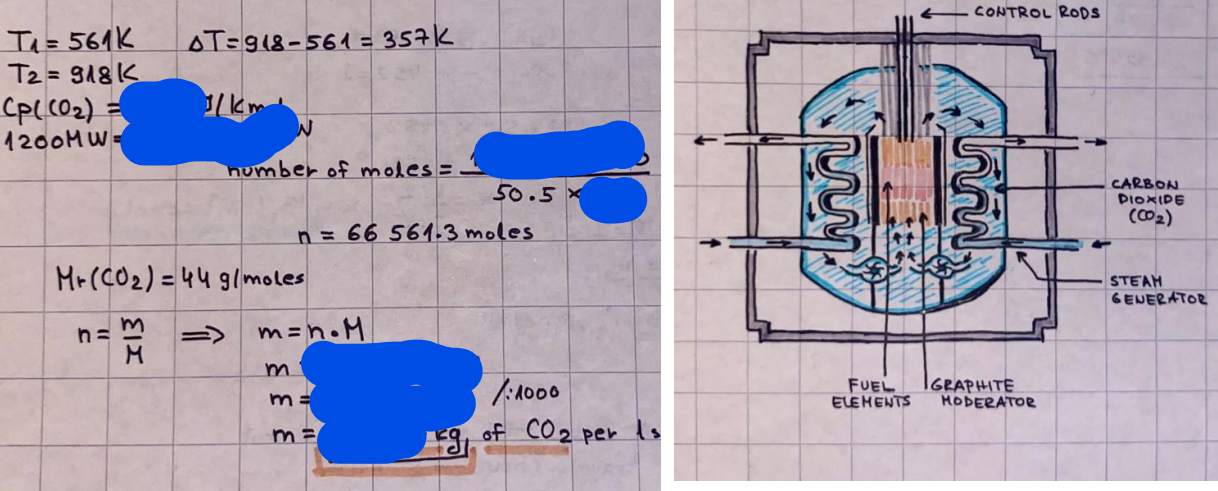
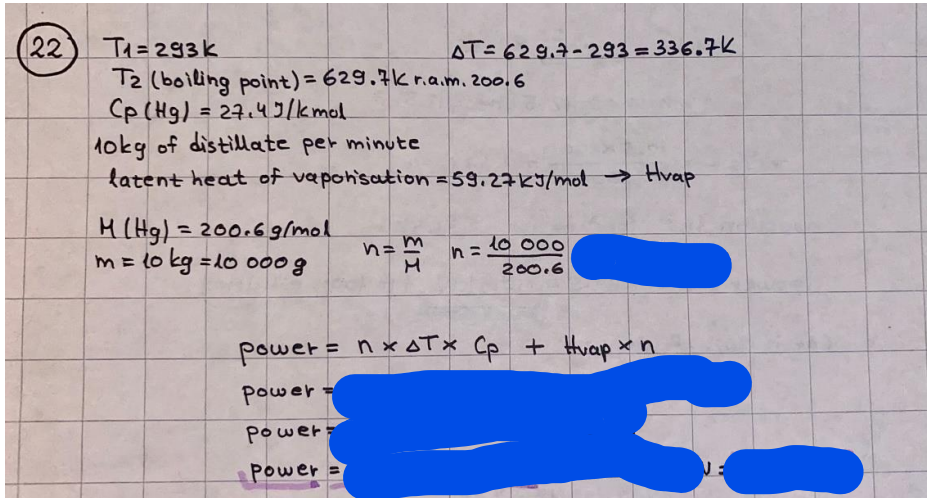


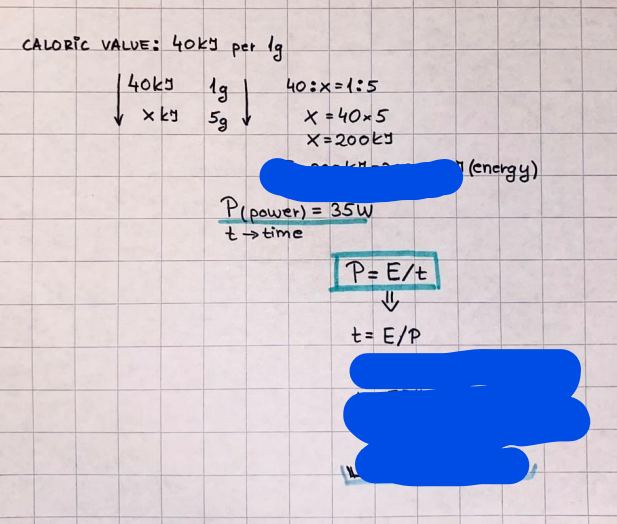
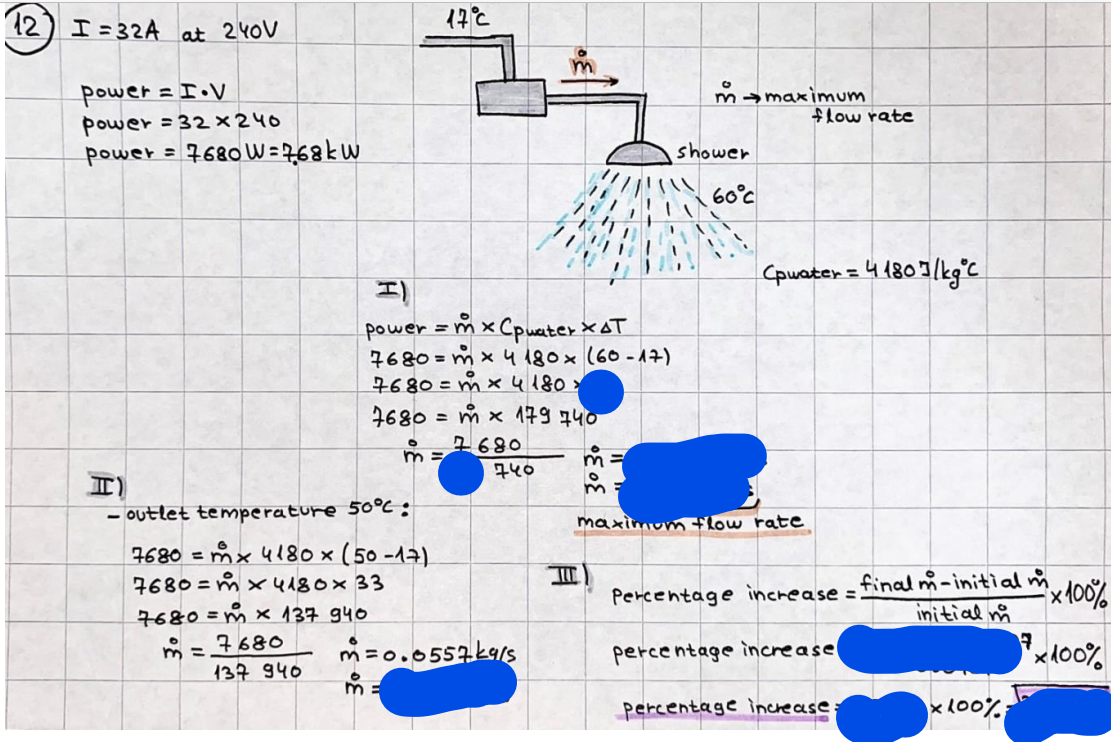
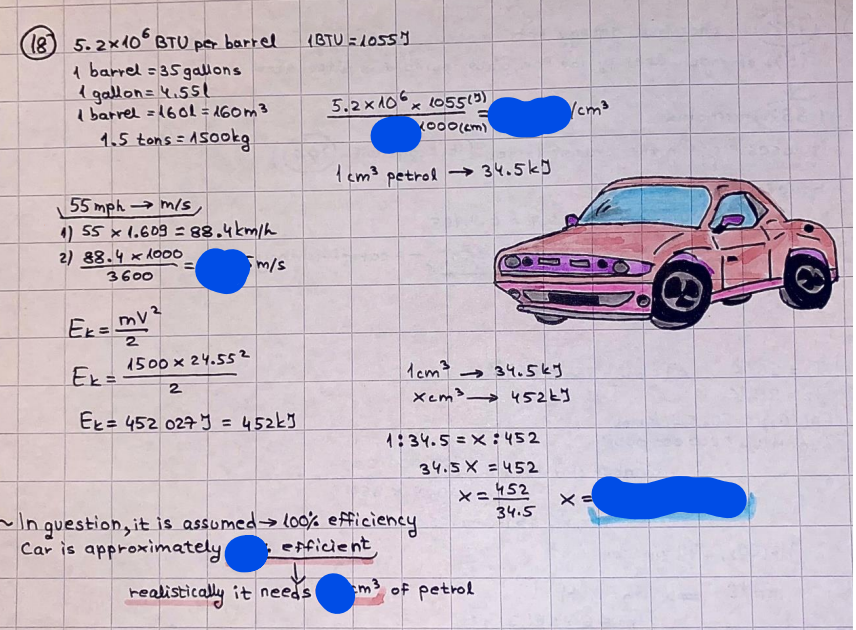
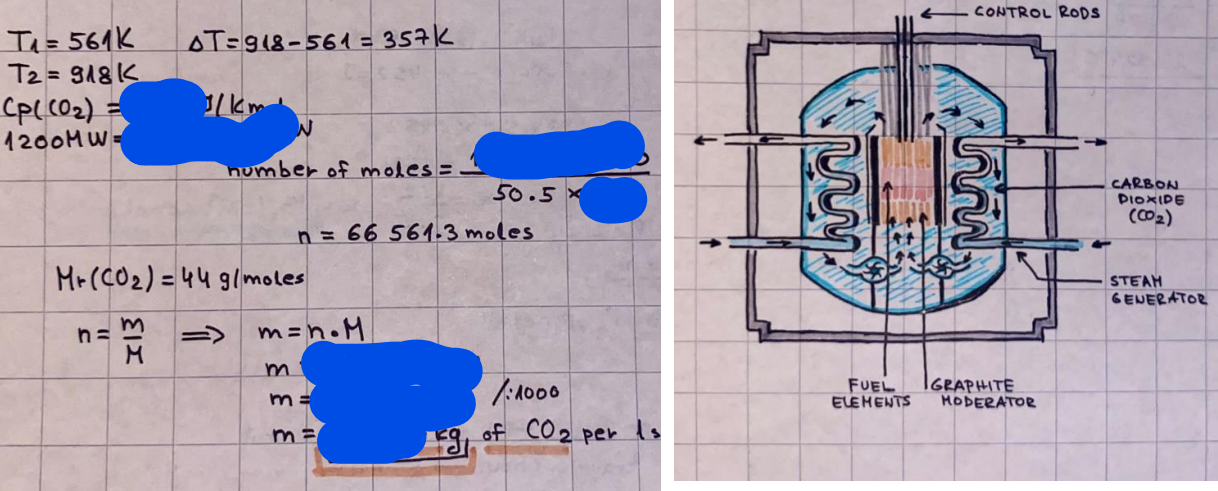
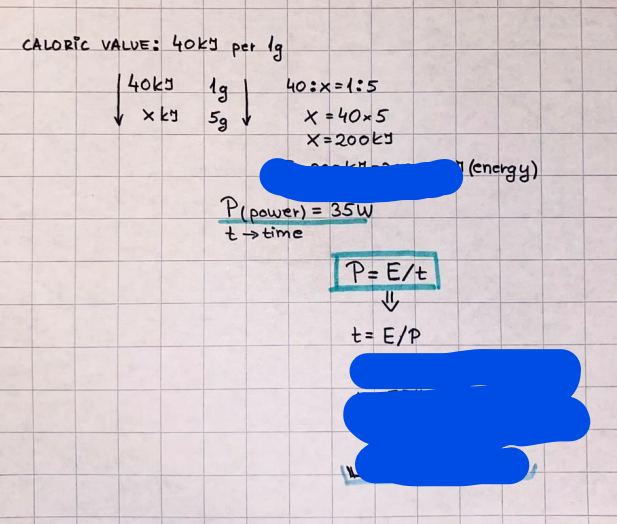
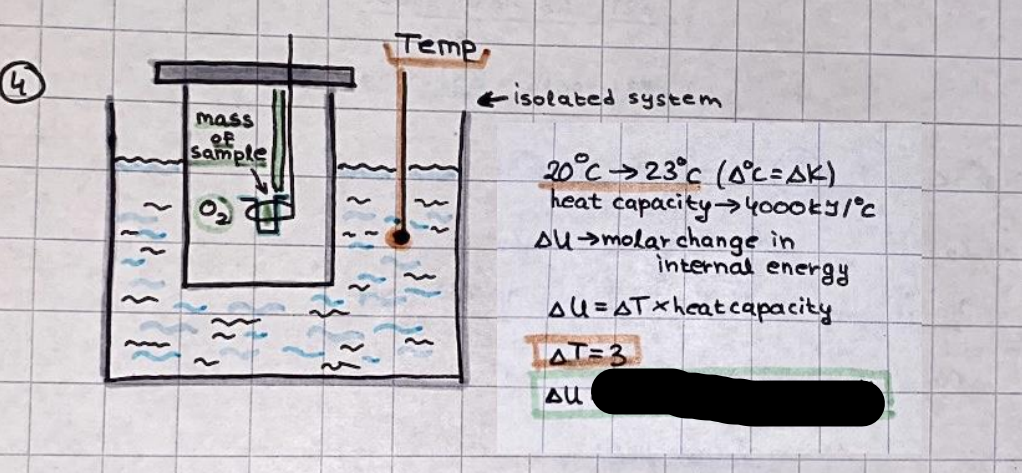
What is the difference between a reversible and irreversible gas expansion? [26] How does a car battery store energy? [27] What are the common muzzle exit velocities for ammunition in normal ries? What are the common bullet weights? What is the kinetic energy of these bullets within range of their targets? [28] Michael Faraday was born very near to the University. He gave a famous lecture to the Royal Society called \"The candle\". What are the mechanisms of heat transfer within the candle. Why does it give of a yellow light. If the calorific value of the candle is 4OKJ/gram then how long does a 5 gram (tea light) candle last for assuming that the ame generated is around 35 Watts. httpforeverin myheartpoemscomffou rcandlesl' \f2 V= 50dm 3 - T= Book h = M 0.05 m 3 02 - 1 kq 32 1) 02 n= 1006 = 31.25 makes He -> 1kg CO - o. 5kg He ne 1009 - 250 moles h = 299. 1 moles CO na 500 = 17.85 moles 28 2) total pressure: 3) partial pressures: PV = hRT P02 = 14 920 304 x 31.25 V= Sodm' =0.05m 299.4 ART . 299.1x 8. 314 + 300 PHe = 14 920 304 x 250 0. 05 299 . 4 PT = 14 920 309 W/m 2 PCo = 14 920 304 X 17.85 299. 43 4 litres per 1 minute; exothermic reaction 1 - molar flow rate V = 4 dm 3 = 0.004 m 3 AHcomb = - 802 kj/mol ( molar enthalpy of combustion) p = 10 N /m2 - atmospheric pressure CHy + 202 CO2 + H20 T = 25 C = 298 K PVSORT V = o. soum3 / min - V= 0.604 60 n = PV 1= 103 x0. 0000667 1 = 6.67 8. 314 x298 2427.57 n = 0. 00 26 9215 1 = 2. 692 * 10 -3 moles / molar flow rate powerrelease rate = molar flow rate x molar combustion enthalpy for CHY power = n x AHcomb [CH4]-+802 (exothermic) Power :Temp 4 * isolated system mass of Sample 20 C -> 23 c ( AC = AK ) heat capacity -> yoooky / "c 02 Au ->molar change in internal energy All = AT * heat capacity 3. TAT= 3 su5 P= 24 16/in2 = 24 psi - 165 474 1/m 2 winter - 5 % = 268k -> T1 summer 35 C = 308 K - T2 ASSUMPTION - volume stays constant: V1= V2 number of moles stays constant PAV1 = NAR T1 2. -> PAV ARTA n = const - = P2V2 = n2RT2 PEV MARTZ P4 T => P2 = PIX T2 P2 T2 P2 =\fpayload at 30 oooft? first: 1) What is the temperature at 30 ooo ft? 2) What is the pressure at 30 cooft? When the altitude increases by 100oft, the temperature decreases by 2"c, starting from sea level temperature . sea level - T = 25 c = 298 k 1000 ft / 2 " c 1000 : 30 000 = 2: X 30 00 0 sty x 1 1000 * = 30 000 * 2 1000 x X X T2 = 25 C - 60"C= - 35"C T2 = 238k 2) pressure decreases as altitude increases P = 4. 3psi= 30 061 Pa (30 00oft) PAYLOAD : PV= hRT (30 00oft) hel RT 30 061 X ( 13-04 => man . H 8.314 x 238 m = 1717.3x 2 n = 1717-3 moles H(He ) = 29/molASSUMPTIONS: Twater = 12ic AT = 88 C= 88K Tvapour = 100's delivery rate - 1ml /cm3 - 1ml of spray falls on lom? surface How much falls on Im 2? 1me Acm 21 1ml : x = lem2: 1m 2 X 1 m 2 * = 1me x 10 000 car2 AmL / cm 2 X = 10 000me = 1OL volume : V= 101 = 0.0 /m3 density: 8= 1000 kg/m3 m = J . V = loookg/ m3 x o. olm3 Cpwater = 4.18 5/gic Cp vapourazation at 12 c = 2 260 9/gic AHA = M CPAT = 10 x 4.18 x 88 = 3698k] D H2 = m x Cpvapourazation= * 2260 = 22 600 ky OH = AHA+ AH2 =m=0. 32129 C6H1206 Hr ( (6 H12 06) = 180. 156g/mal He(heat capacity)- 641 3/K m =o. 32/29 T1= 273. 160 k T2 = 280. 953K M -9. 3212 -0.00478 motes 180. 156 of glucose AT= 7.793k STIRRER C6H1206(5) + 60219) - 6 CO2/9)+ 6#2014) THERMOMETER COMBUSTION - EXOTHERMIC 2 = heat capacity x AT (enthalpy change is negative) 19 = 641 x 4.493 9 = 4 9957 = 4. 995 Ly ORIGEN the internal energy of combustion VESSEL II The enthalpy of combustion: WHPLE WATER A Hcomb = AHcomb 4.995 Ly 0.00148 mot & H comb = 2 806, 18 KM/ mal the enthalpy of combustion III) The enthalpy of formation exothermic reaction - Aftcomb=-2806. (8ky/ mol Atcomb = En sif products - En AHfreactants (1 - number of moles from the reaction ) A Hcomb = ( notts [ co 2 ] tho Hf [ H20] ) - ( notf [glucose] thoHy [o2] ) OHf [ CO2 ] = - 393 ky / mol AHf [ H20] = - 285 ky/mol OHS [0 2] = 0 ( in a free state ) c] the molar enthalpy of formation of glucose(4) the pressure the gas would exert if the temperature was raised to 1000K [2].. A vessel of volume 50 dm3 contains 1kg of 02(g), 0.5kg, He(g) and 0.5kg He(g) and 0.5 kg CO(g) at 300K. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas and the total pressure of the mixture. [3].. 4 litres per minute of methane gas ows into a burner at normal atmospheric and temperature conditions. The heat of combustion of methane is -802 KJ per mole. Work out o Molar flow rate 0 Power release rate [4].. The temperature of a bomb calorimeter increases from 20 C to 23 C. The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter is 4000 KJ/K. What is the change in internal energy assuming an isolated system. [5].. A car type in inflated to a pressure of 24 lbin'2 on a day when the temperature was 5C. What pressure will be found, assume no leaks, on a subsequent summer day when the temperature is 35C? [6].. A gas balloon has a diameter of 8m and is spherical when inated. How much H2(g) is needed to inflate it at a pressure of 1 atm at 25C at sea level?. What is the payload if He were used? What is the payload at 30,000 ft? [7].. How much power would be adsorbed by a ne spray of water directed at a substantial fire if the delivery rate were 1m| per cmz. Answer in kW/mz. [8].. When 0.3212g of glucose (CsH1205) was burnt in excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter OF HEAT CAPACITY 641 JK'1, its temperature rose from 273.160K to 280.953 K Calculate (a)molar internal energy of combustion (b)molar enthalpy of combustion (c)molar enthalpy of formation of glucose m.p.h) can be calculated from Ekm=112mv2 . How many cm3 of petrol is needed to provide this amount of energy [19].. The petrol consumption of the car above is 20 mpg at 55 mph. Calculate the power needed by the car at this speed. [20].. Under these conditions the engine converts 70% of the chemical energy in the fuel to mechanical energy of which 15% is used to drive the fan, water pump and alternator. The remainder is used in the transmission which loses 30%. Calculate the percentage efciency of the car. [21].. The primary coolant for the uranium oxide fuel elements of the Dungeness B AGR (Advanced gas cooled reactor) is C02 gas at high pressure which enters the core at 561 K and leaves at 918K. How many kg's of C02 must pass per second to remove 1200 MW from the core (Cp of 002: 50.5 JK'1mol") [22].. Liquid mercury is fed to a distillation plant at 293K. What is the power requirement of the plant when it delivers 10 kg of distillate per minute? Cp (Hg) = 27.4 JK'1mol'1 latent heat of vaporisation = 59.27 kJmol' 1 Boiling point = 629.7 K. r.a.m 200.6 [23] A 909 block of iron at 60C and a 40g block of aluminium at 85C are placed in 200g of water at 25C. Find the final temperature of the system (which is isolated). [24] Explain the relationship between chemical reaction rate and the Arrhenius rate constant. How does reaction rate depends upon temperature and activation energy. Draw a diagram to show how activation energy and reaction enthalpy are linked. Relate this to bond energies. (bond formation and bond breaking?) [25] One mole of an ideal gas expands from a pressure of 50atm to 1 atm against a constant external pressure of 1 atm while its temperature is held constant at 300 K. Calculate the work done by the gas and , given that for an ideal gas the change in internal energy is zero at constant temperature, the amount of energy absorbed as heat. Standard enthalpy of formation of liquid water is 285kJmol" Standard enthalpy of formation of carbon dioxide gas is 393.51 kJmol" [9].. What are the common methods used to protect against electrical circuit failure for domestic appliances such as kettles, washing machines, stereo ampliers, garden lawn mower. [10].. What are the ideal circumstances for fibrillation due to electric shock. Comment on voltage and current levels required. [11]..Does a steal ball obey Hooks Law. [12].. An electric shower consumes 32 amps at 240V AC. How much electric power is consumed. Assuming that the water inlet temperature is 17C and the outlet temperature is 60C what is the maximum ow rate of water that can be produced. If the outlet temperature is reduced to 50C what is the percentage increase in the ow rate. [13].. In a flammable atmosphere (say kitchen with a leak in the gas cooker) electrical devices may provide an ignition source. How are such sparks produced. [14].. Explain how energy is created in a nuclear reactor and how this is related to the neutron ux? What is a moderator and a control rod? [15] Explain the difference between energy produced by nuclear ssion and that produced by nuclear fusion in terms of binding energy per nucleon [16].. How was absolute zero dened? Can it be obtained? [17].. What is the difference between an ideal gas and a real gas. How do Helium and carbon dioxide behave in this respect. [18].. The chemical energy in petrol is about 5.2x105 BTU per barrel (1 barrel = 35 gallons: 4.55x10'3m3 and 1 BTU= 1055 J). The kinetic energy processed by 1.5 metric ton car with a constant speed of 55 BSc (HONS) FORENSIC SCIENCE Core and Materials Science The "Four candles" COURSE WORK THE FOUR CANDLES https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OCbvCRkl_4U [1].. 48g of Oz are contained in a vessel of 15 dm3 capacity at 320K. Assuming ideality calculate:- ) the number of moles of gas (2 ) the pressure of the gas (3) the density of the gas\f20 70% of chemical energy into mechanical energy 15% of mech energy for fan, water pump and alternator 85% remains it loses in the transmission ( it stays with 70% Therefore: 0. 4165 * 100% -> car efficiency\f22 T1= 293 k AT = 629.7- 293= 336.7K T2 ( boiling point) = 629. 7 kr.aim. 200,6 Cp ( Hg) = 27, 4 7 / kmol 10 kq of distillate per minute latent heat of vaporsation = 59. 27 KJ / mot -> Hrap H ( Hg) = 200. 6 9/mol m = 10 kg = 10 0oog n= 10 000 H 200. 6 power = n * ATX Cp + Huapx n power Power Power =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


