Question: What was the throughput result (in Mbps). Explain why this result is less than the result without the packet loss. (5%) Provide two reasons why

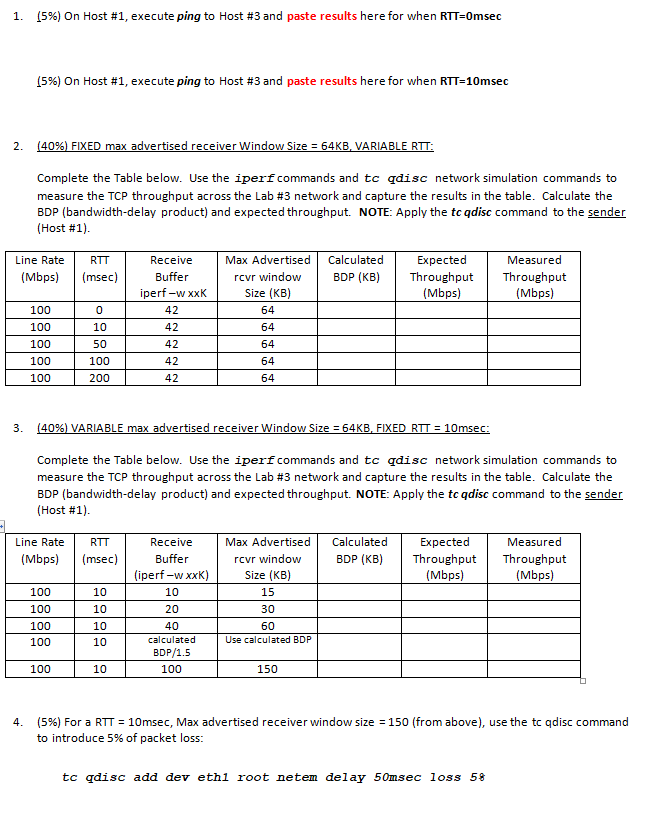
What was the throughput result (in Mbps). Explain why this result is less than the result without the packet loss.
(5%) Provide two reasons why your calculated expected throughput value is higher than the measured bandwidth result collected from iperf (HINT: the first reason relates to how the window size is derived, that is window size = min(cwnd, rwnd)?
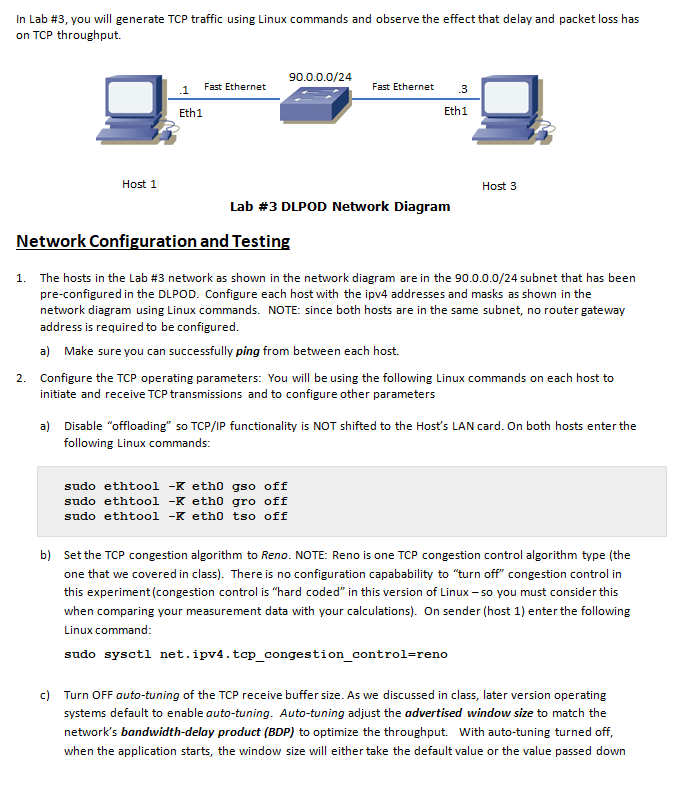
In Lab #3, you will generate TCP traffic using Linux commands and observe the effect that delay and packet loss has on TCP throughput. 90.0.0.0/24 Fast Ethernet Fast Ethernet 3 Eth1 Eth1 Host 1 Host 3 Lab #3 DLPOD Network Diagram Network Configuration and Testin I. The hosts in the Lab #3 network as shown in the network diagram are in the 90.0.0.0/24 subnet that has been pre-configured in the DLPOD. Configure each host with the ipv4 addresses and masks as shown in the network diagram using Linux commands. NOTE: since both hosts are in the same subnet, no router gateway address is required to be configured a) Make sure you can successfully ping from between each host. 2. Configure the TCP operating parameters: You will be using the following Linux commands on each host to initiate and receive TCP transmissions and to configure other parameters Disable "offloading" so TCP/IP functionality is NOT shifted to the Host's LAN card. On both hosts enter the following Linux commands a) sudo ethtool -K eth0 gso off sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off sudo ethtool -K eth0 tso off b) Set the TCP congestion algorithm to Reno. NOTE: Reno is one TCP congestion control algorithm type (the one that we covered in class). There is no configuration capabability to "turn off" congestion control in this experiment (congestion control is "hard coded" in this version of Linux- so you must consider this when comparing your measurement data with your calculations). On sender (host 1) enter the following Linux command sudo sysctl net.ipv4.top _congestion control-reno c) Turn OFF auto-tuning of the TCP receive buffer size. As we discussed in class, later version operating systems default to enable auto-tuning. Auto-tuning adjust the advertised window size to match the network's bandwidth-delay product (BDP) to optimize the throughput. With auto-tuning turned off, when the application starts, the window size will either take the default value or the value passed down In Lab #3, you will generate TCP traffic using Linux commands and observe the effect that delay and packet loss has on TCP throughput. 90.0.0.0/24 Fast Ethernet Fast Ethernet 3 Eth1 Eth1 Host 1 Host 3 Lab #3 DLPOD Network Diagram Network Configuration and Testin I. The hosts in the Lab #3 network as shown in the network diagram are in the 90.0.0.0/24 subnet that has been pre-configured in the DLPOD. Configure each host with the ipv4 addresses and masks as shown in the network diagram using Linux commands. NOTE: since both hosts are in the same subnet, no router gateway address is required to be configured a) Make sure you can successfully ping from between each host. 2. Configure the TCP operating parameters: You will be using the following Linux commands on each host to initiate and receive TCP transmissions and to configure other parameters Disable "offloading" so TCP/IP functionality is NOT shifted to the Host's LAN card. On both hosts enter the following Linux commands a) sudo ethtool -K eth0 gso off sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off sudo ethtool -K eth0 tso off b) Set the TCP congestion algorithm to Reno. NOTE: Reno is one TCP congestion control algorithm type (the one that we covered in class). There is no configuration capabability to "turn off" congestion control in this experiment (congestion control is "hard coded" in this version of Linux- so you must consider this when comparing your measurement data with your calculations). On sender (host 1) enter the following Linux command sudo sysctl net.ipv4.top _congestion control-reno c) Turn OFF auto-tuning of the TCP receive buffer size. As we discussed in class, later version operating systems default to enable auto-tuning. Auto-tuning adjust the advertised window size to match the network's bandwidth-delay product (BDP) to optimize the throughput. With auto-tuning turned off, when the application starts, the window size will either take the default value or the value passed down
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


