Question: When are two random samples independent? Random samples are independent by nature of random sampling. When sample data drawn from one population are related to
When are two random samples independent?
Random samples are independent by nature of random sampling.
When sample data drawn from one population are related to the selection of data from the other population.
When sample data drawn from one population are somewhat unrelated to the selection of data from the other population.
When sample data drawn from one population are completely unrelated to the selection of data from the other population.
When are two random samples dependent?
When each data value in one sample can be paired with a corresponding data value in the other sample.
When sample data drawn from one population are somewhat unrelated to the selection of data from the other population.
When sample data drawn from one population are completely unrelated to the selection of data from the other population.
Random samples are dependent by nature of random sampling.
Given that the standard deviations for two populations are unknown, choose the best answer.
Which of the following correctly calculates the standard error used to determine the margin of error for estimating the difference in means of two independent samples?
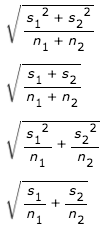
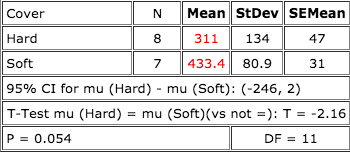
\fCover N Mean StDev SEMean Hard 8 311 134 47 Soft 7 433.4 80.9 31 95% CI for mu (Hard) - mu (Soft): (-246, 2) T-Test mu (Hard) = mu (Soft) (vs not =): T = -2.16 P = 0.054 DF = 11
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


