Question: When creating programs with multiple processes, tracking what's going on in open file tables is essential. It lets you make sure everything is closed properly,

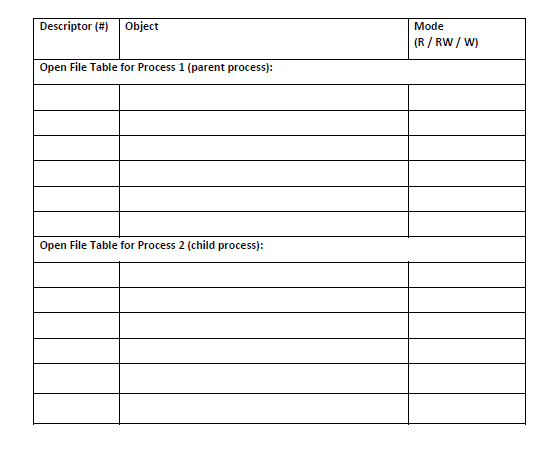
When creating programs with multiple processes, tracking what's going on in open file tables is essential. It lets you make sure everything is closed properly, and allocated to the right file descriptors. Assume a process (called "Process 1") runs the code below, beginning with stdin, stdout, and stderr in their usual locations in the process's open file table. Its child will be "Process 2". What does Process I's open file table look like immediately after executing the line marked with an "----- Location 1"? Do the same for Process 2 immediately after it would execute the line with " #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


