Question: When returns from a project can be assumed to be normally distributed (represented by a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve), the areas under the curve can be
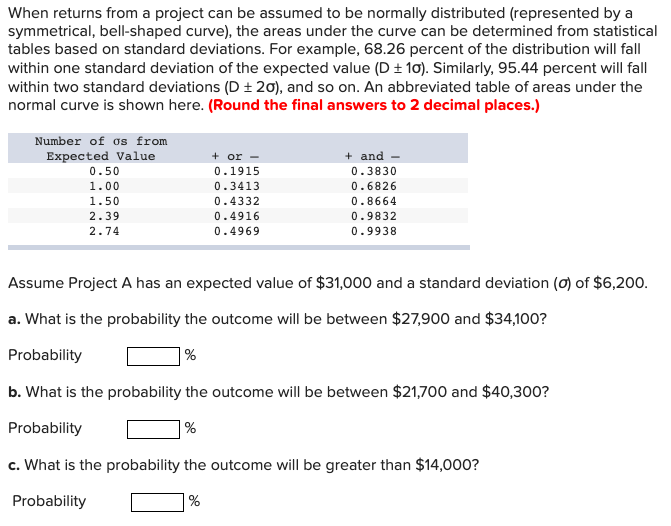
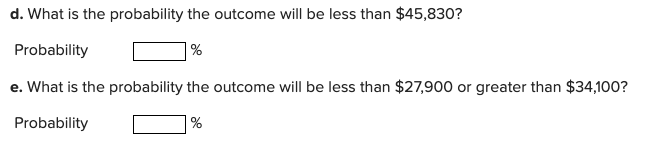
When returns from a project can be assumed to be normally distributed (represented by a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve), the areas under the curve can be determined from statistical tables based on standard deviations. For example, 68.26 percent of the distribution will fall within one standard deviation of the expected value (D + 10). Similarly, 95.44 percent will fall within two standard deviations (D = 20), and so on. An abbreviated table of areas under the normal curve is shown here. (Round the final answers to 2 decimal places.) Number of os from Expected Value 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.39 2.74 + or - 0.1915 0.3413 0.4332 0.4916 0.4969 + and 0.3830 0.6826 0.8664 0.9832 0.9938 Assume Project A has an expected value of $31,000 and a standard deviation () of $6,200. a. What is the probability the outcome will be between $27,900 and $34,100? Probability % b. What is the probability the outcome will be between $21,700 and $40,300? Probability % c. What is the probability the outcome will be greater than $14,000? Probability % d. What is the probability the outcome will be less than $45,830? Probability % e. What is the probability the outcome will be less than $27,900 or greater than $34,100? Probability %
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


