Question: Why we call the if function in Haskell a function? Because everything in Haskell is a function. Because it can be used inside a function

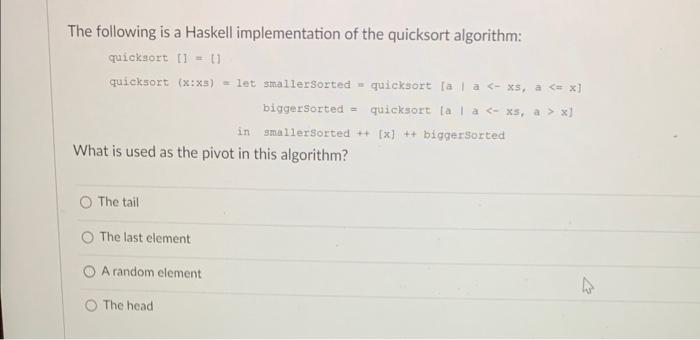
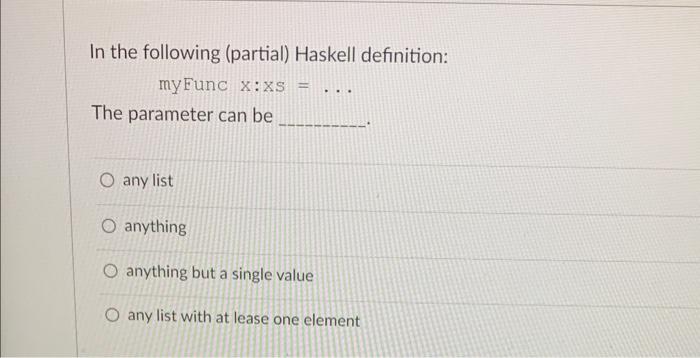
Why we call the "if" function in Haskell a function? Because everything in Haskell is a function. Because it can be used inside a function definition. Because it sounds more fancy this way. Because in Haskell, the "if" function must return a value. The following is a Haskell implementation of the quicksort algorithm: quioksort[1=quicksort(x:xs)=letsmallersorted=quicksort[aa
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


