Question: will upvote if the answer is correct 5. (20) Parsing Consider the CFG for in the slides (of L6) for parsing (Page 16), and an
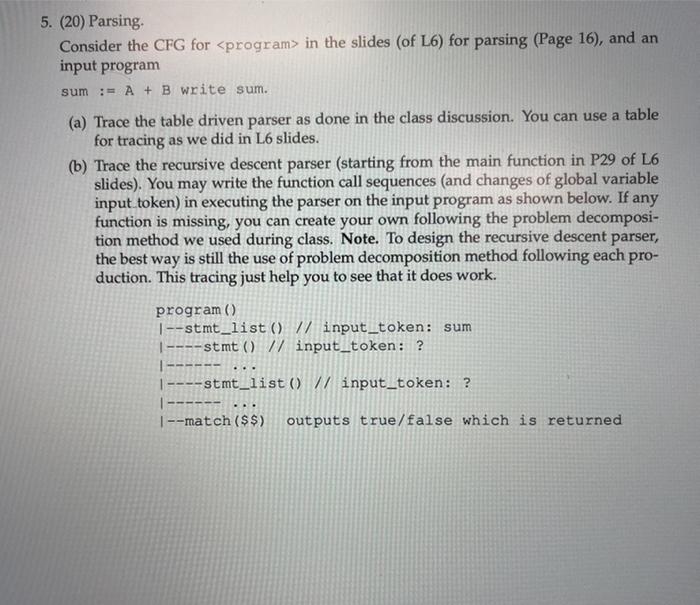
5. (20) Parsing Consider the CFG for
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


