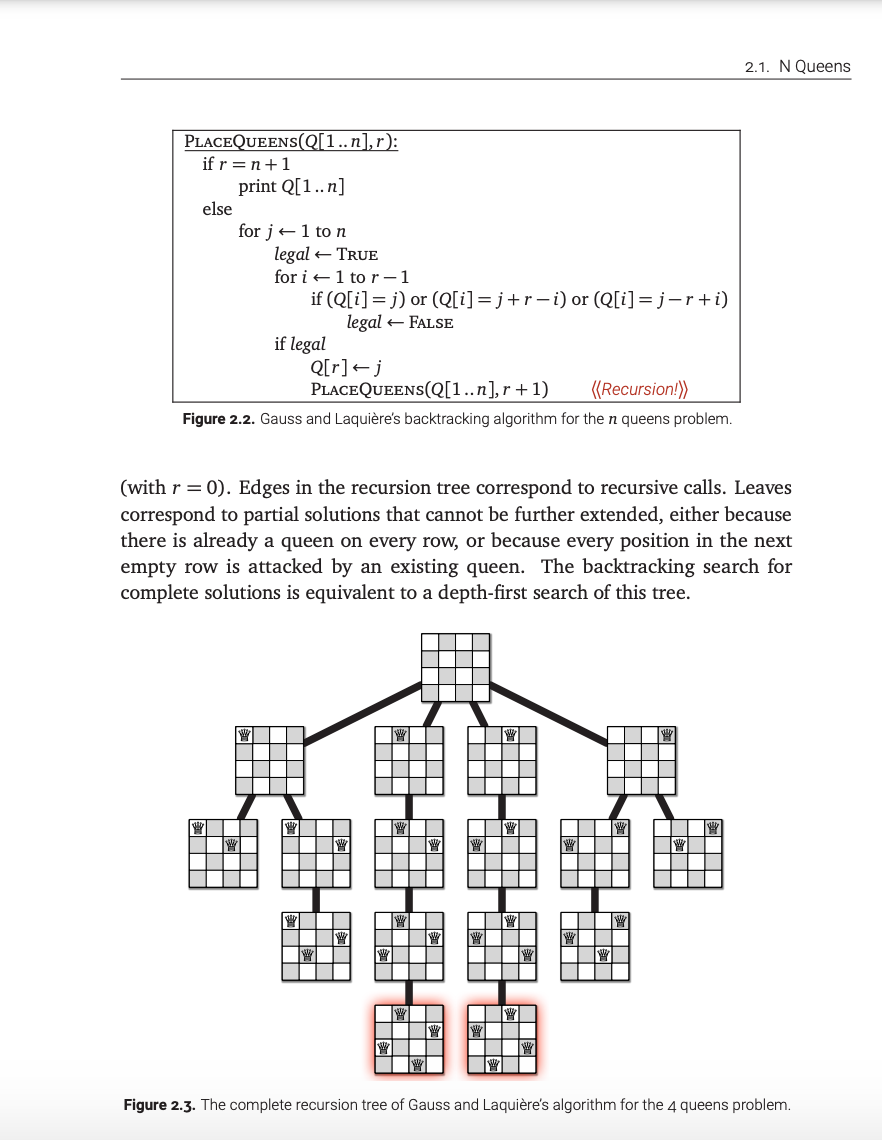
Question: (with r = 0). Edges in the recursion tree correspond to recursive calls. Leaves correspond to partial solutions that cannot be further extended, either because
(with r = 0). Edges in the recursion tree correspond to recursive calls. Leaves correspond to partial solutions that cannot be further extended, either because there is already a queen on every row, or because every position in the next empty row is attacked by an existing queen. The backtracking search for complete solutions is equivalent to a depth-first search of this tree.
Implement the algorithm PlaceQueens
the code to work for n not only 4 and calculate the execution time
Language to be used:
C++
2.1. N Queens PLACEQUEENS(Q[1..n],r): if r=n+1 print Q[1..n] else for j = 1 ton legal TRUE for i 1 to r-1 if (Q[i] = j) or (Q[i]=j+r-i) or (Q[i]=j-r+i) legal FALSE if legal Q[r]; PLACEQUEENS(Q[1..n],r+1) ((Recursion!) Figure 2.2. Gauss and Laquire's backtracking algorithm for the n queens problem. (with r = 0). Edges in the recursion tree correspond to recursive calls. Leaves correspond to partial solutions that cannot be further extended, either because there is already a queen on every row, or because every position in the next empty row is attacked by an existing queen. The backtracking search for complete solutions is equivalent to a depth-first search of this tree. Figure 2.3. The complete recursion tree of Gauss and Laquire's algorithm for the 4 queens
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


