Question: without comments please A graph is a non-linear data structure that enables representing relationships between different types of data. There are two main parts of
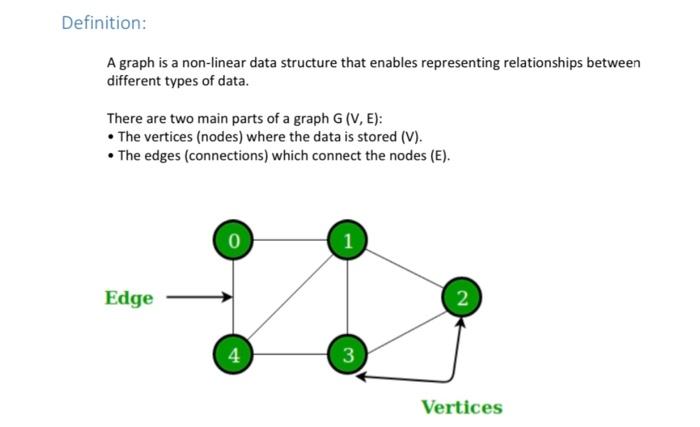




A graph is a non-linear data structure that enables representing relationships between different types of data. There are two main parts of a graph G(V,E) : - The vertices (nodes) where the data is stored (V). - The edges (connections) which connect the nodes (E). A structure, which contains a vertex and a pointer to the connected vertex, is created as follows: struct node\} int vertex; node "next; k Main Operations - Graph Traversal -Breadth-First-Search (BFS) -Depth-First-Search (DFS) - Minimum Spanning Tree: Kruskal Prim Lab Assignment Consider the following Ct+ code, which contains the following : - Define a structure node - All Queve implementation needed to implement BFS - Graph creation function using adjacency list - Main function return removed; 1 roid createGraph()\{ node newl, last; int neighbours,nv; cout n; cins>totNodes; for(int i=1;i That is Total Neighbours of "neighbours; for ( int j=1;jnv; newlunew node; newl->vertex =nv; newl->next=NULL; if (adj[i]=N NULL) adj[i]mastunewl; elsef last->next=newl;last=newl; \} y 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


