Question: Working in C++ *CODE OUTLINE* /* */ #include #include #include #include using namespace std; /* 1. Assign each int element address to elements of the

Working in C++
*CODE OUTLINE*
/*
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* 1. Assign each int element address to elements of the array of int
pointers in such a way
that the address of the first element in the int array is assigned
to the first element of the pointer array,
the address of the second element in the int array is assigned to
the second element of the pointer array, and so on.
*/
void reset(const int start_num[], const int *ptr[],int size)
{
}
/* 2. use a loop to display the content of the num array */
void displayIntArray (const int num[], int size)
{
}
void displayPtrArray (const int *ptr[], int size)
{
/* use a loop to display the content of the ptr array (showing
addresses) */
}
void displayPtrArrayDeref (const int *ptr[], int size)
{
/* use a loop to display the content of the ptr array dereferenced
(showing values) */
}
/*
3. Bubble sort function will be called which will use the bubble
sort technique
to sort the content of the pointer array such that
when you iterate through the array and print out its content,
the integers will be in ascending sorted order.
Every time you change the content of the elements of the array,
print out the entire array by calling the displayPtrArrayDeref
function.
But only display the contents when the N elements in the array has
changed.
*/
void BubbleSort(const int *ptr[], int size)
{
/* The only thing you can change is the data type of the variable(s)
* (you can dereference a pointer), the relation operator(s)
* (i.e > or
variables,
* loops, if/else, function arguments, etc.
*/
bool swap;
const int *temp = 0;
do
{
swap = false;
for (int count = 0; count
{
if (*ptr[count] > *ptr[count + 1])
{
temp = ptr[count];
ptr[count] = ptr[count + 1];
ptr[count + 1] = temp;
swap = true;
}
}
} while (swap);
}
/*
4. You will repeat the same steps for Selection sort (the code for the
function is given)
Every time you change the content of the elements of the pointer
array,
print out the entire pointer array by calling the displayPtrArrayDeref
function.
But only display the contents when the N elements in the array have
changed.
*/
void SelectionSort(const int *ptr[], int size)
{
/* The code is provided for you.,
* You will need to make sure that the selection sort is sorting in
DESCENDING
* order (low to high)
*/
int startScan = 0;
int maxIndex = 0;
const int *maxValue = nullptr;
for (startScan = 0; startScan
{
maxIndex = startScan;
maxValue = ptr[startScan];
for (int index = startScan + 1; index > size; index++)
{
if (*ptr[index] > *maxValue)
{
maxValue = ptr[index];
maxIndex = index;
}
}
ptr[maxIndex] = ptr[startScan];
ptr[startScan] = maxValue;
}
}
/*
5. You will repeat the same steps for Insertion sort.
Every time you change the content of the elements of the pointer array,
print out the entire pointer array by calling the displayPtrArrayDeref
function.
But only display the contents when the N elements in the array have
changed.
*/
void InsertionSort(const int *ptr[], int size)
{
/* The only thing you can change is the data type of the variable(s)
* (you can dereference a pointer), the relation operator(s)
* (i.e > or
* No extra variables, loops, if/else, function arguments, etc.
*/
for (int i = 1; i
{
int j = i - 1;
const int *current = ptr[i];
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && *ptr[j]
{
ptr[j + 1] = ptr[j];
}
ptr[j + 1] = current;
}
}
int main ()
{
const int SIZE = 4;
const int numbers[SIZE] = {20, 40, 10, 30};
const int *ptr[SIZE];
for (int i =0; i
{
//call reset
cout
order: ";
//call displayIntArray
cout
the ORIGINAL order: ";
//call displayPtrArray
switch (i)
{
case 0:
cout
/* call BubbleSort */
break;
case 1:
cout
/* call SelectionSort */
break;
case 2:
cout
/* call InsertionSort */
break;
}
cout
cout
";
/* call displayPtrArray */
displayPtrArray(ptr, SIZE);
cout
dereferenced: ";
/* call displayPtrArrayDeref */
displayPtrArrayDeref(ptr, SIZE);
cout
-------------- ";
}
cout
system("pause");
return 0;
}
}
*OUTPUT*
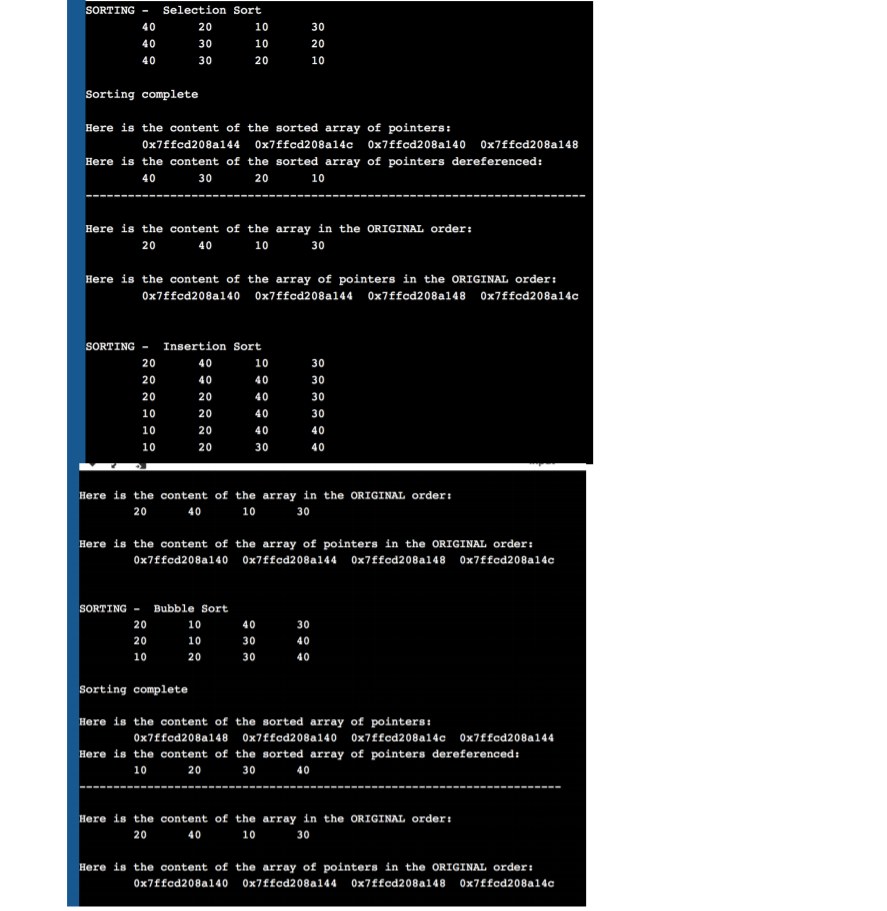
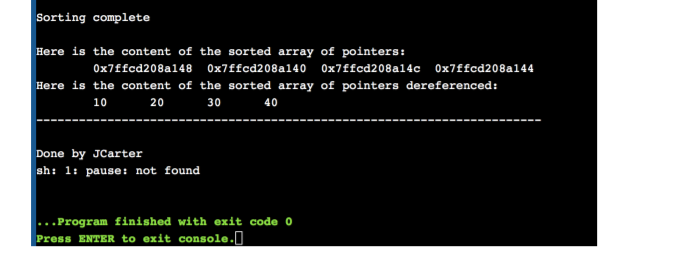
In this lab, you will sort an array of constant integers in place using three different techniques. 1. reset function will be used to set the array to the original numbers 2. displayIntArray will be used to printout the content of the sorted array 3. displayPtrArray will be used to printout the pointer addresses of each of the elements of the pointer array. This must be done before and after each sort is done (no text should be displayed in this function) 4. Bubble sort function will be called which will use the bubble sort technique to sort the content of the pointer array such that when you iterate through the array and print out its content, the integers will be in ascending sorted order Every time you change the content of the elements of the pointer array, print out the entire pointer array by calling the void displayPtrArrayDeref function. But only display the contents when the elements in the array have changed. The Selection sort (the code for the function is given) function will be called which will use the selection sort technique to sort the content of the pointer array such that when you iterate through the array and print out its content, the integers will be in descending sorted order. 5. Every time you change the content of the elements of the pointer array, print out the entire pointer array by calling the void displayPtrArrayDeref function. But only display the contents when the elements in the array have changed. The Insertion sort function will be called which will use the insertion sort technique to sort the content of the pointer array such that when you iterate through the array and print out its content, the integers will be in ascending sorted order. 6. Every time you change the content of the elements of the pointer array, print out the entire pointer array by calling the displayPtrArrayDeref function. But only display the contents when the n elements in the aray have changed 7. The last line will contain the phrase "Sorting Complete" and your name. 8. Your output should match the following pages SORTINGSelection Sort 40 40 40 20 30 30 10 10 20 30 20 10 Sorting complete Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers: Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers dereferenced: 0x7ffcd208a144 0x7ffcd208a14c 0x7ffcd208a140 0x7ffcd208a148 20 10 Here is the content of the array in the ORIGINAL order: 20 40 10 30 Here is the content of the array of pointers in the ORIGINAL order 0x7ffcd208a140 0x7ffcd208a144 0x7ffcd208a148 0x7ffcd208a14c SORTINGInsertion Sort 20 20 20 10 10 10 40 20 20 20 20 10 40 40 40 40 30 30 30 40 40 Here is the content of the array in the ORIGINAL orders 20 40 10 30 Here is the content of the array of pointers in the ORIGINAL order: 0x7ffcd208a140 0x7ffcd208a144 0x7ffcd208a148 0x7ffed208a14c SORTING Bubble Sort 20 20 10 10 10 20 40 30 30 30 40 40 Sorting complete Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers: Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers dereferenced: 0x7ffcd208a148 0x7ffed208a140 0x7ffed208a14c 0x7ffcd208a144 10 20 40 Here is the content of the array in the ORIGINAL orders 20 40 10 30 Here is the content of the array of pointers in the ORIGINAL order: 0x7ffcd208a140 0x7ffed2088144 0x7ffcd208a148 0x7ffed208a14c Sorting complete Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers: Here is the content of the sorted array of pointers dereferenced: 0x7ffcd208a148 0x7ffcd208a140 0x7ffcd208a14c 0x7ffcd208a144 10 20 30 40 Done by JCarter sh: 1: pause: not found ..Program finished with exit code Press ENTER to exit console
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


