Question: Working with floatx numbers will require a lot of bit manipulation. The purpose of bitField.c was to provide bit manipulation tools that you can use
Working with floatx numbers will require a lot of bit manipulation. The purpose of bitField.c was to provide bit manipulation tools that you can use in this project.
Create a floatx number from a doubleprecision floating point value.
For the project, you will need to implement a single function, the doubleToFloatx function that takes a double precision floating point input argument, along with the total number of bits and the number of exponent bits for the floatx version of the value. The function needs to return the floatx version of the number.
At a high level, doing the conversion requires several manipulations:
Extracting the sign bit from the double value, and inserting it into the floatx value at the correct position.
Handle special cases, such as infinity, or notanumber.
Extract the biased exponent from the double value. Check to see if the double value is subnormal. If so handle it Check to make sure the floatx exponent won't overflow or underflow If so handle as a special case. If not, rebias the exponent using the floatx bias which depends on the number of exponent bits and write the result to the correct location in the floatx result.
Extract the fraction bits from the double value. Determine how many bits are available for the fraction in the floatx value, and truncate or extend the original value, and write the resulting bits to the floatx result.
Return the floatx result.
Provided to you: floatx.h and floatx.c
The floatx.h file declares the single floatx function, doubleToFloatx it will be working on for this project. The floatx.h file also contains a typedef statement to define floatx as an unsigned long bit integer. You should not have to edit floatx.h
Your main job will be to complete the definition of the doubleToFloatx function in floatx.c This is the function that takes a double precision floating point value, and returns the floatx representation of that value.
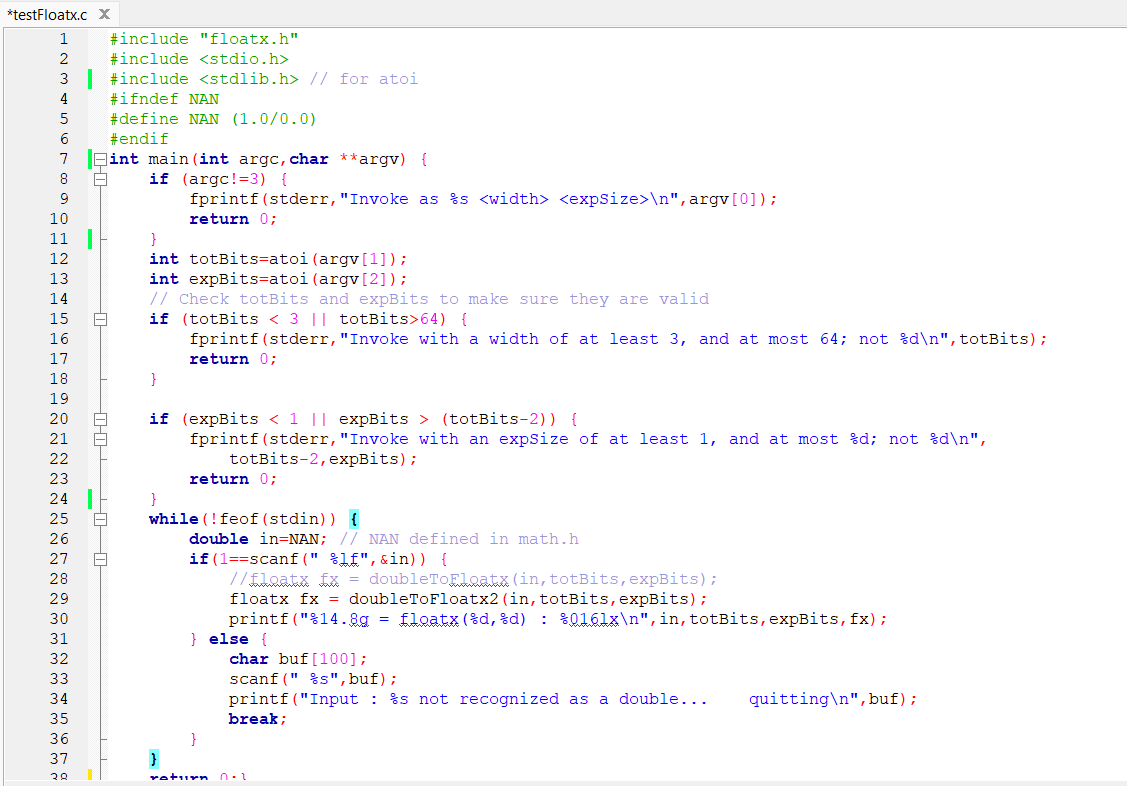
testFloatx.c is a program that uses command line arguments to specify the total number of bits, and the number of exponent bits in a floatx format. It then reads standard input, looking for a double precision floating point value. For each floating point value found in standard input:
the testFloatx program invokes doubleToFloatx with the value read from standard input, and the total bits and exponent size specified in the command line arguments.
prints the original value, the floatx specification, and the floatx value in hexadecimal.
Any nonwhitespace characters from standard input that cannot be translated to a double will cause the program to stop.
We will use UNIX redirection to read and write from files Please do not edit the code in testFloatx.c There is no need to use file IO functions to read or write files for this project.
## Coding the project
After reading through this readme, decide whether you want to use the bitFields library. If so follow the instructions above. Then, start working on floatx.c implementing the doubleToFloatx function. Use make test to check your results. You can use online floating point calculators to figure out what the correct values should be for a float or double specification, so get those working first.
You will have to manually verify the results for other specifications, such as a floatx specification.
Here is an example of the output produced when your program is coded correctly:
floatx : f
floatx : c
floatx : faaaaaa
e floatx : f
e floatx : a
e floatx : fc
e floatx : ffffff
e floatx : ffffff
Input : q not recognized as a double... quitting
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


