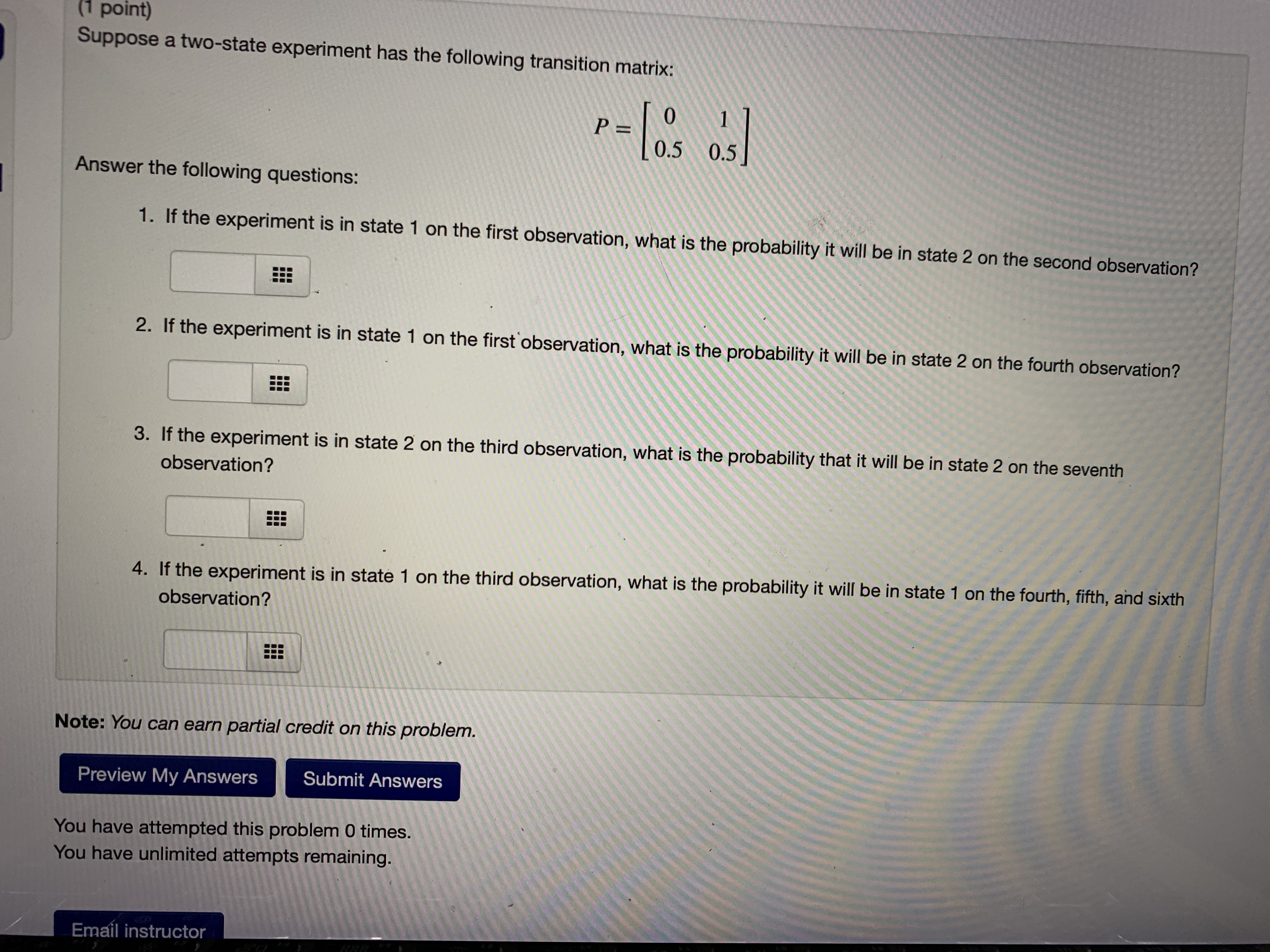
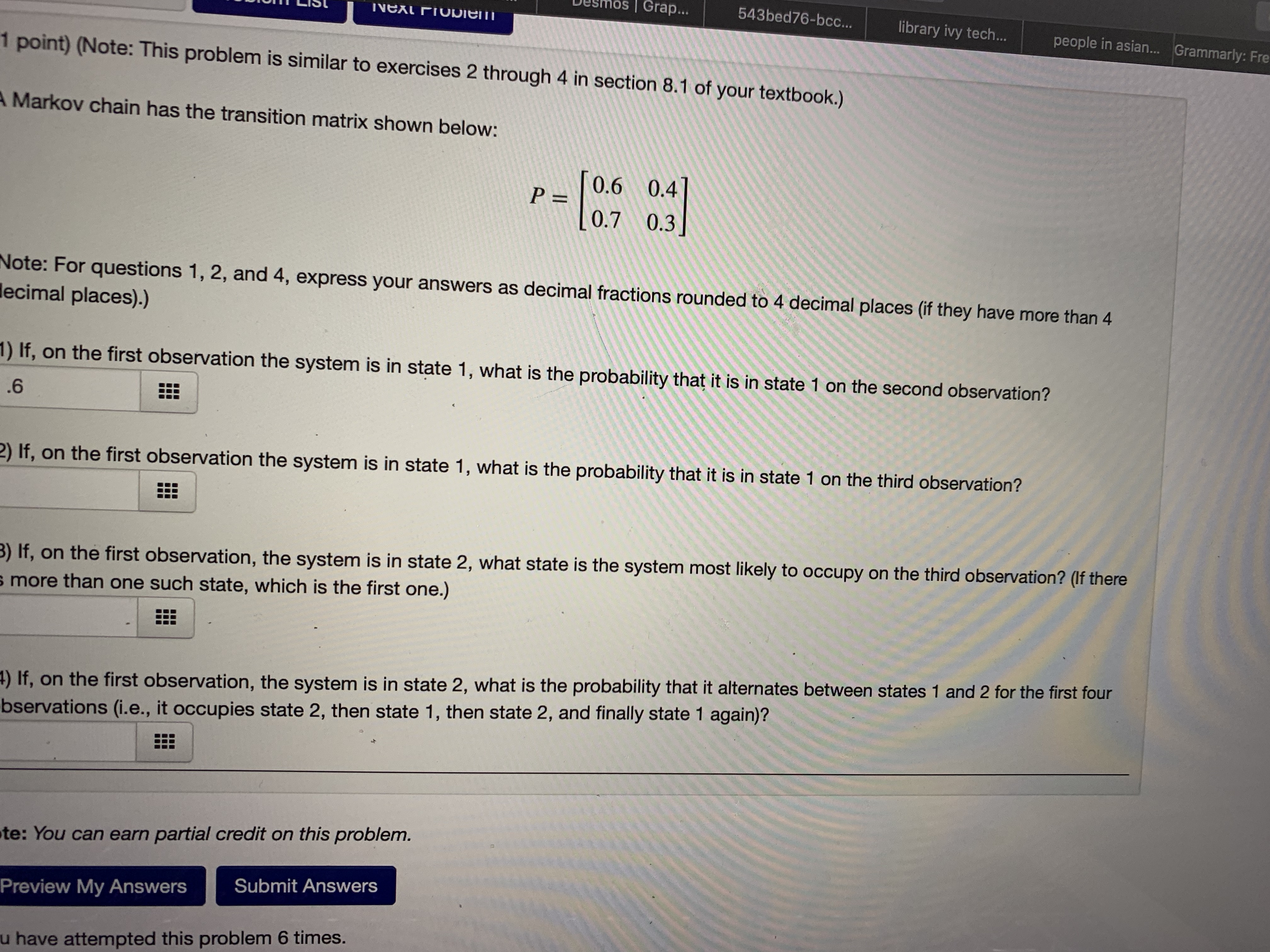
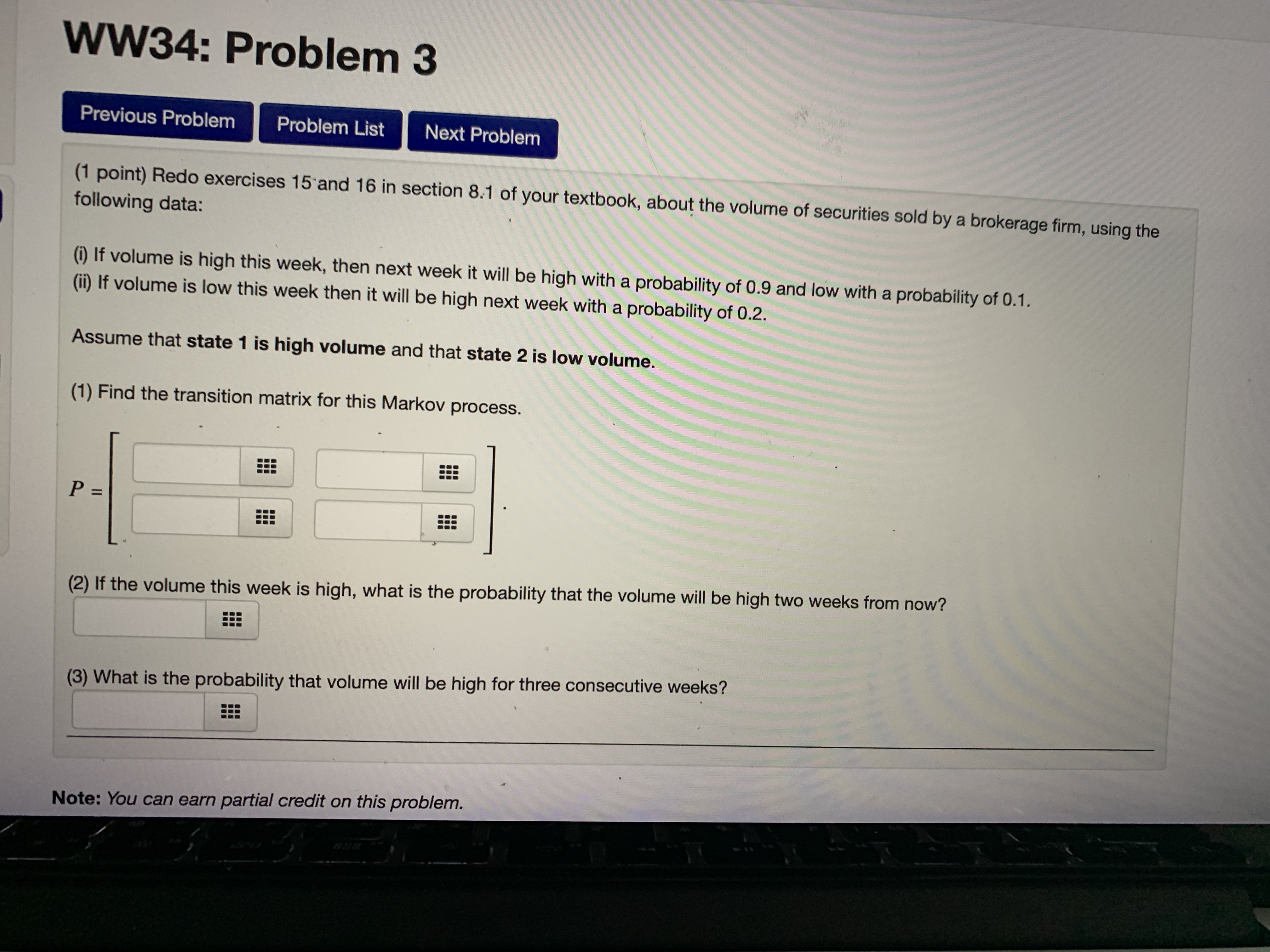
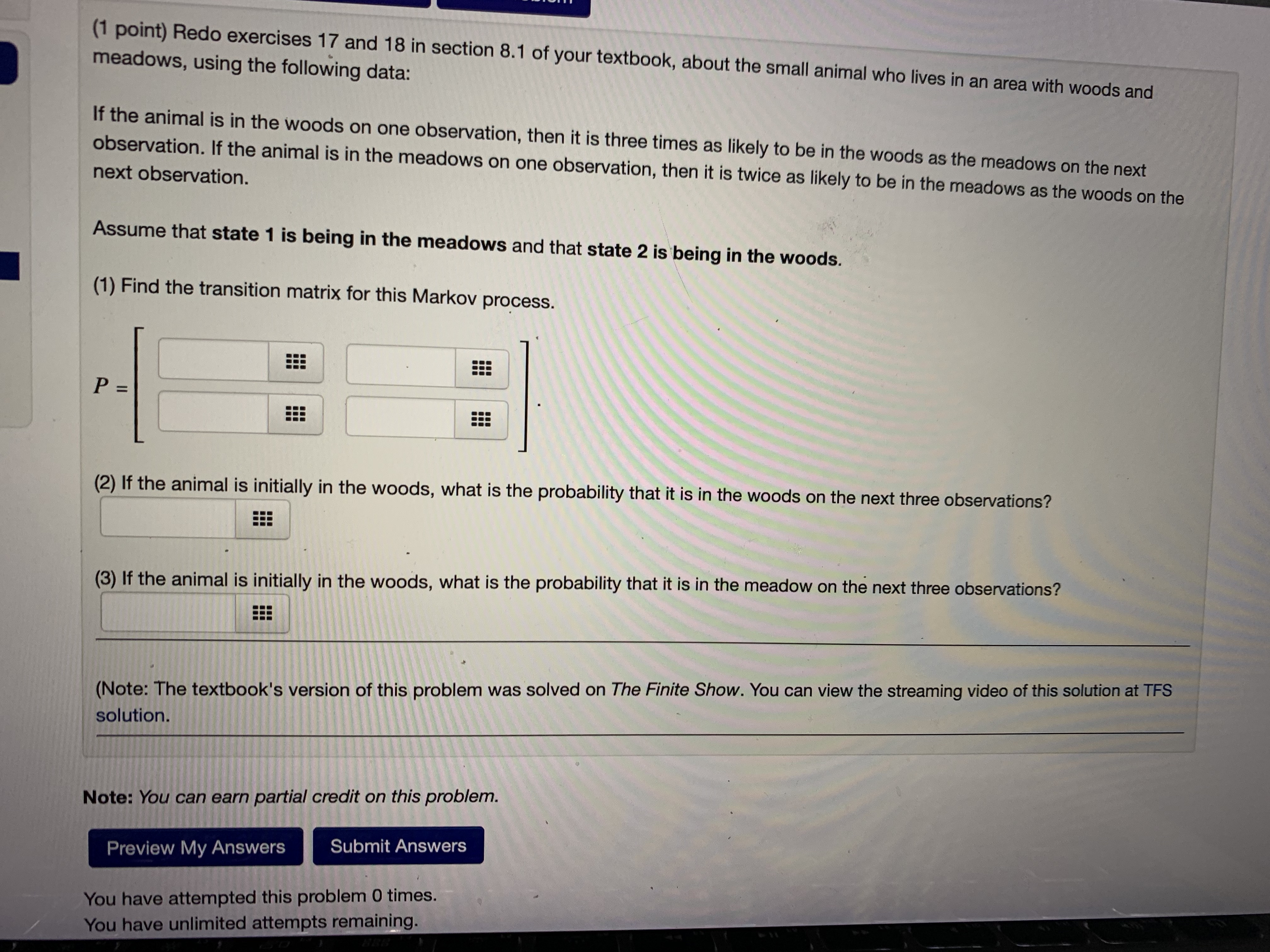
Question: Would you help me solve these problems? (1 point) Suppose a two-state experiment has the following transition matrix: P- lo's osl Answer the following questions:
Would you help me solve these problems?
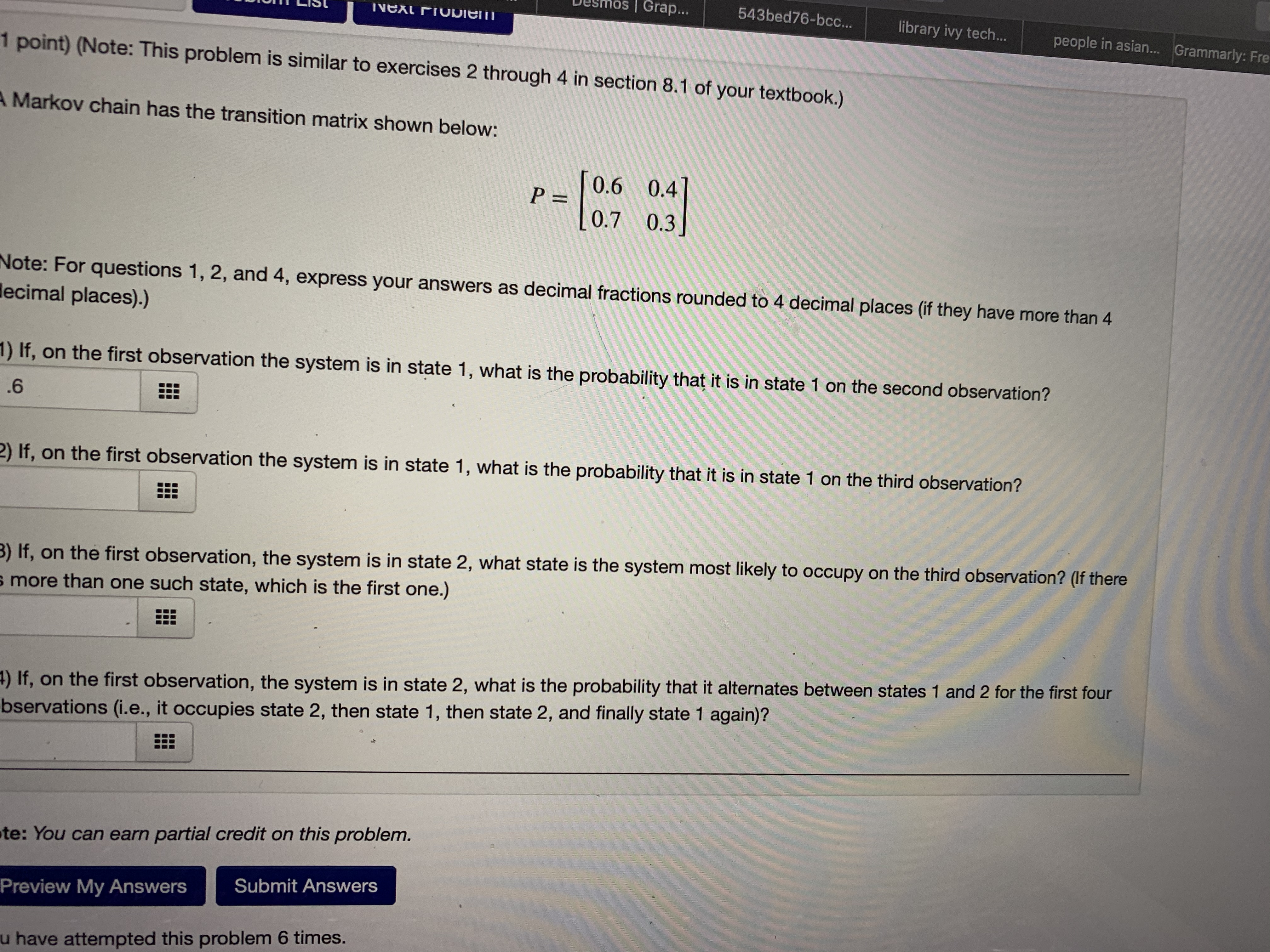
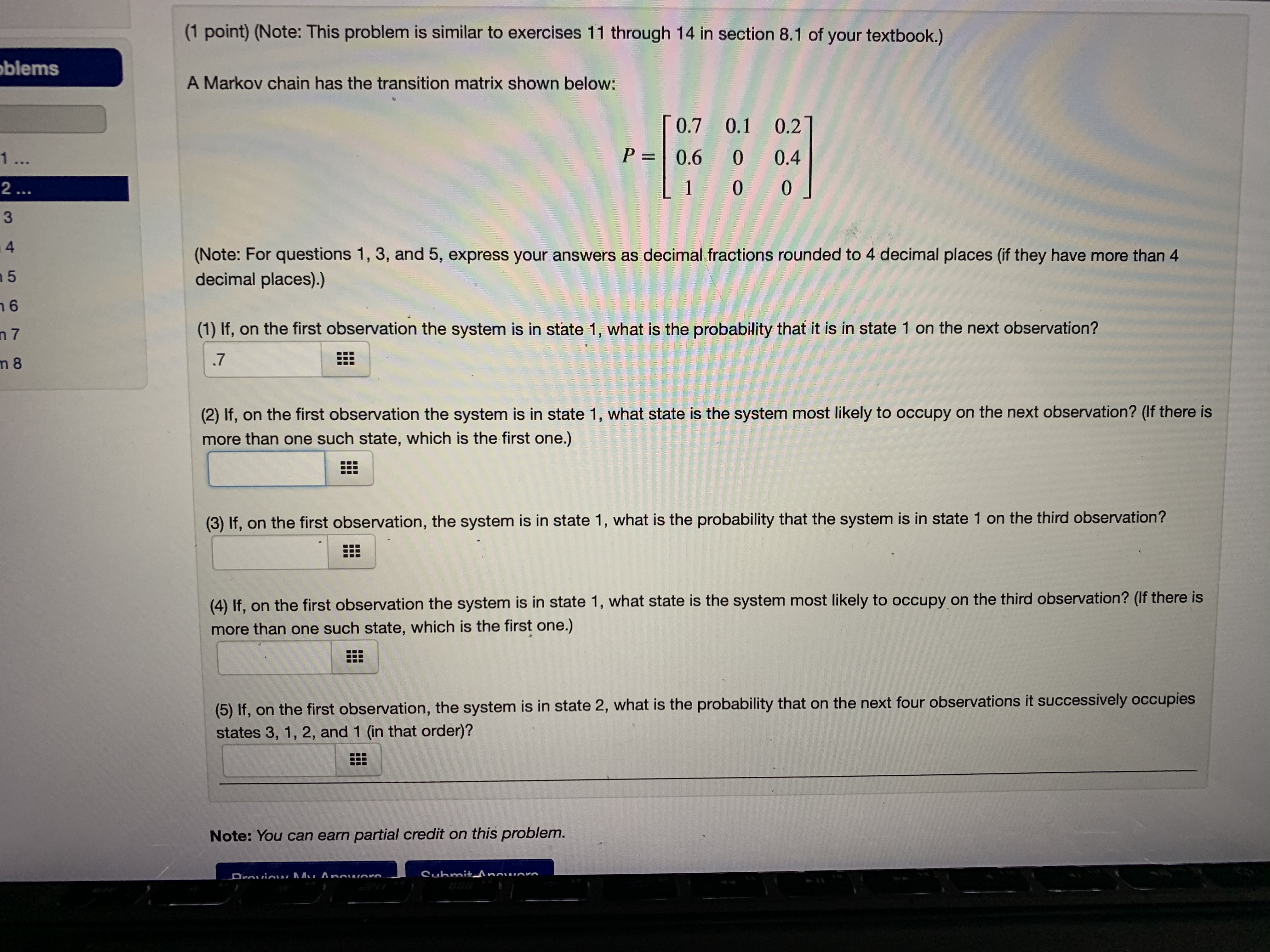
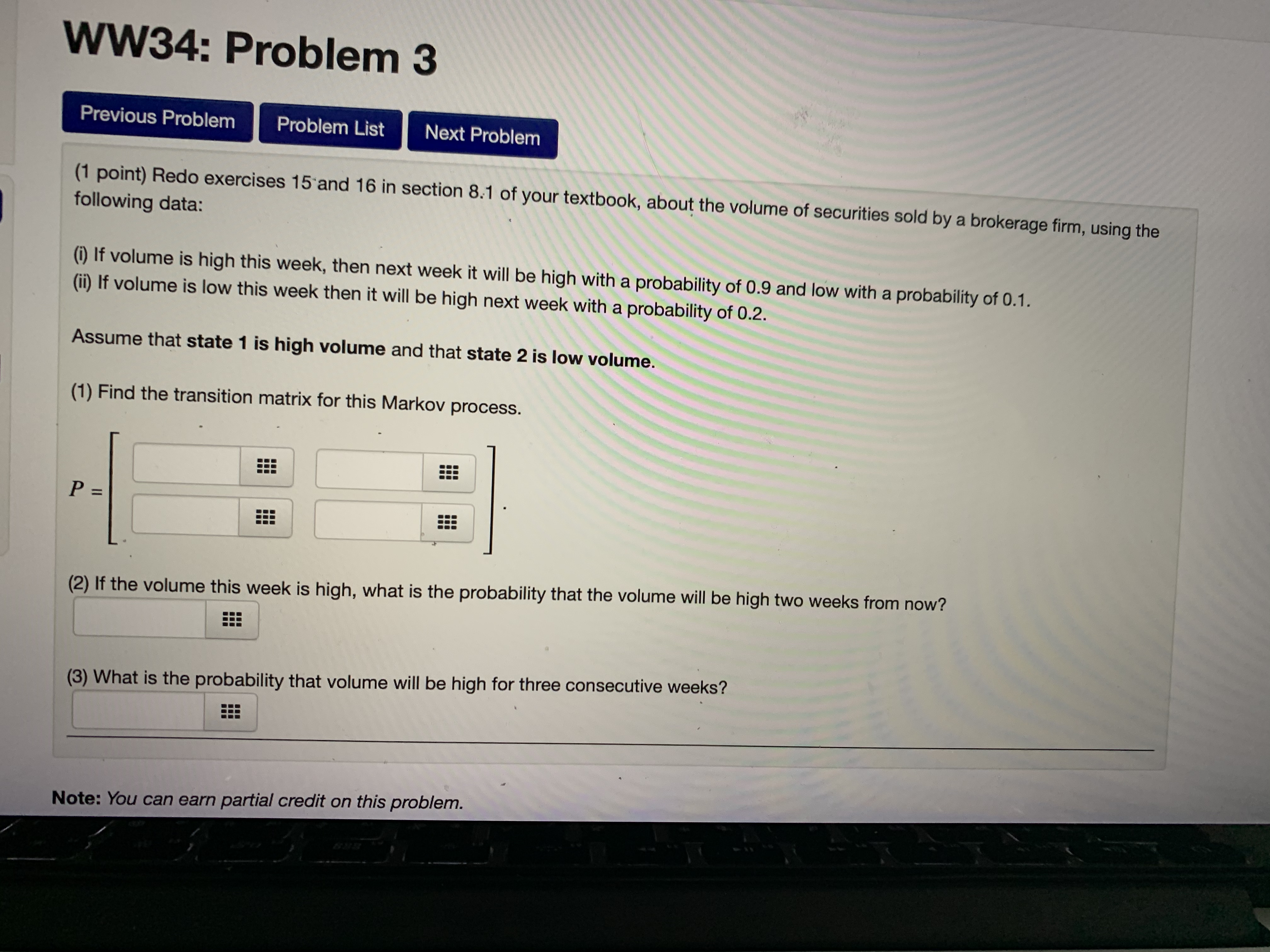
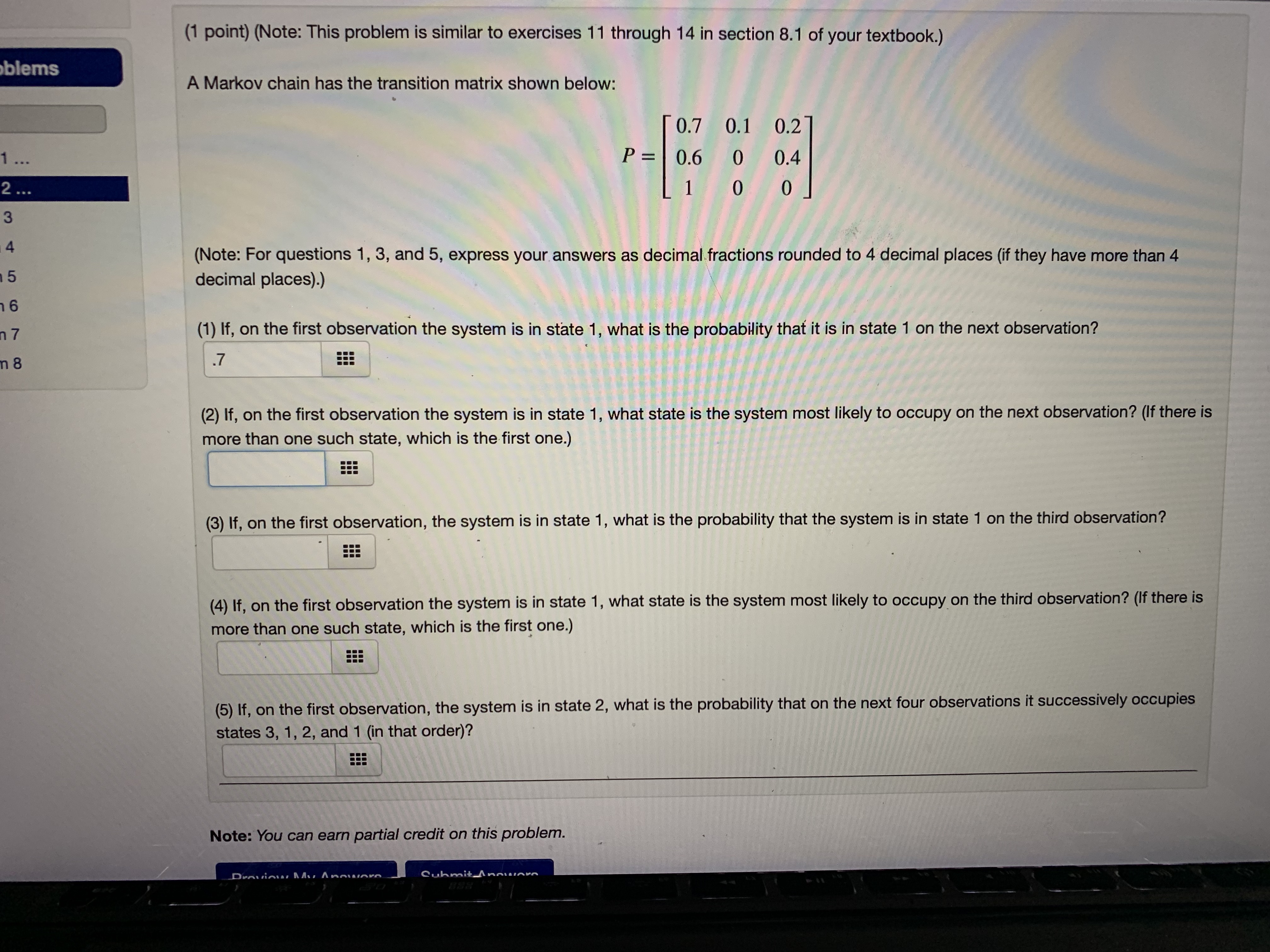
(1 point) Suppose a two-state experiment has the following transition matrix: P- lo's osl Answer the following questions: 1. If the experiment is in state 1 on the first observation, what is the probability it will be in state 2 on the second observation? 2. If the experiment is in state 1 on the first observation, what is the probability it will be in state 2 on the fourth observation? 3. If the experiment is in state 2 on the third observation, what is the probability that it will be in state 2 on the seventh observation? 4. If the experiment is in state 1 on the third observation, what is the probability it will be in state 1 on the fourth, fifth, and sixth observation? Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Preview My Answers Submit Answers You have attempted this problem 0 times. You have unlimited attempts remaining. Email instructorsmos | Grap... INGAL FIODIEIII 543bed76-bcc... library ivy tech.. people in asian... Grammarly: Fre 1 point) (Note: This problem is similar to exercises 2 through 4 in section 8.1 of your textbook.) Markov chain has the transition matrix shown below: P = [0.6 0.4 0.7 0.3 Note: For questions 1, 2, and 4, express your answers as decimal fractions rounded to 4 decimal places (if they have more than 4 lecimal places).) 1) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the second observation? .6 2) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the third observation? 3) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the third observation? (If there more than one such state, which is the first one.) 4) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what is the probability that it alternates between states 1 and 2 for the first four bservations (i.e., it occupies state 2, then state 1, then state 2, and finally state 1 again)? te: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Preview My Answers Submit Answers have attempted this problem 6 times.WW34: Problem 3 Previous Problem Problem List Next Problem (1 point) Redo exercises 15 and 16 in section 8.1 of your textbook, about the volume of securities sold by a brokerage firm, using the following data: (i) If volume is high this week, then next week it will be high with a probability of 0.9 and low with a probability of 0.1. (ii) If volume is low this week then it will be high next week with a probability of 0.2. Assume that state 1 is high volume and that state 2 is low volume. (1) Find the transition matrix for this Markov process. P (2) If the volume this week is high, what is the probability that the volume will be high two weeks from now? (3) What is the probability that volume will be high for three consecutive weeks? Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem.(1 point) Redo exercises 17 and 18 in section 8.1 of your textbook, about the small animal who lives in an area with woods and meadows, using the following data: If the animal is in the woods on one observation, then it is three times as likely to be in the woods as the meadows on the next observation. If the animal is in the meadows on one observation, then it is twice as likely to be in the meadows as the woods on the next observation. Assume that state 1 is being in the meadows and that state 2 is being in the woods. (1) Find the transition matrix for this Markov process. P = (2) If the animal is initially in the woods, what is the probability that it is in the woods on the next three observations? (3) If the animal is initially in the woods, what is the probability that it is in the meadow on the next three observations? (Note: The textbook's version of this problem was solved on The Finite Show. You can view the streaming video of this solution at TFS solution. Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Preview My Answers Submit Answers You have attempted this problem 0 times. You have unlimited attempts remaining.smos | Grap... INGAL FIODIEITI 543bed76-bcc... library ivy tech.. people in asian... Grammarly: Fre 1 point) (Note: This problem is similar to exercises 2 through 4 in section 8.1 of your textbook.) Markov chain has the transition matrix shown below: P = [0.6 0.4 0.7 0.3 Note: For questions 1, 2, and 4, express your answers as decimal fractions rounded to 4 decimal places (if they have more than 4 lecimal places).) 1) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the second observation? .6 2) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the third observation? 3) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the third observation? (If there more than one such state, which is the first one.) 4) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what is the probability that it alternates between states 1 and 2 for the first four bservations (i.e., it occupies state 2, then state 1, then state 2, and finally state 1 again)? te: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Preview My Answers Submit Answers u have attempted this problem 6 times.(1 point) (Note: This problem is similar to exercises 11 through 14 in section 8.1 of your textbook.) blems A Markov chain has the transition matrix shown below: 0.7 0.1 0.2 1 ... P = 0.6 0 0.4 2 ... 1 0 0 3 (Note: For questions 1, 3, and 5, express your answers as decimal fractions rounded to 4 decimal places (if they have more than 4 decimal places).) 16 17 (1) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the next observation? .7 (2) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the next observation? (If there is more than one such state, which is the first one.) (3) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 1, what is the probability that the system is in state 1 on the third observation? (4) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the third observation? (If there is more than one such state, which is the first one.) (5) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what is the probability that on the next four observations it successively occupies states 3, 1, 2, and 1 (in that order)? EEE Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Cuhmit AnnounceWW34: Problem 3 Previous Problem Problem List Next Problem (1 point) Redo exercises 15 and 16 in section 8.1 of your textbook, about the volume of securities sold by a brokerage firm, using the following data: (i) If volume is high this week, then next week it will be high with a probability of 0.9 and low with a probability of 0.1. (ii) If volume is low this week then it will be high next week with a probability of 0.2. Assume that state 1 is high volume and that state 2 is low volume. (1) Find the transition matrix for this Markov process. P (2) If the volume this week is high, what is the probability that the volume will be high two weeks from now? (3) What is the probability that volume will be high for three consecutive weeks? Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem.(1 point) (Note: This problem is similar to exercises 11 through 14 in section 8.1 of your textbook.) blems A Markov chain has the transition matrix shown below: 0.7 0.1 0.2 1 ... P = 0.6 0 0.4 2 ... 1 0 0 3 (Note: For questions 1, 3, and 5, express your answers as decimal fractions rounded to 4 decimal places (if they have more than 4 decimal places).) 16 17 (1) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what is the probability that it is in state 1 on the next observation? .7 (2) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the next observation? (If there is more than one such state, which is the first one.) (3) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 1, what is the probability that the system is in state 1 on the third observation? (4) If, on the first observation the system is in state 1, what state is the system most likely to occupy on the third observation? (If there is more than one such state, which is the first one.) EEE (5) If, on the first observation, the system is in state 2, what is the probability that on the next four observations it successively occupies states 3, 1, 2, and 1 (in that order)? Note: You can earn partial credit on this problem. Cuhmit Anminus