Question: Write a C++ program that will implement First-fit, memory management algorithm. Your program must do the following: 1. Input the memory size and the number
Write a C++ program that will implement First-fit, memory management algorithm. Your program must do the following: 1. Input the memory size and the number and sizes of all the partitions (limit the max number of the partitions to 5). 2. Input the job list that includes: - Job's name - Job's size 3. For each job you should create in your program a data structure that will include the job status (Run/Wait) and the partition number (if the job was allocated). 4. Calculate and display initial memory allocation. 5. Display the memory waste and the jobs that could not be allocated and have to wait. Code Quality Requirement: 1. Do not put every single logic in the main() function. 2. You must use functions to separate your programs logic into smaller readable pieces. 3. You must use descriptive variable names. Dont use int b = 5. Whats b?! - Its okay to use i or j or any other letters for loops (only loops).
 4. You must write meaningful comments to explain your code.
4. You must write meaningful comments to explain your code.
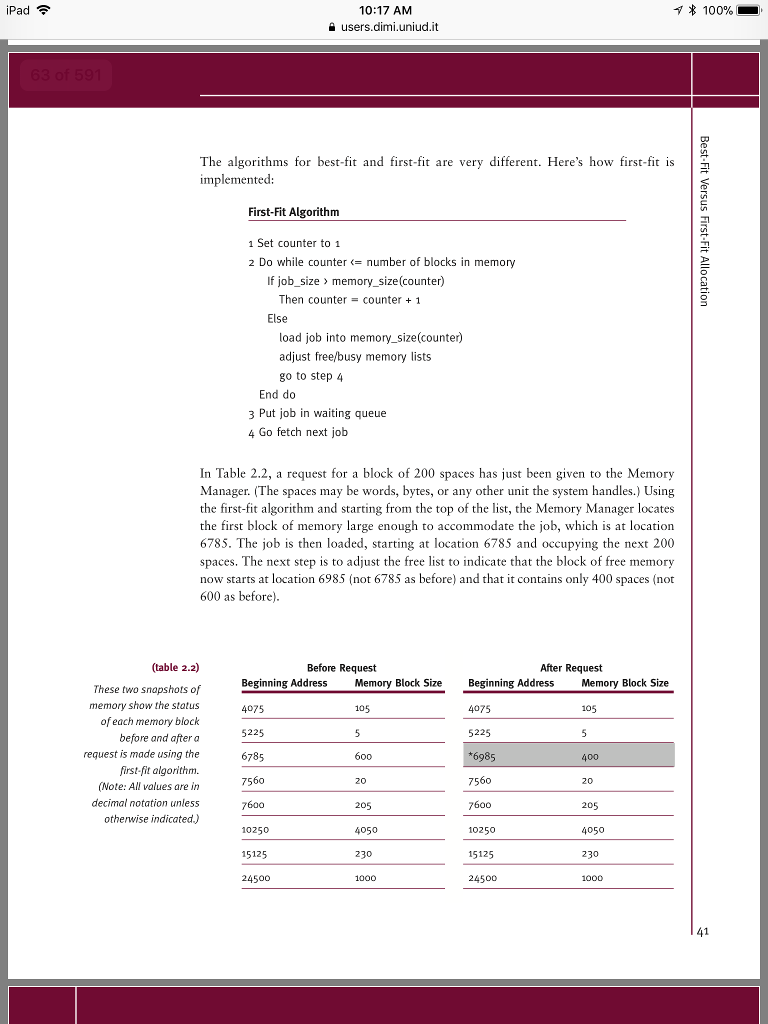
* 100% 10:17 AM users.dim..unud.it The algorithms for best-fit and first-fit are very different. Here's how first-fit is S implemented: First-Fit Algorithm Set counter to 1 2 Do while counter number of blocks in memory If job_size memory_size(counter) Then counter = counter + 1 Else load job into memory_size(counter) adjust free/busy memory lists go to step 4 End do 3 Put job in waiting queue 4 Go fetch next job In Table 2.2, a request for a block of 200 spaces has just been given to the Memory Manager. (The spaces may be words, bytes, or any other unit the system handles.) Using the first-fit algorithm and starting from the top of the list, the Memory Manager locates the first block of memory large enough to accommodate the job, which is at location 6785. The job is then loaded, starting at location 6785 and occupying the next 200 spaces. The next step is to adjust the free list to indicate that the block of free memory now starts at location 6985 (not 6785 as before) and that it contains only 400 spaces (not 600 as before) (table 2.2) These two snapshots of memory show the status of each memory block before and after a request is made using the first-fit algorithm. (Note: All values are in decimal notation unless otherwise indicated) Before Request After Request Beginning Address 4075 5225 6785 7560 Memory Block Size Beginning Address Memory Block Size 5225 *6985 7560 7600 10250 5125 24500 20 205 4050 230 205 10250 15125 24500 4050 230 1000 1000 41
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


