Question: Write a class named MyVector using the following UML diagram and class attribute descriptions. MyVector will use an unordered, pointer-based linked list to store a
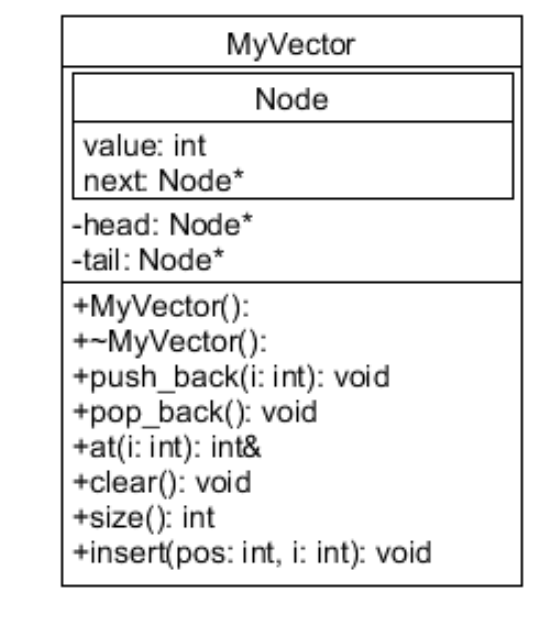 Write a class named MyVector using the following UML diagram and class attribute descriptions. MyVector will use an unordered, pointer-based linked list to store a collection of integers.
Write a class named MyVector using the following UML diagram and class attribute descriptions. MyVector will use an unordered, pointer-based linked list to store a collection of integers.
UML Diagram:
Class Attributes:
Node:
A private, embedded struct.
Members:
value - stores the integer being stored in the MyVector object.
next - stores the memory address of the next node of the linked list.
Variables:
head - a Node pointer that stores the memory address of the first node in the linked list.
tail - a Node pointer that stores the memory address of the last node in the linked list.
Methods:
constructor - initializes head and tail to nullptr.
destructor - frees all memory used by the list.
push_back - Creates a new node, stores it's argument in the node, and appends it to the list.
pop_back - if the list isn't empty (head == nullptr), removes the last node from memory. Throws an exception otherwise. The exception is a c-string: "EMPTY VECTOR".
at - uses it's argument as a subscript for the MyVector. Returns the value from that corresponding node. It's return type is an integer reference (int&). Throws an exception if the argument is an invalid index. The exception is a c-string: "OUT OF BOUNDS". If the MyVector object is empty, throws "EMPTY VECTOR" exception.
clear - removes all nodes from memory, and sets head and tail back to nullptr.
size - counts and returns the number of nodes in the list.
insert - inserts new value i before position pos in the MyVector list. So, if the list contained the values : 8 6 7 and the method was invoked as: v.insert(2, 9) then the list would be updated to: 8 6 9 7 Throws an exception "OUT OF BOUNDS" if an invalid position is specified.
None of the above methods interacts with the user in any way. You are not writing a program, just a class in it's own header file.
Place the class declaration in it's own header file named MyVector.h. Place the method definitions in it's own file named MyVector.cpp.
MyVector Node value: int next Node -head: Node -tail: Node* +MyVector): +-MyVector): +push_back(i: int): void +pop_back(): void +at(i: int): int& +clear: void +size(): int tinsert (pos: int, i: int): voidStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


