Question: Write a generic data type for a deque and a randomized queue. The goal of this assignment is to implement elementary data structures using arrays
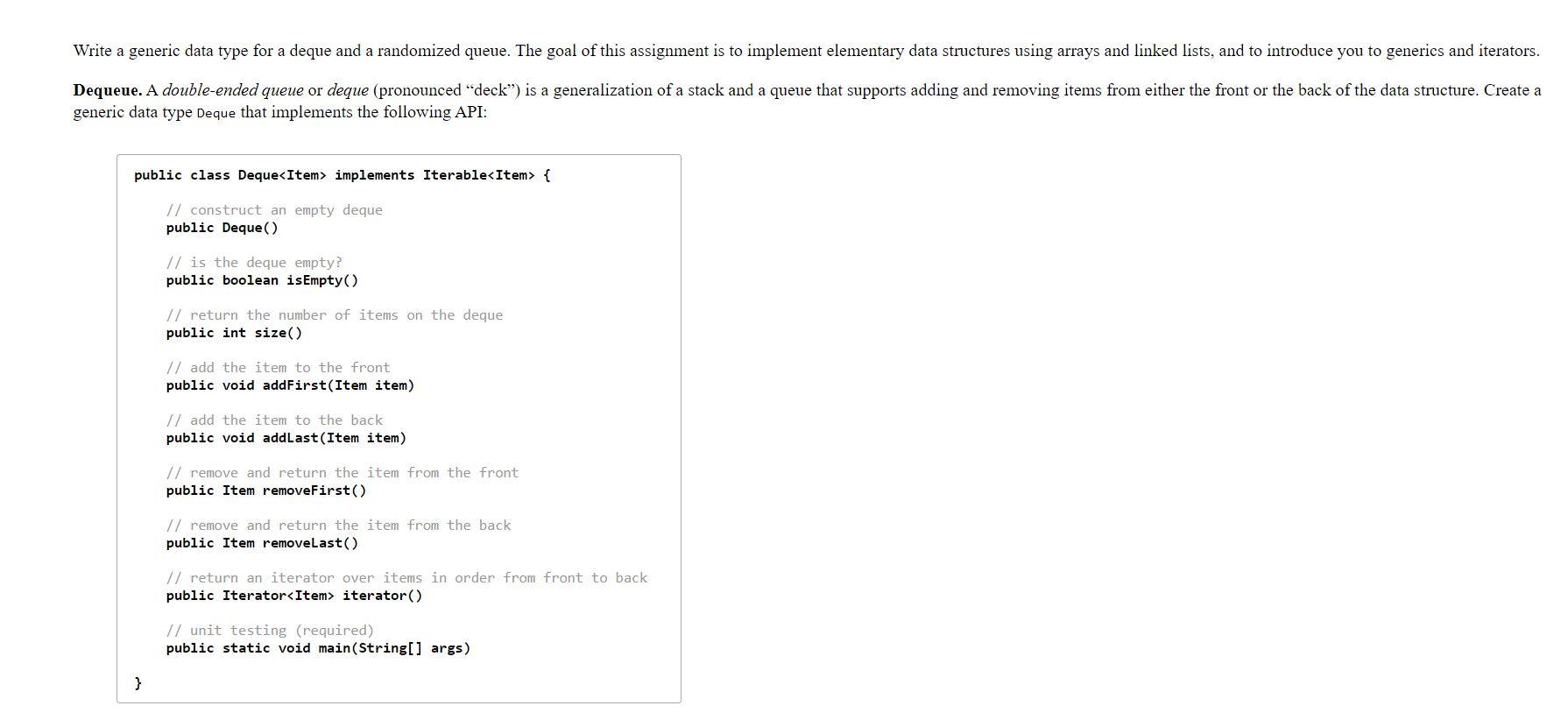
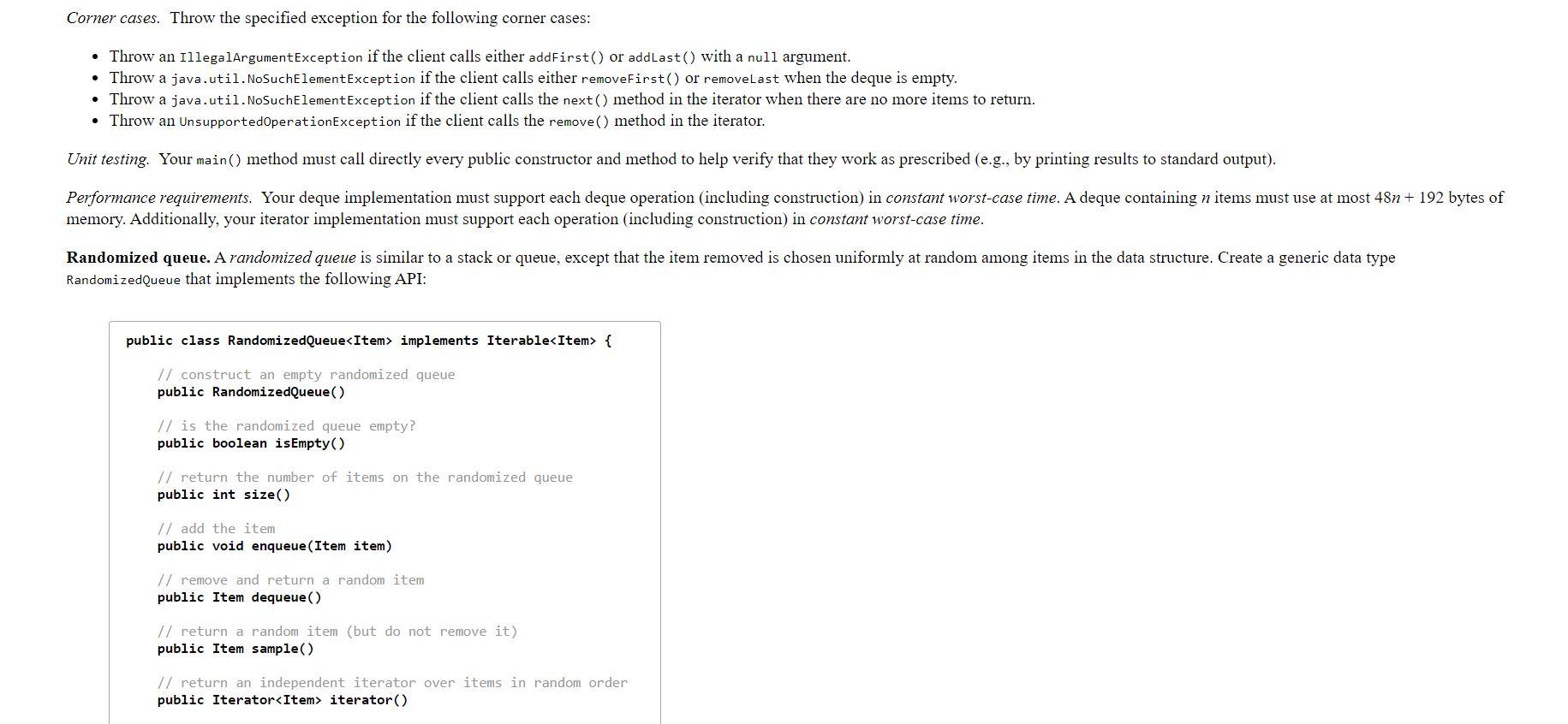
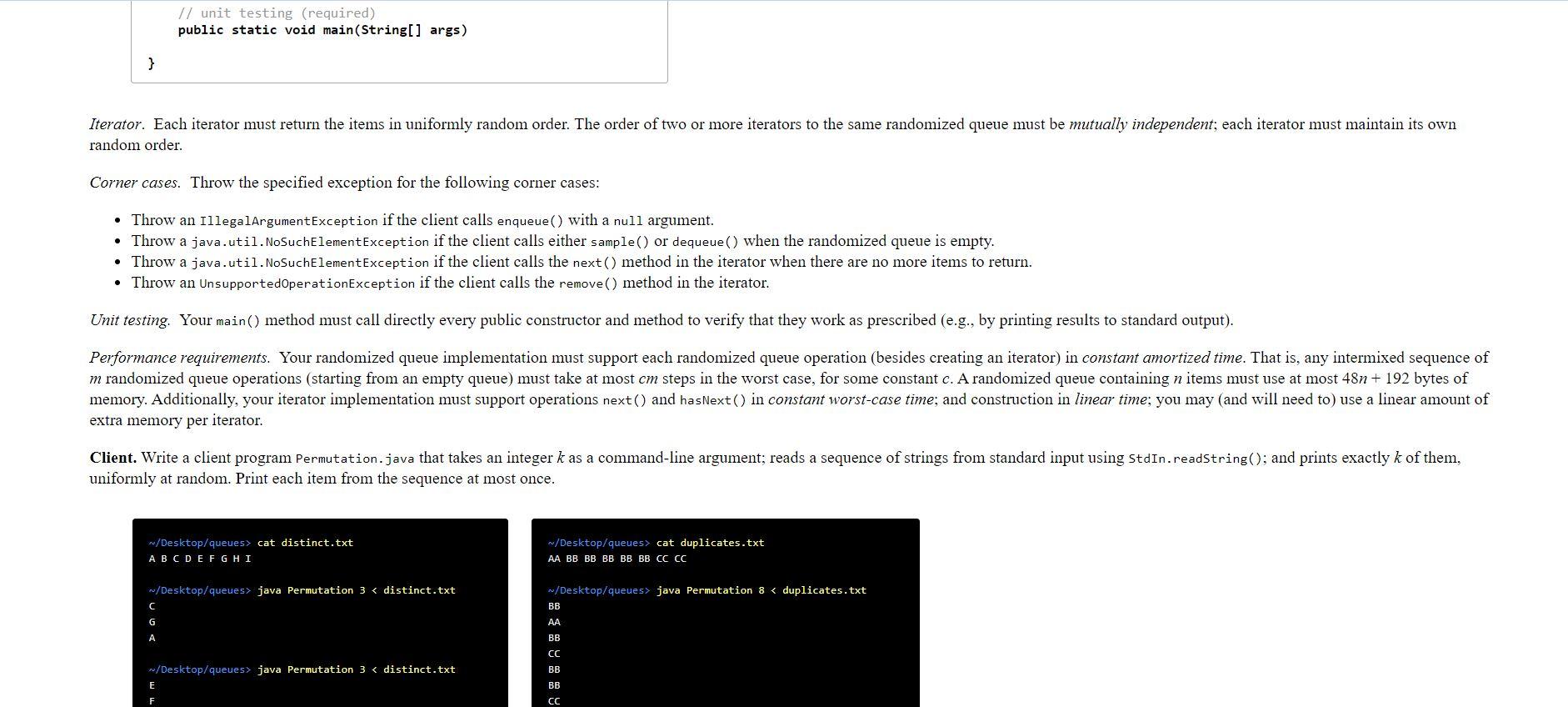
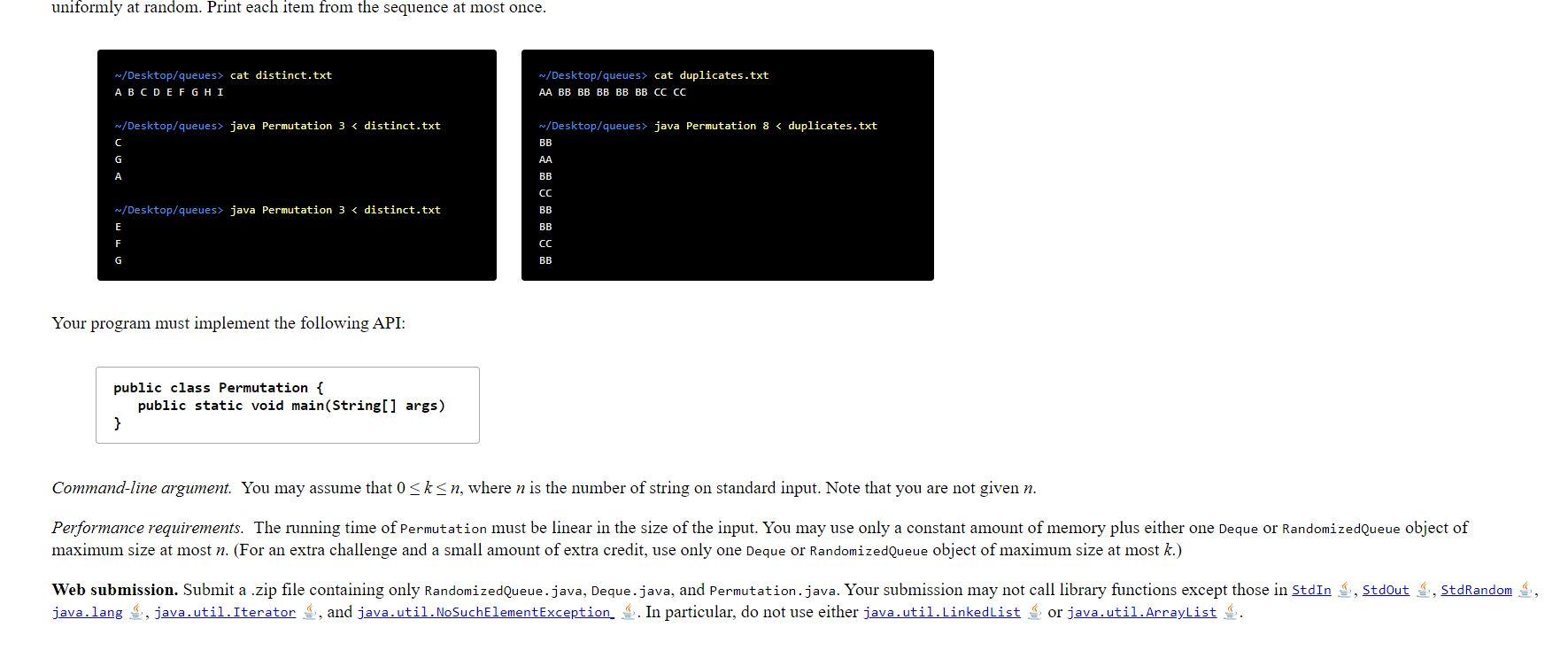
Write a generic data type for a deque and a randomized queue. The goal of this assignment is to implement elementary data structures using arrays and linked lists, and to introduce you to generics and iterators. Dequeue. A double-ended queue or deque (pronounced "deck) is a generalization of a stack and a queue that supports adding and removing items from either the front or the back of the data structure. Create a generic data type Deque that implements the following API: public class Deque
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


