Question: Write a Java Program: I need help with fixing my Java code below for the given question, please read the requirements first for a thorough
Write a Java Program:
I need help with fixing my Java code below for the given question, please read the requirements first for a thorough explanation and you will find my code attached

The test cases could be found here: http://bit.ly/CS_assn_trees.
These test cases uses random different inputs that check if the program outputs the corresponding values.
Please visit the link for the test cases and also below are some of the cases that I have failed
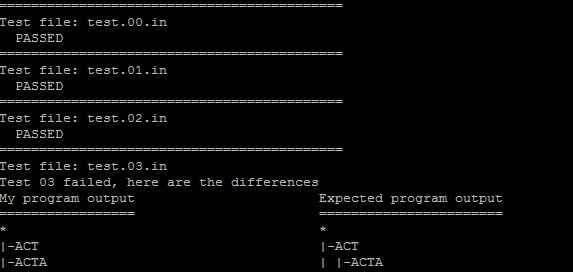
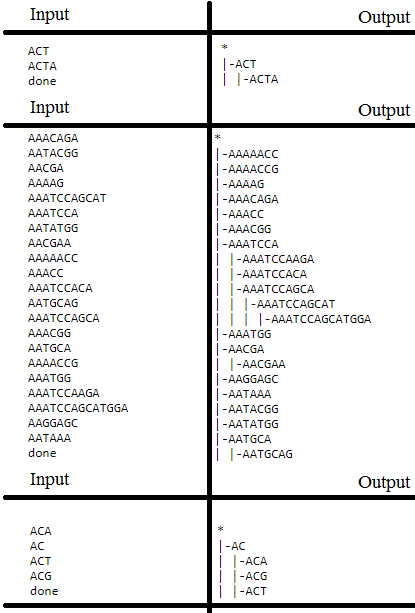
Currently my current code passes 7 out of twenty test cases and must be changed and modified to pass the 20 given test cases. Listed below are my two Java programs TreeBuilder.java and Node.java. If anyone has a better solution and implementation (e.g.: by using just a one java file) please answer the question with your method instead, because the more simple and lesser lines yield better efficiency
Node.java
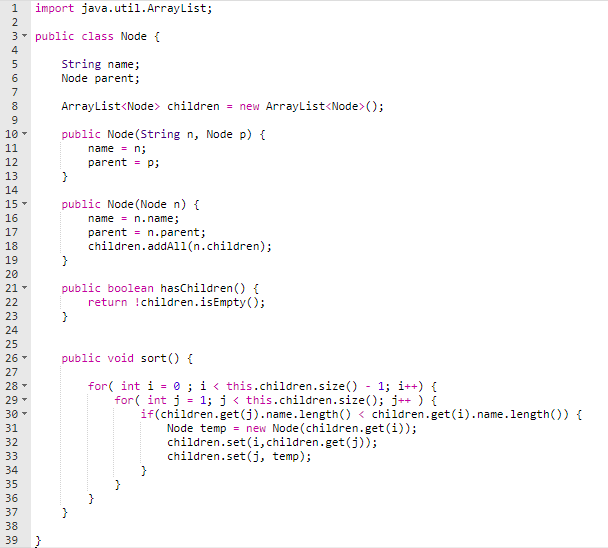
TreeBuilder.java
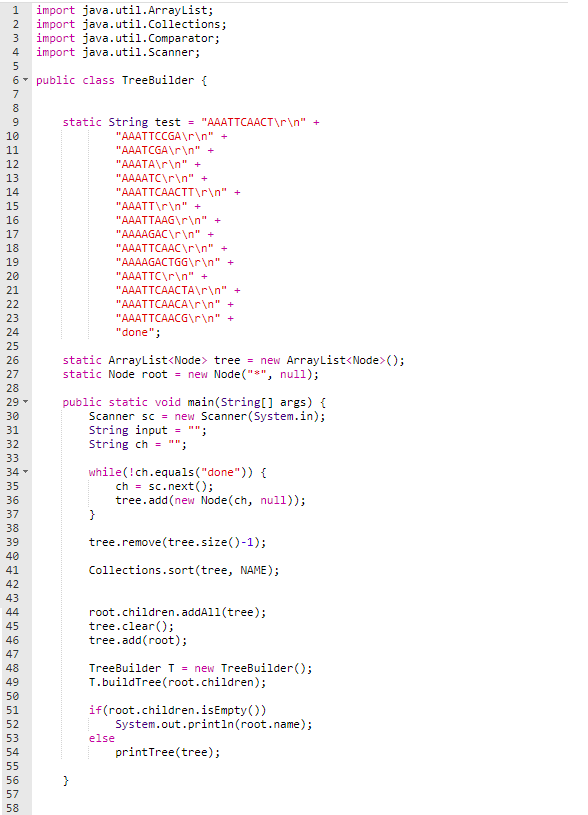
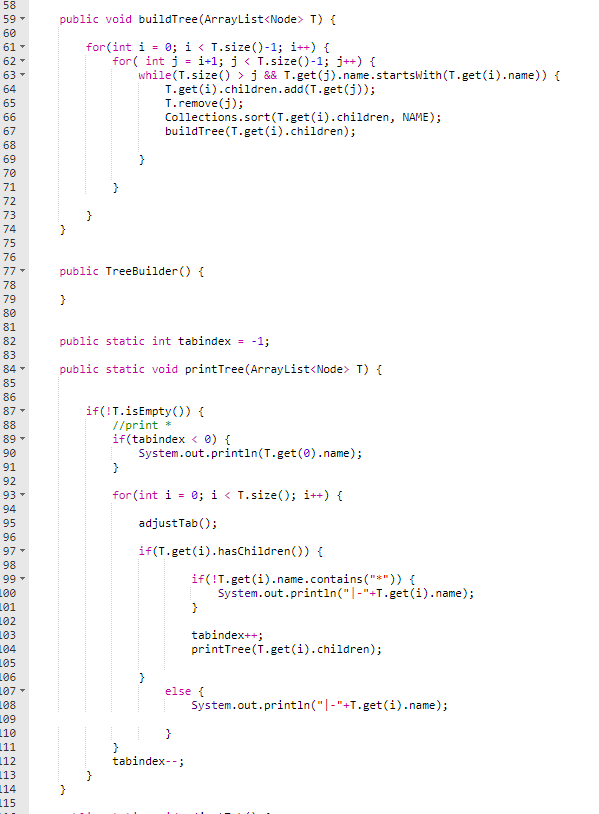

These are the copyable codes below:
Node.java:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; public class TreeBuilder { static String test = "AAATTCAACT " + "AAATTCCGA " + "AAATCGA " + "AAATA " + "AAAATC " + "AAATTCAACTT " + "AAATT " + "AAATTAAG " + "AAAAGAC " + "AAATTCAAC " + "AAAAGACTGG " + "AAATTC " + "AAATTCAACTA " + "AAATTCAACA " + "AAATTCAACG " + "done"; static ArrayList tree = new ArrayList(); static Node root = new Node("*", null); public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String input = ""; String ch = ""; while(!ch.equals("done")) { ch = sc.next(); tree.add(new Node(ch, null)); } tree.remove(tree.size()-1); Collections.sort(tree, NAME); root.children.addAll(tree); tree.clear(); tree.add(root); TreeBuilder T = new TreeBuilder(); T.buildTree(root.children); if(root.children.isEmpty()) System.out.println(root.name); else printTree(tree); } public void buildTree(ArrayList T) { for(int i = 0; i j && T.get(j).name.startsWith(T.get(i).name)) { T.get(i).children.add(T.get(j)); T.remove(j); Collections.sort(T.get(i).children, NAME); buildTree(T.get(i).children); } } } } public TreeBuilder() { } public static int tabindex = -1; public static void printTree(ArrayList T) { if(!T.isEmpty()) { //print * if(tabindex n2.name.length()) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } }; public static Comparator NAME = new Comparator( ) { @Override public int compare(Node n1, Node n2) { return n1.name.compareTo(n2.name); } }; } TreeBuilder.java:import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; public class TreeBuilder { static String test = "AAATTCAACT " + "AAATTCCGA " + "AAATCGA " + "AAATA " + "AAAATC " + "AAATTCAACTT " + "AAATT " + "AAATTAAG " + "AAAAGAC " + "AAATTCAAC " + "AAAAGACTGG " + "AAATTC " + "AAATTCAACTA " + "AAATTCAACA " + "AAATTCAACG " + "done"; static ArrayList tree = new ArrayList(); static Node root = new Node("*", null); public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String input = ""; String ch = ""; while(!ch.equals("done")) { ch = sc.next(); tree.add(new Node(ch, null)); } tree.remove(tree.size()-1); Collections.sort(tree, NAME); root.children.addAll(tree); tree.clear(); tree.add(root); TreeBuilder T = new TreeBuilder(); T.buildTree(root.children); if(root.children.isEmpty()) System.out.println(root.name); else printTree(tree); } public void buildTree(ArrayList T) { for(int i = 0; i j && T.get(j).name.startsWith(T.get(i).name)) { T.get(i).children.add(T.get(j)); T.remove(j); Collections.sort(T.get(i).children, NAME); buildTree(T.get(i).children); } } } } public TreeBuilder() { } public static int tabindex = -1; public static void printTree(ArrayList T) { if(!T.isEmpty()) { //print * if(tabindex n2.name.length()) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } }; public static Comparator NAME = new Comparator( ) { @Override public int compare(Node n1, Node n2) { return n1.name.compareTo(n2.name); } }; } 58 public void buildTree (ArrayList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


