Question: Write a Java program that reverses a singly linked list based on the instructions below. A UML diagram, sample runs, and skeleton program is provided
Write a Java program that reverses a singly linked list based on the instructions below. A UML diagram, sample runs, and skeleton program is provided below.

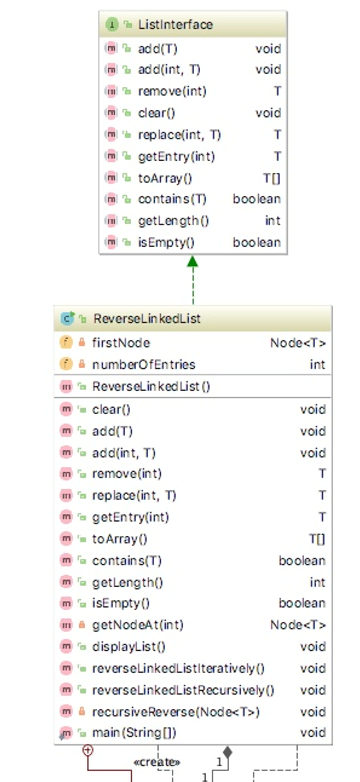
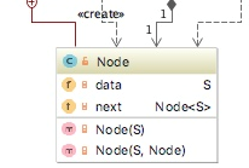
-----
SKELETON PROGRAM: ReverseLinkedList.java
package Lab09; /** * A class that implements the ADT list by using a chain of nodes. * The list has an iterator. The class is similar to LList. * * @author Frank M. Carrano * @author Timothy M. Henry * @modifiedBy atb * @version 10/23/2018 */ public class ReverseLinkedListimplements ListInterface { private Node firstNode; private int numberOfEntries; public ReverseLinkedList() { clear(); } // end default constructor public void clear() { this.firstNode = null; this.numberOfEntries = 0; } // end clear public void add(T newEntry) // OutOfMemoryError possible { Node newNode = new Node(newEntry); if (isEmpty()) this.firstNode = newNode; else // Add to end of non-empty list { Node lastNode = getNodeAt(this.numberOfEntries); lastNode.next = newNode; // Make last node reference new node } this.numberOfEntries++; } // end add public void add(int newPosition, T newEntry) // OutOfMemoryError possible { if ((newPosition >= 1) && (newPosition newNode = new Node(newEntry); if (newPosition == 1) // Case 1 { newNode.next = this.firstNode; this.firstNode = newNode; } else // Case 2: list is not empty { // and newPosition > 1 Node nodeBefore = getNodeAt(newPosition - 1); Node nodeAfter = nodeBefore.next; newNode.next = nodeAfter; nodeBefore.next = newNode; } this.numberOfEntries++; } else throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal position given to add operation."); } // end add public T remove(int givenPosition) { T result = null; // Return value if ((givenPosition >= 1) && (givenPosition nodeBefore = getNodeAt(givenPosition - 1); Node nodeToRemove = nodeBefore.next; Node nodeAfter = nodeToRemove.next; nodeBefore.next = nodeAfter; result = nodeToRemove.data; // Save entry to be removed } this.numberOfEntries--; return result; // Return removed entry } else throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal position given to remove operation."); } // end remove public T replace(int givenPosition, T newEntry) { if ((givenPosition >= 1) && (givenPosition desiredNode = getNodeAt(givenPosition); T originalEntry = desiredNode.data; desiredNode.data = newEntry; return originalEntry; } else throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal position given to replace operation."); } // end replace public T getEntry(int givenPosition) { if ((givenPosition >= 1) && (givenPosition currentNode = this.firstNode; while ((index currentNode = this.firstNode; while (!found && (currentNode != null)) { if (anEntry.equals(currentNode.data)) found = true; else currentNode = currentNode.next; } return found; } // end contains public int getLength() { return this.numberOfEntries; } // end getLength public boolean isEmpty() { boolean result; if (this.numberOfEntries == 0) { assert this.firstNode == null; result = true; } else { assert this.firstNode != null; result = false; } return result; } // end isEmpty // Returns a reference to the node at a given position. // Precondition: List is not empty; // 1 getNodeAt(int givenPosition) { assert !isEmpty() && (1 currentNode = this.firstNode; // Traverse the chain to locate the desired node (skipped // if givenPosition is 1) for (int counter = 1; counter out.print("The list contains: " ); Node currentNode = this.firstNode; while (currentNode != null) { System.out.print(currentNode.data + " "); currentNode = currentNode.next; } System.out.println(); } // end displayList public void reverseLinkedListIteratively() { // TODO Project 7 // please put here the link to the video you followed in your solution } public void reverseLinkedListRecursively() { recursiveReverse(this.firstNode); } private void recursiveReverse(Node currentNode) { // TODO Project 7 // please put here the link to the video you followed in your solution } private class Node { private S data; // Entry in list private Nodenext; // Link to next node private Node(S dataPortion) { this(dataPortion, null); } // end constructor private Node(S dataPortion, Node nextNode) { this.data = dataPortion; this.next = nextNode; } // end constructor } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("*** Create a list ***"); ReverseLinkedListmyList = new ReverseLinkedList(); myList.add("15"); myList.add("25"); myList.add("35"); myList.add("45"); myList.add("55"); myList.add("65"); myList.add("75"); myList.add("85"); myList.add("95"); myList.displayList(); System.out.println(" *** Calling reverseLinkedListIteratively ***"); myList.reverseLinkedListIteratively(); System.out.println(" Expected result: 95 85 75 65 55 45 35 25 15"); myList.displayList(); System.out.println("==========================================================="); System.out.println(" *** Calling reverseLinkedListRecursively ***"); myList.reverseLinkedListRecursively(); System.out.println(" Expected result: 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95"); myList.displayList(); System.out.println("*** Done ***"); } // end main } // end LinkedListWithIterator
------------------------
SKELETON PROGRAM: ListInterface.java
package Lab09; /** * An interface for the ADT list. * Entries in a list have positions that begin with 1. * * @author Frank M. Carrano * @author Timothy M. Henry * @version 03/27/2018 */ public interface ListInterface{ /** * Adds a new entry to the end of this list. * Entries currently in the list are unaffected. * The list's size is increased by 1. * * @param newEntry The object to be added as a new entry. */ public void add(T newEntry); /** * Adds a new entry at a specified position within this list. * Entries originally at and above the specified position * are at the next higher position within the list. * The list's size is increased by 1. * * @param newPosition An integer that specifies the desired * position of the new entry. * @param newEntry The object to be added as a new entry. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either * newPosition getLength() + 1. */ public void add(int newPosition, T newEntry); /** * Removes the entry at a given position from this list. * Entries originally at positions higher than the given * position are at the next lower position within the list, * and the list's size is decreased by 1. * * @param givenPosition An integer that indicates the position of * the entry to be removed. * @return A reference to the removed entry. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either * givenPosition getLength(). */ public T remove(int givenPosition); /** * Removes all entries from this list. */ public void clear(); /** * Replaces the entry at a given position in this list. * * @param givenPosition An integer that indicates the position of * the entry to be replaced. * @param newEntry The object that will replace the entry at the * position givenPosition. * @return The original entry that was replaced. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either * givenPosition getLength(). */ public T replace(int givenPosition, T newEntry); /** * Retrieves the entry at a given position in this list. * * @param givenPosition An integer that indicates the position of * the desired entry. * @return A reference to the indicated entry. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either * givenPosition getLength(). */ public T getEntry(int givenPosition); /** * Retrieves all entries that are in this list in the order in which * they occur in the list. * * @return A newly allocated array of all the entries in the list. * If the list is empty, the returned array is empty. */ public T[] toArray(); /** * Sees whether this list contains a given entry. * * @param anEntry The object that is the desired entry. * @return True if the list contains anEntry, or false if not. */ public boolean contains(T anEntry); /** * Gets the length of this list. * * @return The integer number of entries currently in the list. */ public int getLength(); /** * Sees whether this list is empty. * * @return True if the list is empty, or false if not. */ public boolean isEmpty(); } // end ListInterface
------------
SAMPLE RUN:
*** Create a list ***
The list contains: 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95
*** Calling reverseLinkedListIteratively ***
Expected result: 95 85 75 65 55 45 35 25 15
The list contains: 95 85 75 65 55 45 35 25 15
===========================================================
*** Calling reverseLinkedListRecursively ***
Expected result: 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95
The list contains: 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95
*** Done ***
Process finished with exit code
VI ReverseLinkedList Your task is to reverse a singly linked list. You are to write two reverse methods: one iterative (reverseLinkedListIteratively()) and the other one recursive (reverseLinkedListRecursively)) solving the same problem. Given the first node (head of the list) need to reverse the list by changing the next pointers so the original last node of the list (tail of the list) is now the first as shown in the picture below: Input Output This is a classical interview question which surprisingly is unexpected by many candidates. But most of all this is a basic problem, and understanding both solutions will help you to solve number of linked list problems. Watch educational videos on YouTube, using the search: "How To Reverse Linked List YouTube". In your code please put the link to the video you followed in your solution. VI ReverseLinkedList Your task is to reverse a singly linked list. You are to write two reverse methods: one iterative (reverseLinkedListIteratively()) and the other one recursive (reverseLinkedListRecursively)) solving the same problem. Given the first node (head of the list) need to reverse the list by changing the next pointers so the original last node of the list (tail of the list) is now the first as shown in the picture below: Input Output This is a classical interview question which surprisingly is unexpected by many candidates. But most of all this is a basic problem, and understanding both solutions will help you to solve number of linked list problems. Watch educational videos on YouTube, using the search: "How To Reverse Linked List YouTube". In your code please put the link to the video you followed in your solution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


