Question: The following is a set of tables for the Art Course database shown in Figure 1-10. For the data for these tables, use the data
The following is a set of tables for the Art Course database shown in Figure 1-10. For the data for these tables, use the data shown in Figure 1-10.
CUSTOMER (CustomerNumber, CustomerLastName, CustomerFirstName, Phone) COURSE (CourseNumber, Course, CourseDate, Fee) ENROLLMENT (CustomerNumber, CourseNumber, AmountPaid)
where:
CustomerNumber in ENROLLMENT must exist in CustomerNumber in CUSTOMER CourseNumber in ENROLLMENT must exist in CourseNumber in COURSE
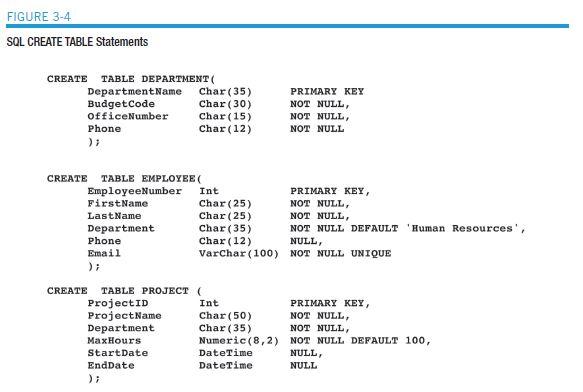
CustomerNumber and CourseNumber are surrogate keys. Therefore, these numbers will never be modified, and there is no need for cascading updates. No customer data are ever deleted, so there is no need to cascade deletions. Courses can be deleted. If there are enrollment entries for a deleted class, they should also be deleted. These tables, referential integrity constraints, and data are used as the basis for the SQL statements you will create in the exercises that follow. If possible, run these statements in an actual DBMS, as appropriate, to obtain results. Name your database ART_COURSE_ DATABASE. For each SQL statement you write, show the results based on these data. Use data types consistent with the DBMS you are using. If you are not using an actual DBMS, consistently represent data types using either the SQL Server, Oracle Database, or MySQL data types shown in Figure 3-4.
3.52 Write and run the SQL statements necessary to create the tables and their referential integrity constraints.
3.53 Populate the tables with data.
3.54 Write and run an SQL query to list all occurrences of Adv. Pastels. Include all associated data for each occurrence of the class.
3.55 Write and run an SQL query to list all students and courses they are registered for. Include, in this order, CustomerNumber, CustomerLastName, CustomerFirstName, Phone, CourseNumber, and AmountPaid.
3.56 Write and run an SQL query to list all students registered in Adv. Pastels starting on October 1, 2013. Include, in this order, Course, CourseDate, Fee, CustomerLastName, CustomerFirstName, and Phone.
3.57 Write and run an SQL query to list all students registered in Adv. Pastels starting on October 1, 2013. Include in this order, Course, CourseDate, CustomerLastName, CustomerFirstName, Phone, Fee, and AmountPaid. Use a join.
3.58 Modify your query to include all students, regardless of whether they regis tered in Adv. Pastels, starting October 1, 2013. Include, in this order, CustomerLastName, CustomerFirstName, Phone, Course, CourseDate, Fee, and AmountPaid.
3.59 Write a set of SQL statements (Hint: Use the SQL ALTER TABLE command.) to add a FullFeePaid column to ENROLLMENT and populate the column, assuming that the column is NULL. The only possible values for this column are Yes and No. (Compare COURSE.Fee to ENROLLMENT.AmountPaid to determine data values.)
3.60 Write a set of SQL statements (Hint: Use the SQL ALTER TABLE command.) to add a FullFeePaid column to ENROLLMENT and populate the column, assuming that the column is NOT NULL. The only possible values for this column are Yes and No. (Compare COURSE.Fee to ENROLLMENT.AmountPaid to determine data values.) What is the difference between your answer to this question and your answer to question 3.59?
3.61 Write an ALTER TABLE statement to add a CHECK constraint to the ENROLLMENT table to ensure that the value of FullFeePaid is either Yes or No. The following exercises are intended for use with a DBMS other than Microsoft Access. If you are using Microsoft Access, see the equivalent questions in the “Access Workbench Exercises” that follow.
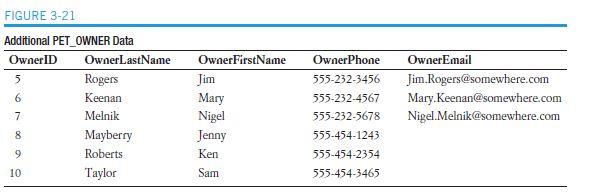
3.62 If you haven’t done so, create the WPC database, tables, and relationships described in this chapter, using the SQL DBMS of your choice. Be sure to populate the tables with the data shown in Figure 3-2.
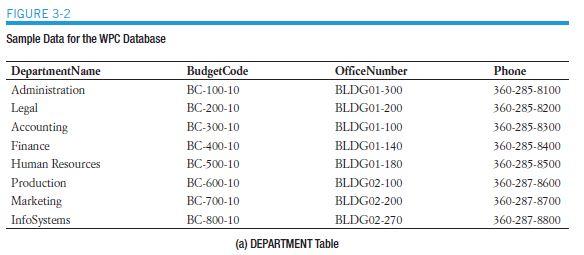
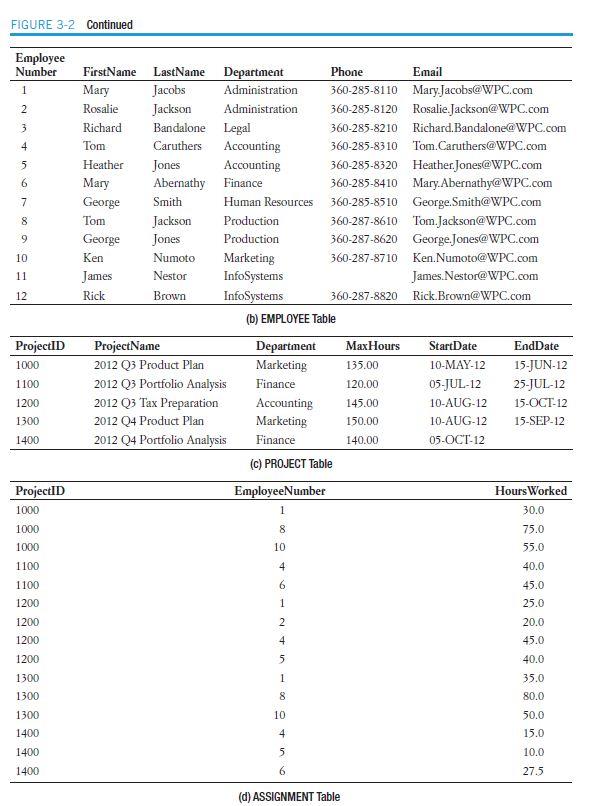
FIGURE 3-21 Additional PET OWNER Data OwnerID 5 6 7 8 9 10 OwnerLastName Rogers Keenan Melnik Mayberry Roberts Taylor OwnerFirstName Jim Mary Nigel Jenny Ken Sam OwnerPhone OwnerEmail 555-232-3456 Jim Rogers@somewhere.com 555-232-4567 Mary.Keenan@somewhere.com 555-232-5678 Nigel.Melnik@somewhere.com 555-454-1243 555-454-2354 555-454-3465
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (148 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
352 create table CUSTOMER create table COURSE Customer Number int Customer LastName varchar 20 Custo... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


