Question: Write a small C++ program that defines a recursive function GCD based on the model of the Lisp function discussed in the lecture. In the
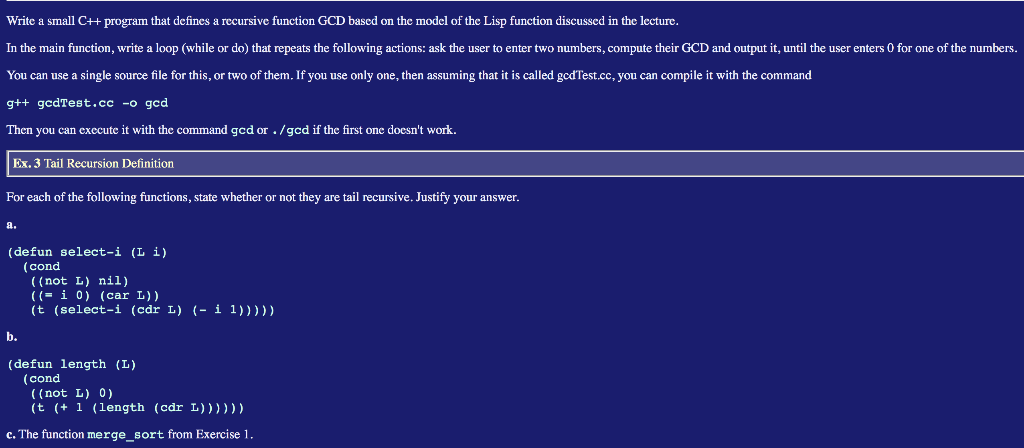
Write a small C++ program that defines a recursive function GCD based on the model of the Lisp function discussed in the lecture. In the main function, write a loop (while or do) that repeats the following actions: ask the user to enter two numbers, compute their GCD and output it, until the user enters 0 for one of the numbers. You can use a single source file for this, or two of them. If you use only one, then assuming that it is called godTest.cc, you can compile it with the command g++ gcdTest.cc -o god Then you can execute it with the command gcd or ./god if the first one doesn't work. Ex. 3 Tail Recursion Definition For each of the following functions, state whether or not they are tail recursive. Justify your answer. a. (defun select-i (Li) (cond ((not L) nil) ((= i 0) (car L)) (t (select-i (cdr L) (- i 1))))) b. (defun length (L) (cond ((not L) 0) (t (+ 1 (length (cdr L)))))) c. The function merge_sort from Exercise 1. Write a small C++ program that defines a recursive function GCD based on the model of the Lisp function discussed in the lecture. In the main function, write a loop (while or do) that repeats the following actions: ask the user to enter two numbers, compute their GCD and output it, until the user enters 0 for one of the numbers. You can use a single source file for this, or two of them. If you use only one, then assuming that it is called godTest.cc, you can compile it with the command g++ gcdTest.cc -o god Then you can execute it with the command gcd or ./god if the first one doesn't work. Ex. 3 Tail Recursion Definition For each of the following functions, state whether or not they are tail recursive. Justify your answer. a. (defun select-i (Li) (cond ((not L) nil) ((= i 0) (car L)) (t (select-i (cdr L) (- i 1))))) b. (defun length (L) (cond ((not L) 0) (t (+ 1 (length (cdr L)))))) c. The function merge_sort from Exercise 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


