Question: Write a Unix shell program (i.e. script) to simulate a simple calculator. Please make sure the program works perfectly and has the exact output as
Write a Unix shell program (i.e. script) to simulate a simple calculator. Please make sure the program works perfectly and has the exact output as the second picture. I will upvote if the output is same. please read the instructions carefully.
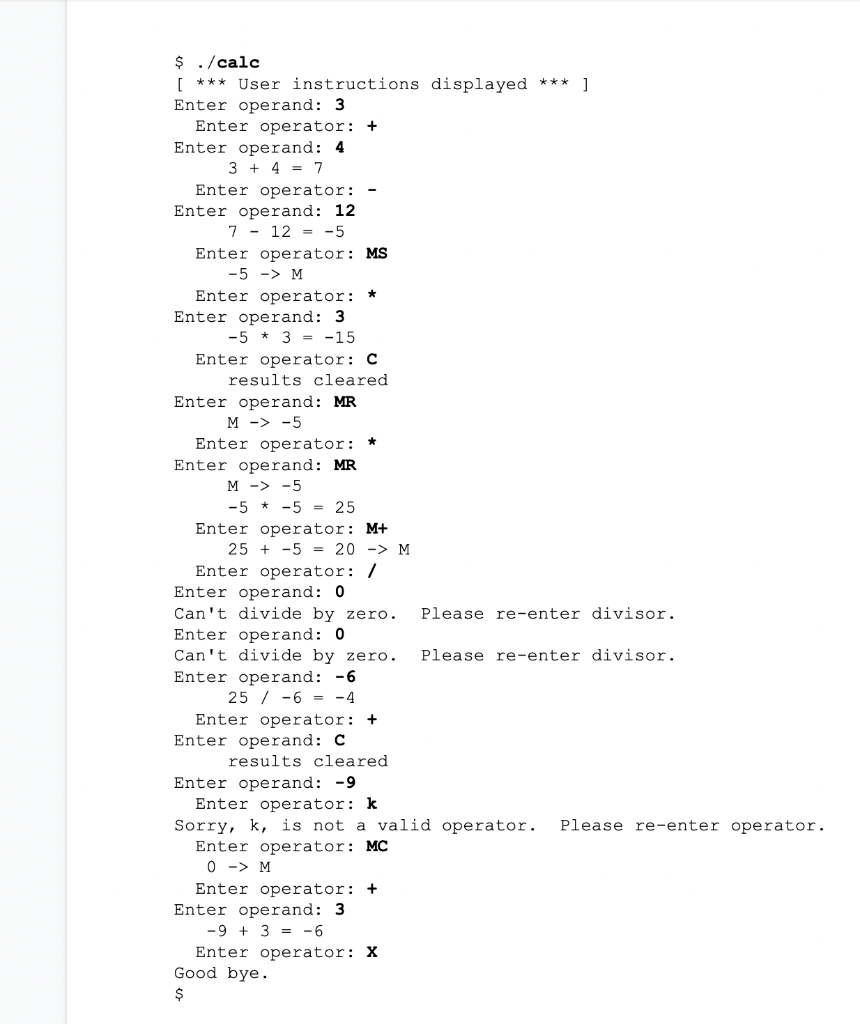
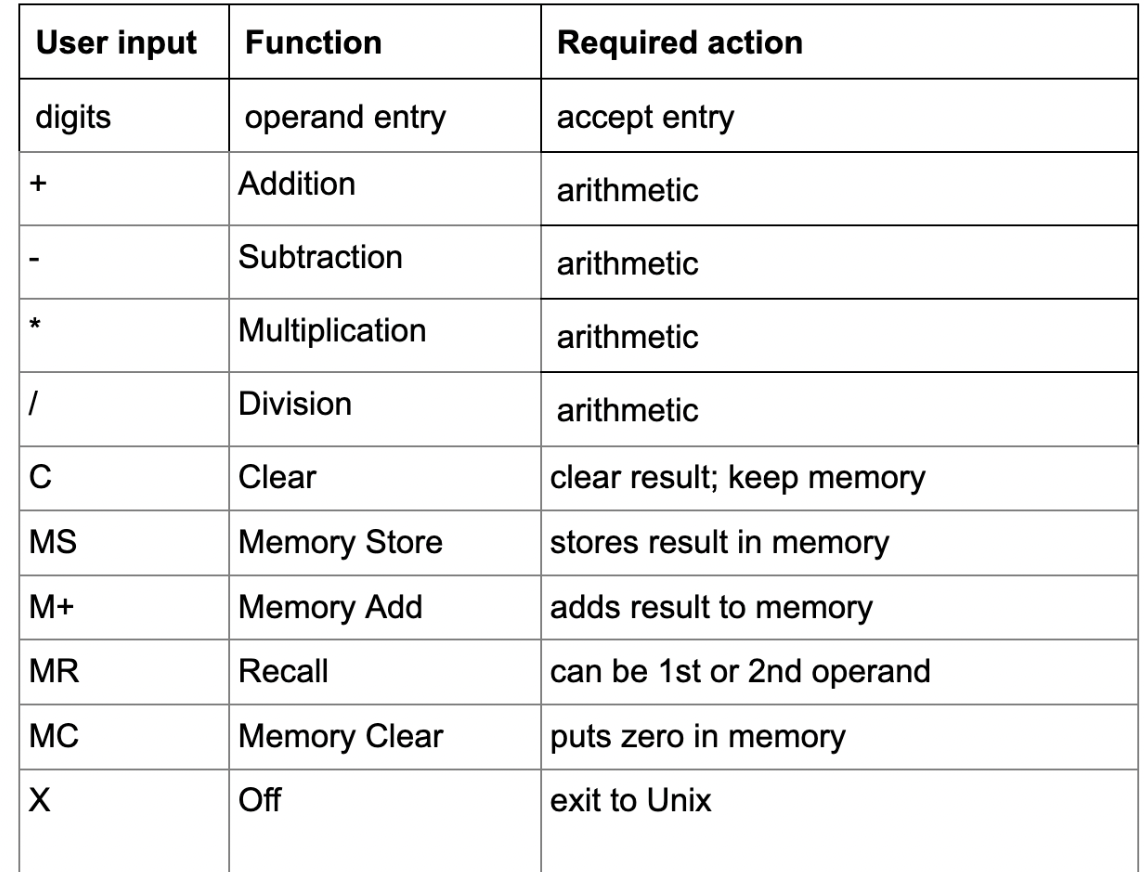
- Prompt the user for an operand followed by an operator and then the second operand. - Display the two numbers, the operation and the answer (see example sequence below). - As each subsequent operation will use the previous result, prompt the user for the next operator and operand. - Implement integer arithmetic only (no need for floating point support). - Check for division by zero; display warning and continually ask the user to re-enter the divisor. - At the "Operand" prompt, the user can enter: Any digit, MR, MC, Clear (C), Off (X) - At the "Operator" prompt, the user can enter: +,,,l,MS,M+,MC, Clear (C), Off (X) - At both prompts (treat as operand or operator): MC, Clear (C), Off (X) - Error checking: For the operand, assume valid input (no error checking required). For the operator, check for an invalid operator, display a brief informative message, then re-ask the user for input; do not "clear" the transaction. - Initialize variables appropriately (hint: memory). - Program (script) must be directly executable (i.e. run with "./calc" NOT "bash calc") - Do not implement operator precedence, or Reverse Polish Notation, or anything complicated: Think dollar store calculator. - Work towards a solution which minimizes code duplication. - Match your code behaviour to the sample dialog below. \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline User input & Function & Required action \\ \hline digits & operand entry & accept entry \\ \hline+ & Addition & arithmetic \\ \hline & Subtraction & arithmetic \\ \hline & Multiplication & arithmetic \\ \hlineI & Division & arithmetic \\ \hline C & Clear & clear result; keep memory \\ \hline MS & Memory Store & stores result in memory \\ \hline M+ & Memory Add & adds result to memory \\ \hline MR & Recall & can be 1st or 2 nd operand \\ \hline MC & Memory Clear & puts zero in memory \\ \hline X & Off & exit to Unix \\ \hline \end{tabular}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


