Question: Write Grafstate code for a context-free grammar that is equivalent to N. Your Grafstate code Type your answers in a Grafstate file (.graf.txt) must run
Write Grafstate code for a context-free grammar that is equivalent to N.

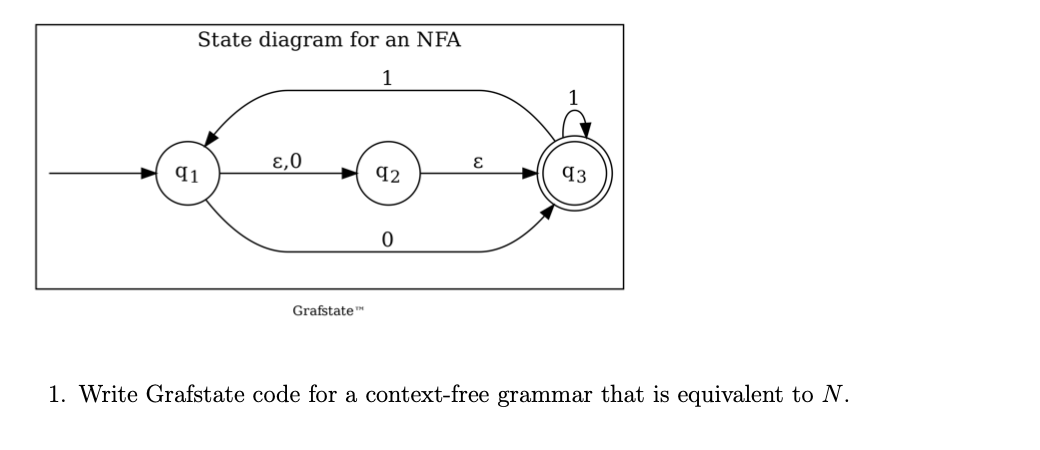
Your Grafstate code Type your answers in a Grafstate file (.graf.txt) must run with no errors. We defined a context-free grammar G as a 4-tuple G = (V, E, R, vo), where 1. V is a finite and nonempty set of variables, 2. E is an alphabet, 3. R is a finite and nonempty set of context-free rules, 4. vo e V is the starting variable. Any context-free rule must be of the form A w, where w E (V UE)*. You can write context-free grammars with Grafstate here: http://grafstate.com/grammar/cfg/. Any variable may be used as the left-hand side of multiple rules. The following are three context-free rules from a variable A: A +0A1 A +1A0 A + The above three rules can be written on one line using the vertical bar separator as follows: A +0A1|1A0 Grafstate will support either notation. Note that variables and symbols must be separated by a space. You can experiment with CFGs with Grafstate at grafstate.com/grammar/cfg/. Enter an input string. The CFG will be used to determine if the string can be derived from the starting variable using the grammar. If there is a derivation of the inpu starting with the variable vo, then Grafstate will produce a sequence showing how the string can be derived. Consider the following NFA (M1) over the alphabet ? = {0,1}: State diagram for an NFA 1 ,0 E 91 92 0 Grafstate 1. Write Grafstate code for a context-free grammar that is equivalent to N. Your Grafstate code Type your answers in a Grafstate file (.graf.txt) must run with no errors. We defined a context-free grammar G as a 4-tuple G = (V, E, R, vo), where 1. V is a finite and nonempty set of variables, 2. E is an alphabet, 3. R is a finite and nonempty set of context-free rules, 4. vo e V is the starting variable. Any context-free rule must be of the form A w, where w E (V UE)*. You can write context-free grammars with Grafstate here: http://grafstate.com/grammar/cfg/. Any variable may be used as the left-hand side of multiple rules. The following are three context-free rules from a variable A: A +0A1 A +1A0 A + The above three rules can be written on one line using the vertical bar separator as follows: A +0A1|1A0 Grafstate will support either notation. Note that variables and symbols must be separated by a space. You can experiment with CFGs with Grafstate at grafstate.com/grammar/cfg/. Enter an input string. The CFG will be used to determine if the string can be derived from the starting variable using the grammar. If there is a derivation of the inpu starting with the variable vo, then Grafstate will produce a sequence showing how the string can be derived. Consider the following NFA (M1) over the alphabet ? = {0,1}: State diagram for an NFA 1 ,0 E 91 92 0 Grafstate 1. Write Grafstate code for a context-free grammar that is equivalent to N
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


