Question: write in java 8 You have three stacks of cylinders where each cylinder has the same diameter, but they may vary in height. You can
write in java 8


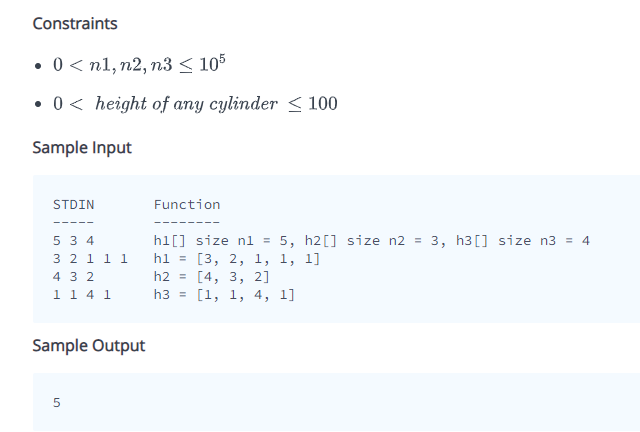
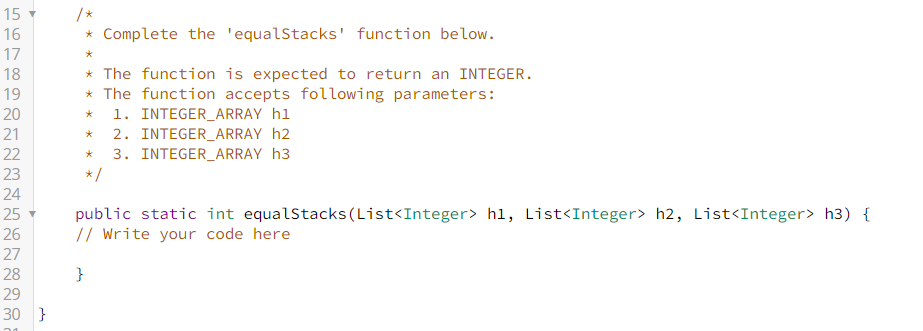

![2, 1, 1] h2 = (1,1,2] h3 = [1,1] There are 4,](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f50fd724bc5_40666f50fd6b7d50.jpg)
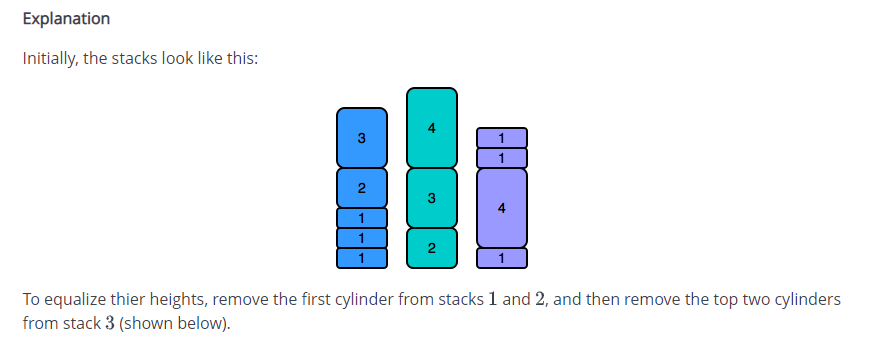
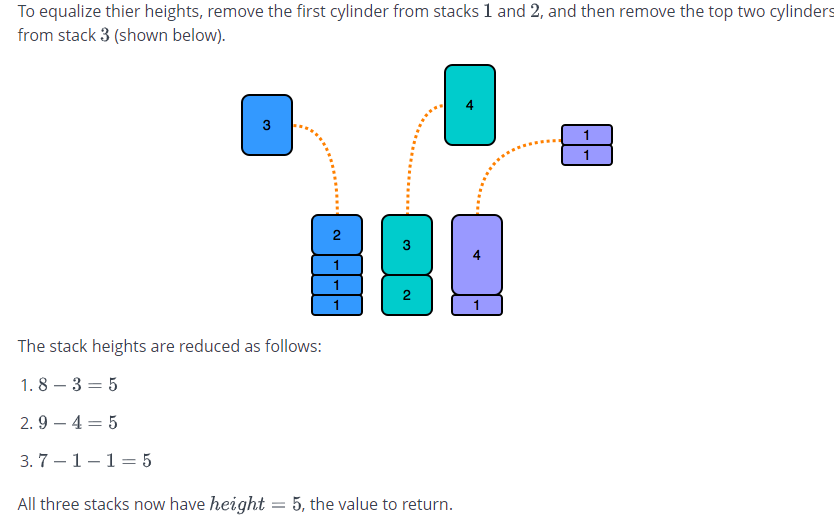
You have three stacks of cylinders where each cylinder has the same diameter, but they may vary in height. You can change the height of a stack by removing and discarding its topmost cylinder any number of times. Find the maximum possible height of the stacks such that all of the stacks are exactly the same height. This means you must remove zero or more cylinders from the top of zero or more of the three stacks until they are all the same height, then return the height. Example hl = [1, 2, 1, 1] h2 = (1,1,2] h3 = [1,1] There are 4, 3 and 2 cylinders in the three stacks, with their heights in the three arrays. Remove the top 2 cylinders from hl (heights = [1, 2]) and from h2 (heights = [1, 1) so that the three stacks all are 2 units tall. Return 2 as the answer. Note: An empty stack is still a stack. Function Description Complete the equalStacks function in the editor below. equalStacks has the following parameters: int h1 [n 1]: the first array of heights int h2[n2] the second array of heights int h33]: the third array of heights Returns int: the height of the stacks when they are equalized Input Format The first line contains three space-separated integers, nl, n2, and n3, the numbers of cylinders in stacks 1, 2, and 3. The subsequent lines describe the respective heights of each cylinder in a stack from top to bottom: The second line contains nl space-separated integers, the cylinder heights in stack 1. The first element is the top cylinder of the stack. The third line contains n2 space-separated integers, the cylinder heights in stack 2. The first element is the top cylinder of the stack. The fourth line contains n3 space-separated integers, the cylinder heights in stack 3. The first element is the top cylinder of the stack. Constraints 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


