Question: write in java8 Given a directed graph as an adjacency list, you need to determine whether it is acyclic or not. Input Format Each of
write in java8


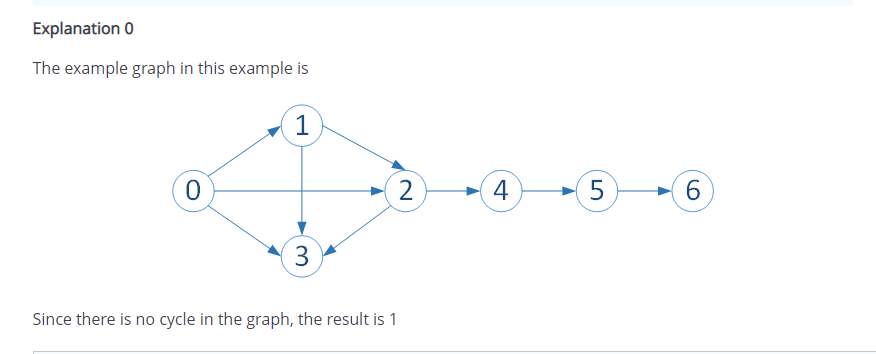


Given a directed graph as an adjacency list, you need to determine whether it is acyclic or not. Input Format Each of the lines in the input contains two space-separated integers, s and d, that represents an edge from the node sto d. Constraints Node numbers are 0 based, i.e. if there n nodes, the nodes are numnered as 0,1,2,...,n-1. Output Format The output of the program is 0 or 1, depending on the result of the isDag() function. If it returns TRUE, output is 1, otherwise it is 0. Sample Input 0 1 02 3 1 2 13 23 24 4 5 5 6 Sample Output 0 1 Explanation o The example graph in this example is 1 0 2 4. 5 6 3 Since there is no cycle in the graph, the result is 1 1 import java.io.*; 2 import java.math.*; 3 import java. security.*; 4 import java.text.*; 5 import java.util.*; 6 import java.util.concurrent.*; 7 import java.util. function.*; 8 import java.util.regex.*; 9 import java.util.stream.*; 10 11 public class Solution { 12 13 public static class DirectedGraph { 14 /* Adjacency List representation of the given graph */ 15 private Map> adjList = new HashMap>(); 16 17 public String toString() { 18 StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(); 19 for (Integer v: adjlist.keySet()) 20 s.append(" " + v + " -> " + adjlist.get()); 21 return s.toString(); 22 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public void add (Integer vertex) { if (adj List.containsKey(vertex)) return; adj List.put(vertex, new ArrayList(); } public void add (Integer source, Integer dest) { add (source); add (dest); adj list.get(source).add(dest); } 37 21 12 13 14 15 76 47 18 /* Indegree of each vertex as a Map */ public Map inDegree() { Map result = new HashMap(); for (Integer v: adj List.keySet() result.put(v, 0); for (Integer from : adjlist.keySet()) { for (Integer to : adjlist.get(from)) { result.put(to, result.get(to) + 1); } } return result; } 48 49 50 51 public Map outDegree () { Map result = new HashMap(); for (Integer v: adj List.keySet()) result.put(v, adj list.get(v).size()); return result; } 52 53 54 55 } 56 57 58 // Complete the isdag function below. public static boolean isDAG(int z, boolean[] visited, boolean[] recursionStack) { if (recursionStack [z]) return true; if (visited [z]) return false; 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 visited [z] = true; recursionStack [z] = true; List children = adj.get(z); 72 for (Integer b: children) { if (isDAG(b, visited, recursionStack)) return true; 73 74 75 76 recursionStack [z] false; } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 BufferedWriter bufferredWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv ("OUTPUT_PATH")); BufferedReader bufferredReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader (System.in); DirectedGraph digraph = new DirectedGraph(); 5 -6 7 8 -9 10 11 String line; while ((line = bufferredReader.readLine()) != null) { String[] v = line.split(" "); digraph.add(Integer.parseInt(v[0]), Integer.parseInt(v[1])); } 3 14 15 bufferredWriter.write((isDag(digraph) ? "1" : "0")); bufferredReader.close(); bufferredwriter.close(); 17 8 19 10} 11 }










