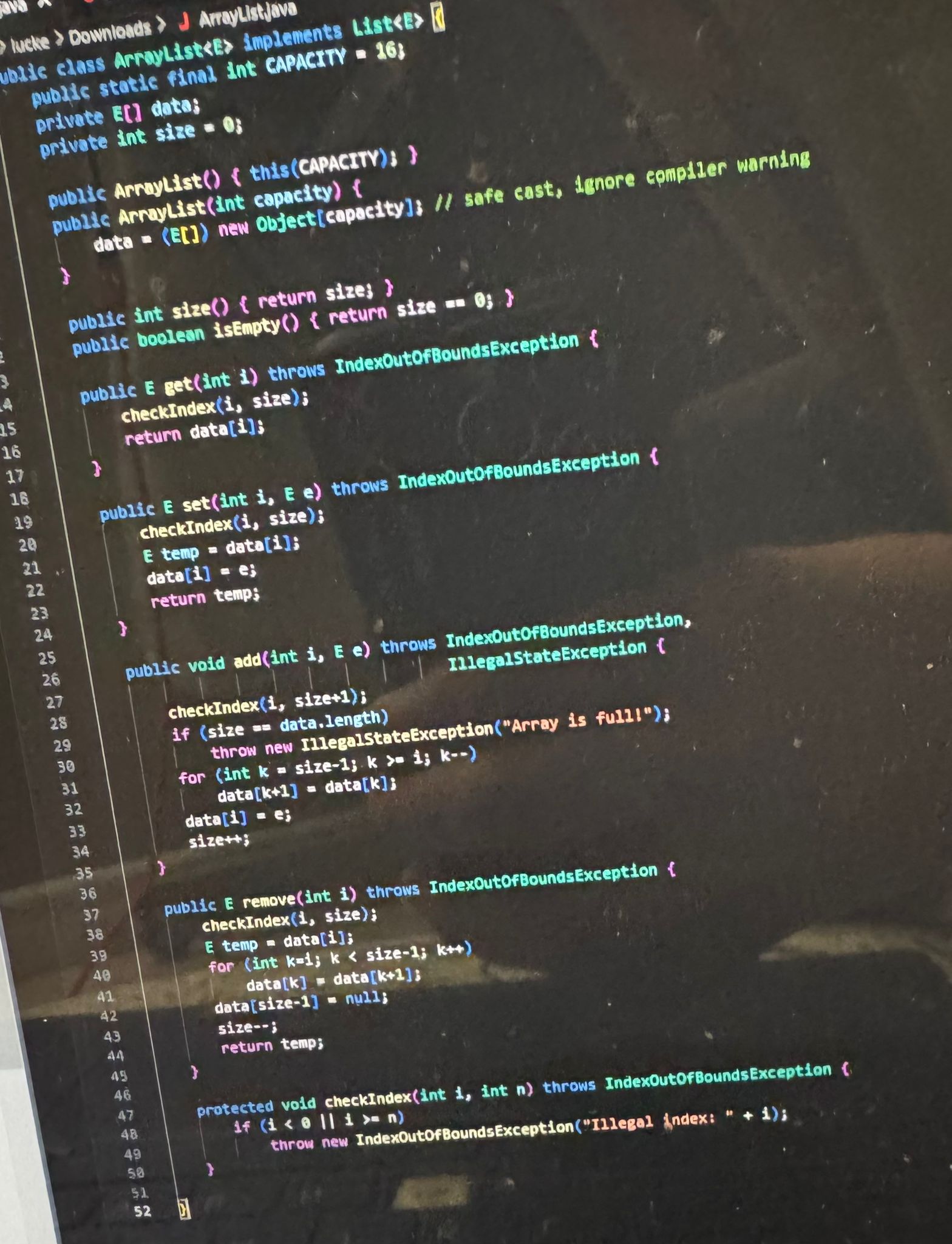
Question: Write the ArrayList class using a fixed - size array provided in the picture. The class should implement the List interface. Taking this as a
Write the ArrayList class using a fixedsize array provided in the picture. The class should implement the List interface. Taking this as a base, modify the ArrayList so that it works circularly. That is if elements would be inserted past the bounds of the array, they should wrap around to the other side. You can find the strategy for this with the circular arraybased queue.
However, in this case it should be possible to insert elements anywhere within the
bounds of the list. Important info waic class Arroylistse implaments List;data;data You will need to keep track of the starting index of the list and the size of the list.
Knowing these and the length of the array will let you identify where the beginning and
the end of the list are. Note you will need modular arithmetic to do so as shown in the
notes.
Adding or removing at a certain index in the list will actually need to be offset. If the
list elements are at indices then calling add e should actually
insert at index of the array, and addlistsize e or add e should insert at index
Consider writing a helper method to perform this offset calculation.
The bounds checking with checkIndex will also have to be modified, because the
start of the list is no longer guaranteed to be at
In case you need it Java's modulo operator works in a way where taking a modulo on
a negative number will result in a negative number, which is not useful for indexing.
For example, is but results in instead of
To fix this issue, compute these like instead.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


