Question: WRITE THE CODE & THE OUTPUTS 7. Smoothing filter. Although it is a really useful function, Matlab does not contain an easy to use smoothing
WRITE THE CODE & THE OUTPUTS
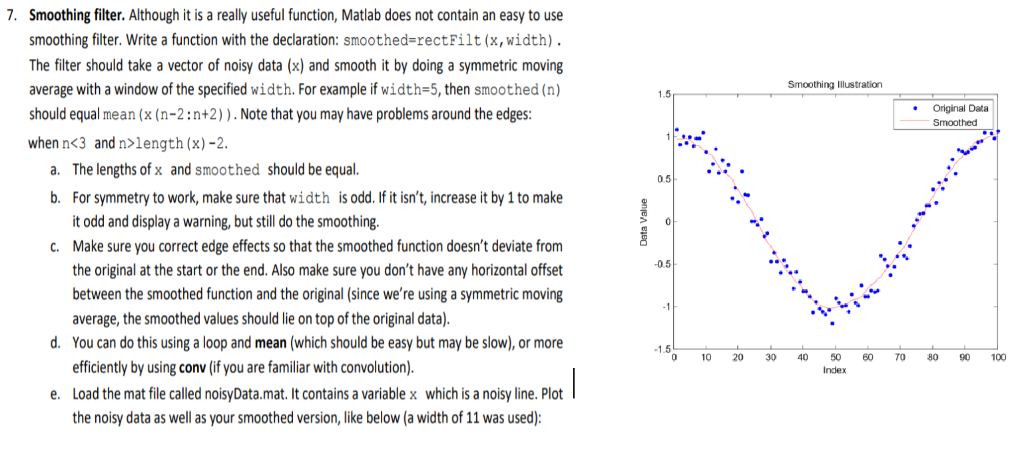
7. Smoothing filter. Although it is a really useful function, Matlab does not contain an easy to use smoothing filter. Write a function with the declaration: smoothed-rectFilt(x, width) . The filter should take a vector of noisy data (x) and smooth it by doing a symmetric moving average with a window of the specified width. For example if width-5, then smoothed (n) should equal mean (x (n-2:n+2)). Note that you may have problems around the edges when nlength (x)-2 Smoothing "lustration 1.5 Original Data Smoothed a. The lengths of x and smoothed should be equal b. For symmetry to work, make sure that width is odd. If it isn't, increase it by 1 to make 0.5 it odd and display a warning, but still do the smoothing Make sure you correct edge effects so that the smoothed function doesn't deviate from the original at the start or the end. Also make sure you don't have any horizontal offset between the smoothed function and the original (since we're using a symmetric moving average, the smoothed values should lie on top of the original data) You can do this using a loop and mean (which should be easy but may be slow), or more efficiently by using conv (if you are familiar with convolution) Load the mat file called noisyData.mat. It contains a variable x the noisy data as well as your smoothed version, like below (a width of 11 was used) c. 0.5 d. 1.5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 TO 80 90 100 Index e. which is a noisy line. Plot 7. Smoothing filter. Although it is a really useful function, Matlab does not contain an easy to use smoothing filter. Write a function with the declaration: smoothed-rectFilt(x, width) . The filter should take a vector of noisy data (x) and smooth it by doing a symmetric moving average with a window of the specified width. For example if width-5, then smoothed (n) should equal mean (x (n-2:n+2)). Note that you may have problems around the edges when nlength (x)-2 Smoothing "lustration 1.5 Original Data Smoothed a. The lengths of x and smoothed should be equal b. For symmetry to work, make sure that width is odd. If it isn't, increase it by 1 to make 0.5 it odd and display a warning, but still do the smoothing Make sure you correct edge effects so that the smoothed function doesn't deviate from the original at the start or the end. Also make sure you don't have any horizontal offset between the smoothed function and the original (since we're using a symmetric moving average, the smoothed values should lie on top of the original data) You can do this using a loop and mean (which should be easy but may be slow), or more efficiently by using conv (if you are familiar with convolution) Load the mat file called noisyData.mat. It contains a variable x the noisy data as well as your smoothed version, like below (a width of 11 was used) c. 0.5 d. 1.5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 TO 80 90 100 Index e. which is a noisy line. Plot
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


