Question: **Written In Java Eclipse** package algs14; import stdlib.*; public class hw7 { // To check for properly sorted arrays, enable assertion checks in eclipse. //
**Written In Java Eclipse**
package algs14; import stdlib.*;
public class hw7 { // To check for properly sorted arrays, enable assertion checks in eclipse. // To turn on assertions for a program in eclipse, // run the program once, then go to the menu bar and select // Run > Run Configurations... > Arguments > VM Arguments // And add // -ea // As a VM argument. IMPLEMENT THE FUNCTION BODIES WHERE IT SAYS "TODO". public static void insertionSort(Comparable[] a) { // TODO assert isSorted(a, 0, a.length-1) : "Array is not sorted."; } public static void selectionSort(Comparable[] a) { // TODO assert isSorted(a, 0, a.length-1) : "Array is not sorted."; }
public static void mergeSort(Comparable[] a) { // TODO assert isSorted(a, 0, a.length-1) : "Array is not sorted."; } public static void quickSort(Comparable[] a) { // TODO assert isSorted(a, 0, a.length-1) : "Array is not sorted."; }
/* ********************************************************************* * bubbleSort provided as an example ***********************************************************************/ public static void bubbleSort(Comparable[] a) { int N = a.length; for (int i = 0; i
/* ********************************************************************* * Helper sorting functions ***********************************************************************/
// is v > boolean less(T v, T w) { DoublingTest.incOps (); return (v.compareTo(w)
// exchange a[i] and a[j] private static // The goal of this is to find the best and worst case inputs // for each of the above four sorting algorithms, and make note of them // For each such sorting algorithm and input type (best, average, worst). We'll treat the random list of integers as the average case. // To check for properly sorted arrays, enable assertion checks in eclipse // by added the -ea option to the VM arguments for the program. // System.out.println(" ///////////////// BubbleSort "); System.out.println("Random"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerRandomUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> bubbleSort (x)); System.out.println("Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> bubbleSort (x)); System.out.println("Reverse"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerReverseSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> bubbleSort (x)); System.out.println("Partially Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerPartiallySortedUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> bubbleSort (x)); System.out.println(" ///////////////// InsertionSort "); System.out.println("Random"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerRandomUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> insertionSort (x)); System.out.println("Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> insertionSort (x)); System.out.println("Reverse"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerReverseSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> insertionSort (x)); System.out.println("Partially Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerPartiallySortedUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> insertionSort (x)); System.out.println(" ///////////////// SelectionSort "); System.out.println("Random"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerRandomUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> selectionSort (x)); System.out.println("Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> selectionSort (x)); System.out.println("Reverse"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerReverseSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> selectionSort (x)); System.out.println("Partially Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerPartiallySortedUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> selectionSort (x)); System.out.println(" ///////////////// MergeSort "); System.out.println("Random"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerRandomUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> mergeSort (x)); System.out.println("Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> mergeSort (x)); System.out.println("Reverse"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerReverseSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> mergeSort (x)); System.out.println("Partially Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerPartiallySortedUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> mergeSort (x)); System.out.println(" ///////////////// QuickSort "); System.out.println("Random"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerRandomUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> quickSort (x)); System.out.println("Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> quickSort (x)); System.out.println("Reverse"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerReverseSortedUnique(N), (Integer[] x) -> quickSort (x)); System.out.println("Partially Sorted"); DoublingTest.run (32, 12, N -> ArrayGenerator.integerPartiallySortedUnique (N), (Integer[] x) -> quickSort (x)); } } /* ********************************************************************* * Fill out data as shown in example log file below: ***********************************************************************/ 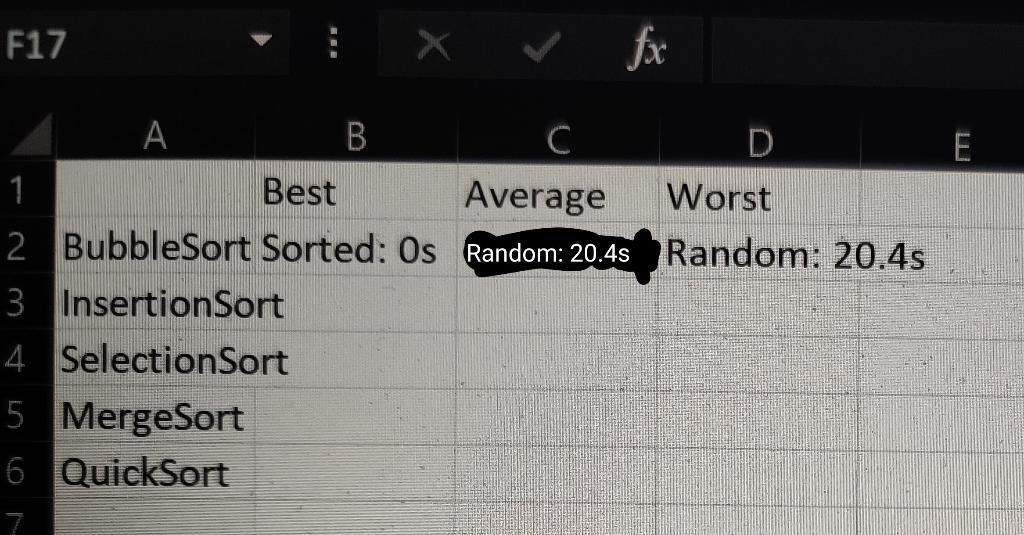
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


