Question: X Homework Help - Q&A from On X + DF File viewer | Microsoft Team: X > course hero log in - Search microsoft.com/_#/pdf/viewer/teams/https:~2F~2Fcardmaillouisville.sharepoint.com~2Fsites~2FPHYS224-Section 75.
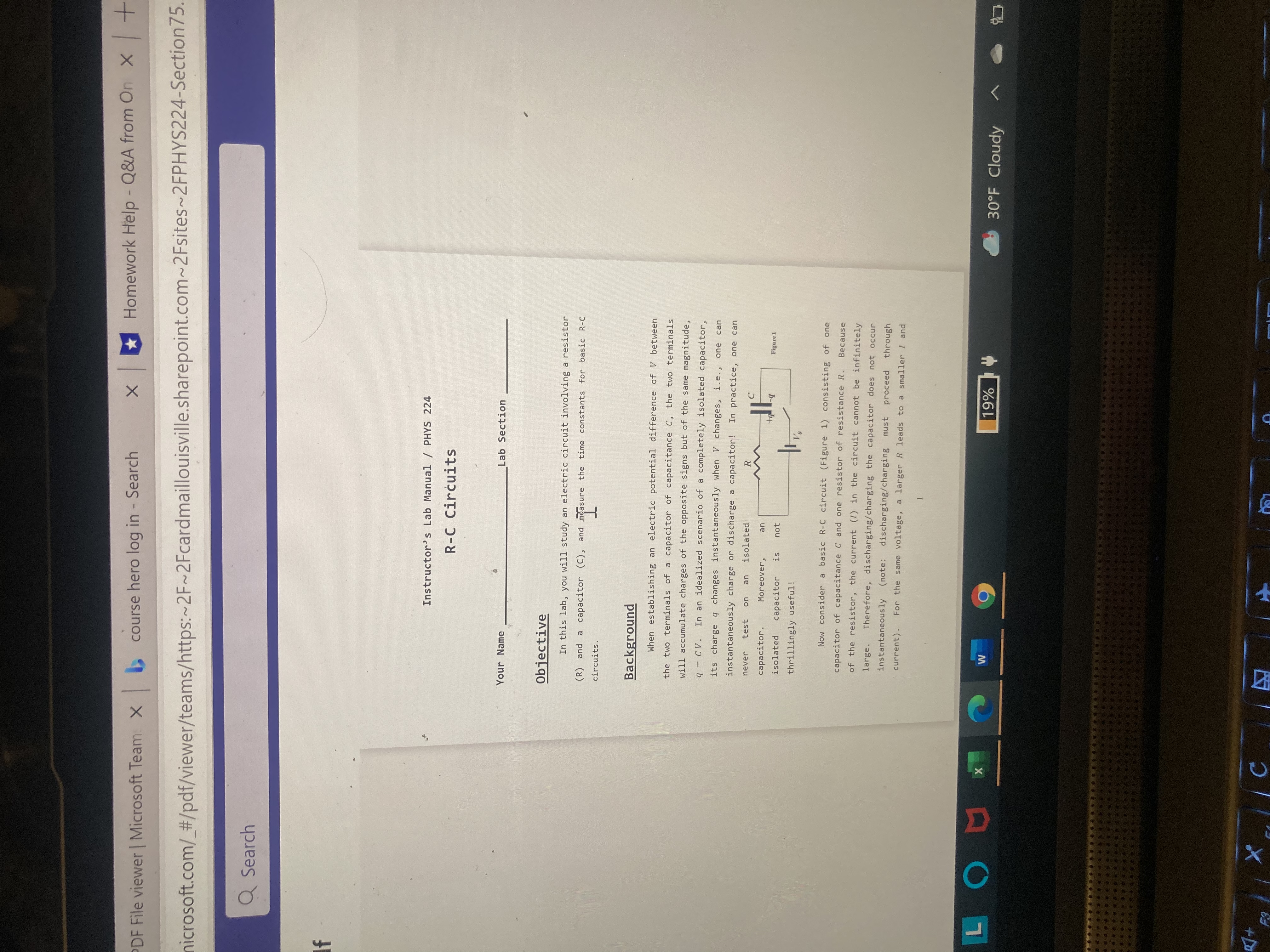
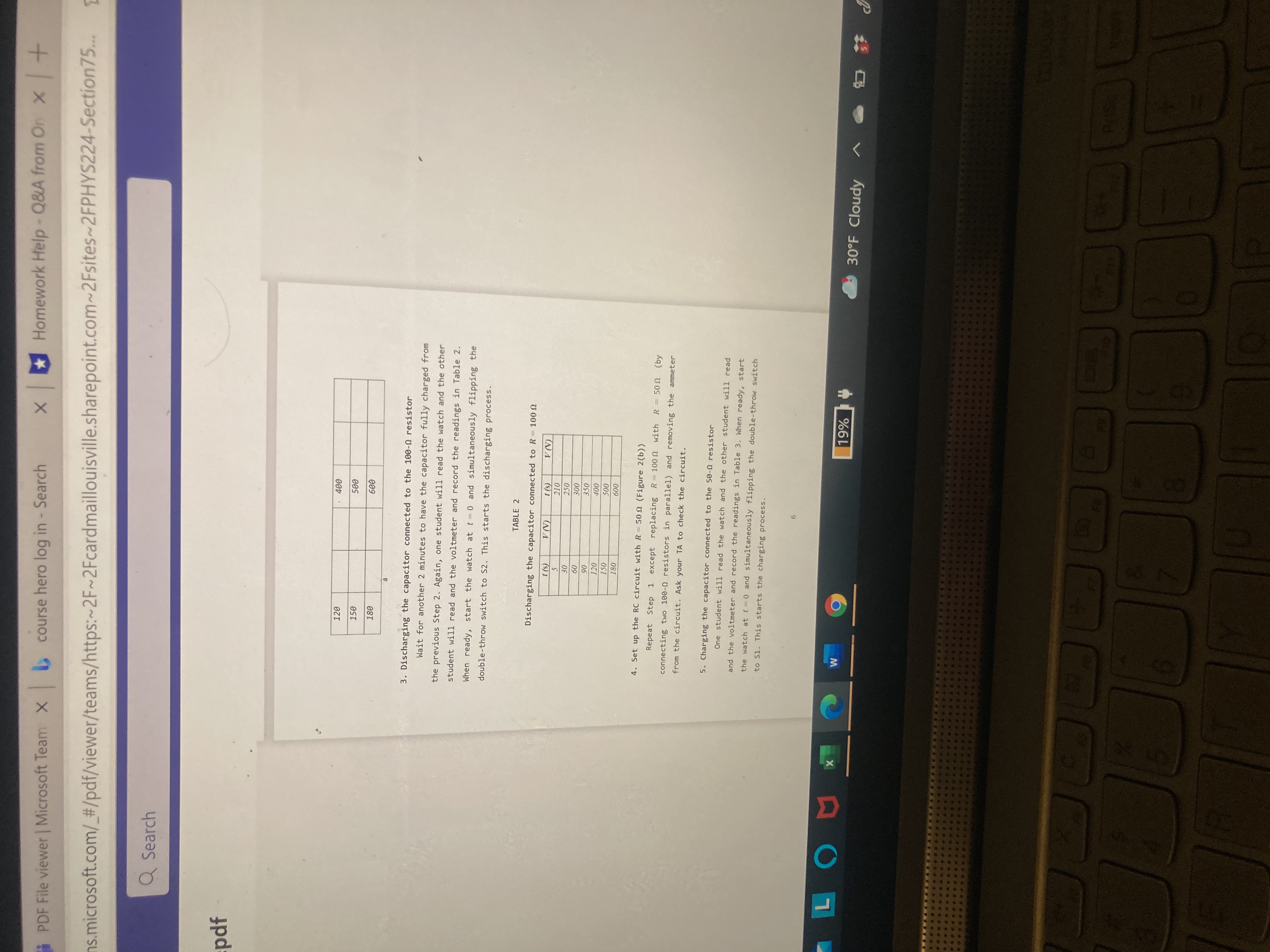
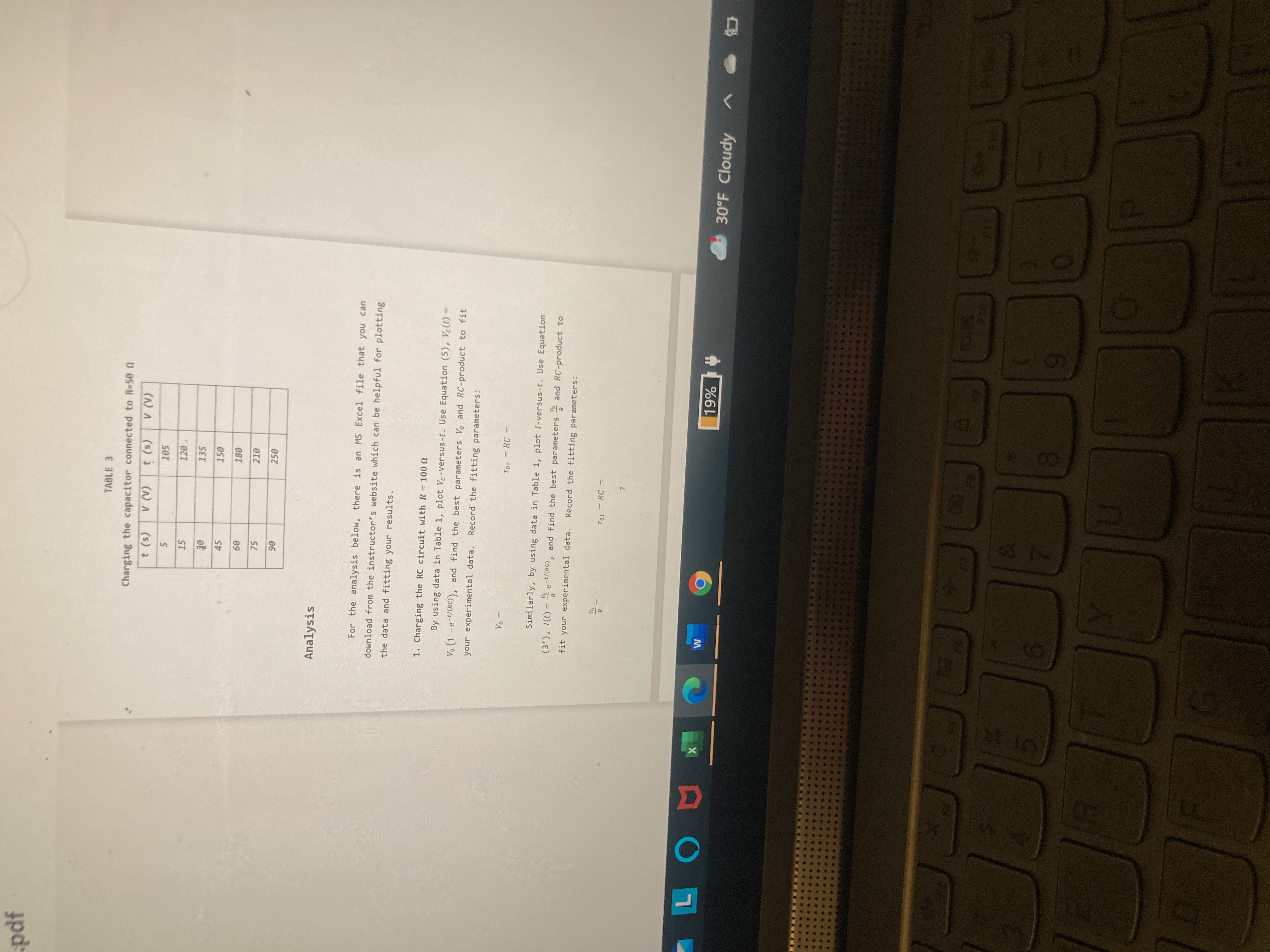
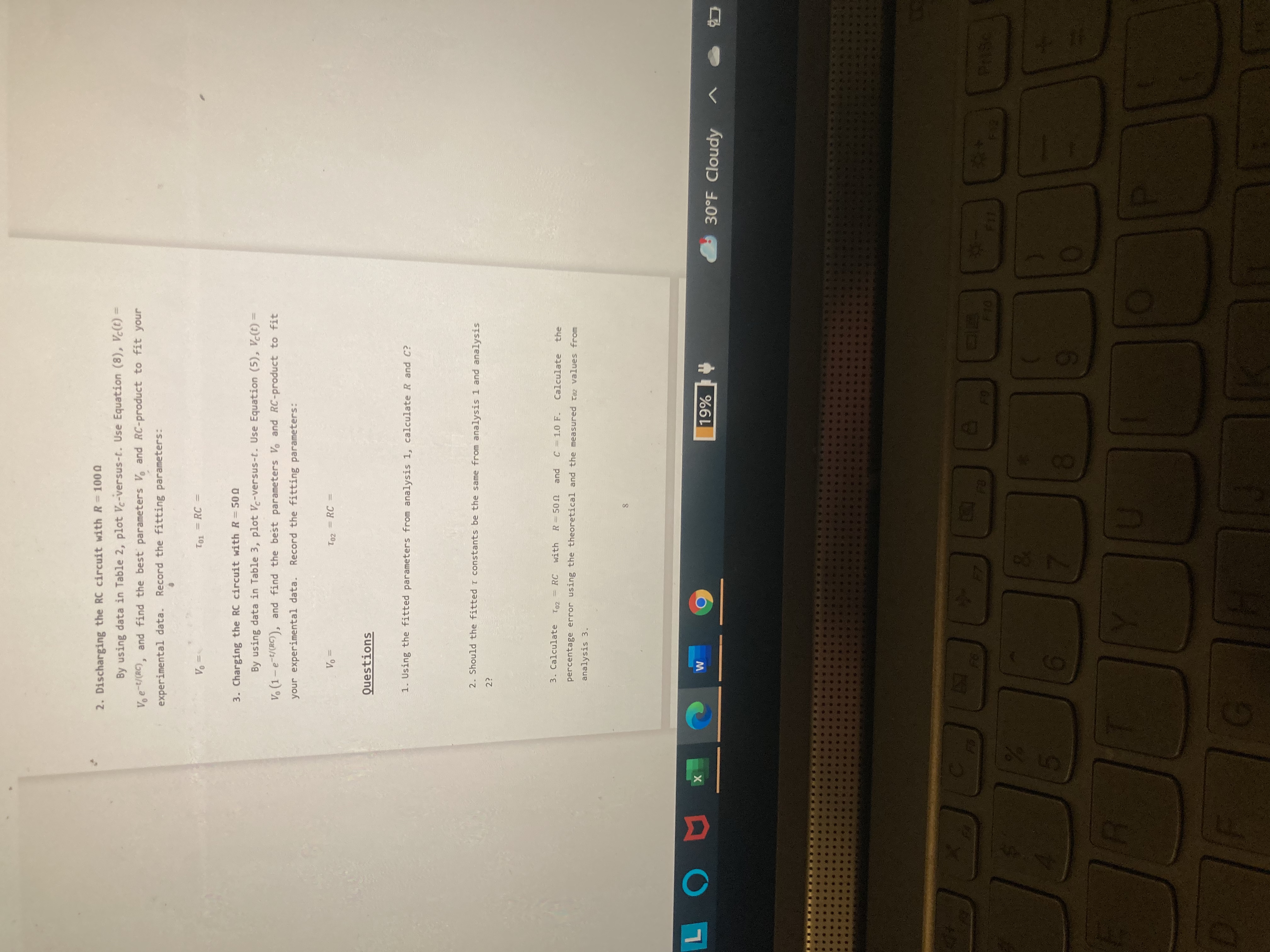
X Homework Help - Q&A from On X + DF File viewer | Microsoft Team: X > course hero log in - Search microsoft.com/_#/pdf/viewer/teams/https:~2F~2Fcardmaillouisville.sharepoint.com~2Fsites~2FPHYS224-Section 75. Q Search Instructor's Lab Manual / PHYS 224 R-C Circuits Your Name _Lab Section Objective In this lab, you will study an electric circuit involving a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C), and measure the time constants for basic R-C circuits. Background When establishing an electric potential difference of V between the two terminals of a capacitor of capacitance C, the two terminals will accumulate charges of the opposite signs but of the same magnitude, 1 = CV. In an idealize nario of a completely isolated capacitor, its charge q changes instantaneously when V changes, i.e. , one can instantaneously charge or discharge a capacitor! In practice, one can never test on an isolated capacitor . Moreover, isolated capacitor is not Figure 1 thrillingly useful! Now consider a basic R-C circuit (Figure 1) consisting of one capacitor of capacitance C and one resistor of resistance R. Because of the resistor, the current (1) in the circuit cannot be infinitely large. Therefore, discharging/ charging the capacitor does not occur instantaneously (note: discharging/charging must proceed through current) . For the same voltage, a larger R leads to a smaller / and LOU x W 9 19% 30OF Cloudy X C AVx *Homework Help - Q&A from On x T PDF File viewer | Microsoft Team X > course hero log in - Search (/teams.microsoft.com/_#/pdf/viewer/teams/https:~2F~2Fcardmaillouisville.sharepoint.com~2Fsites~2FPHYS224-Sect Q Search rcuit.pdf thus leads to a longer discharging/charging time. To change the voltage across the capacitor by the same magnitude, a larger C leads to a larger change of q and thus also leads to a longer discharging/charging time. Therefore, larger R or C leads to larger time constant for the R-C circuit. Such relationships make the time constant a controllable and useful parameter! For the R-C circuit shown in Figure 1, the sum of the voltage across the resistor, VR(t) = I(t) R, and the voltage across the capacitor, Vc(t) = q(t)/C, is: V(t) = 1(t) R += q(t). (1) The current carries the electric charge to or from the two terminals of the capacitor. Because of the conservation of charge, the current must equal the rate of change of the charges on the terminals of the capacitor. Using calculus, it means that I(t) - dac, at , and Equation (1) can be rewritten as: V (t) = - R + - 9(t). (2) Charging a Capacitor: Consider an initially discharged capacitor. When we turn on the switch at t = 0, the total voltage changes from 0 to Vo at t = 0, such that V(t) = 0 at t
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


