Question: x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. On the basis of the information in part (b), compute cost of goods sold. (Round ratios for computational

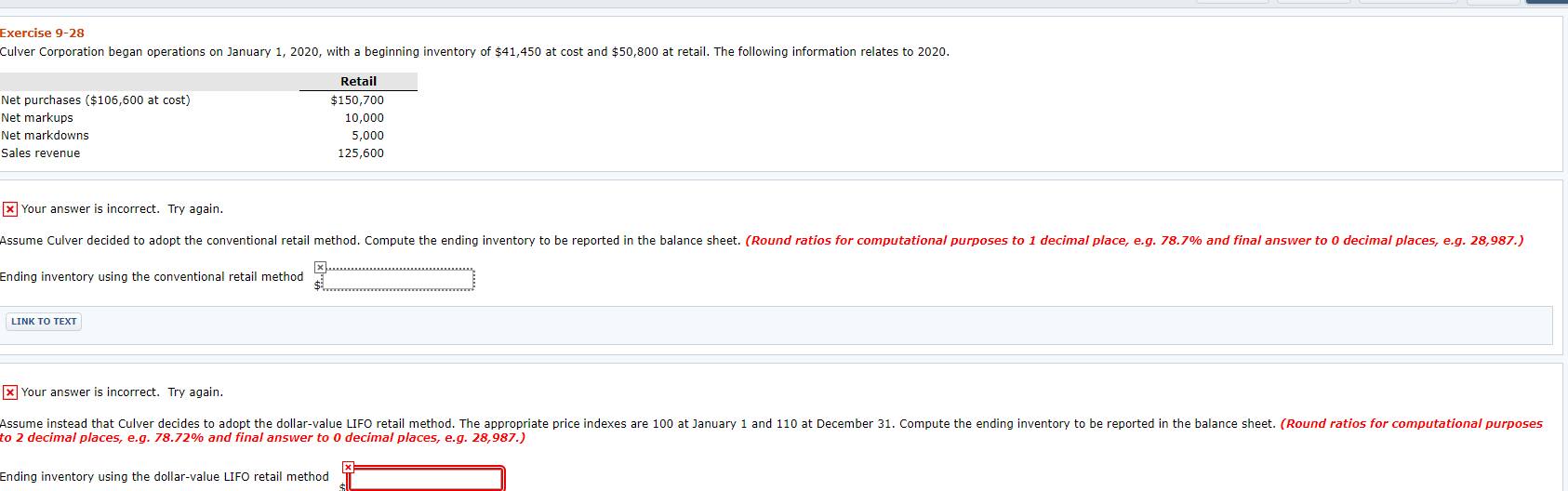

x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. On the basis of the information in part (b), compute cost of goods sold. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to o decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Cost of goods sold using the dollar-value LIFO retail method Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work Exercise 9-28 Culver Corporation began operations on January 1, 2020, with a beginning inventory of $41,450 at cost and $50,800 at retail. The following information relates to 2020. Net purchases ($106,600 at cost) Net markups Net markdowns Sales revenue Retail $150,700 10,000 5,000 125,600 x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. Assume Culver decided to adopt the conventional retail method. Compute the ending inventory to be reported in the balance sheet. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 1 decimal place, e.g. 78.7% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Ending inventory using the conventional retail method LINK TO TEXT * Your answer is incorrect. Try again. Assume instead that Culver decides to adopt the dollar-value LIFO retail method. The appropriate price indexes are 100 at January 1 and 110 at December 31. Compute the ending inventory to be reported in the balance sheet. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Ending inventory using the dollar-value LIFO retail method x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. On the basis of the information in part (b), compute cost of goods sold. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to o decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Cost of goods sold using the dollar-value LIFO retail method Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. On the basis of the information in part (b), compute cost of goods sold. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to o decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Cost of goods sold using the dollar-value LIFO retail method Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work Exercise 9-28 Culver Corporation began operations on January 1, 2020, with a beginning inventory of $41,450 at cost and $50,800 at retail. The following information relates to 2020. Net purchases ($106,600 at cost) Net markups Net markdowns Sales revenue Retail $150,700 10,000 5,000 125,600 x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. Assume Culver decided to adopt the conventional retail method. Compute the ending inventory to be reported in the balance sheet. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 1 decimal place, e.g. 78.7% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Ending inventory using the conventional retail method LINK TO TEXT * Your answer is incorrect. Try again. Assume instead that Culver decides to adopt the dollar-value LIFO retail method. The appropriate price indexes are 100 at January 1 and 110 at December 31. Compute the ending inventory to be reported in the balance sheet. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Ending inventory using the dollar-value LIFO retail method x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. On the basis of the information in part (b), compute cost of goods sold. (Round ratios for computational purposes to 2 decimal places, e.g. 78.72% and final answer to o decimal places, e.g. 28,987.) Cost of goods sold using the dollar-value LIFO retail method Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


