Question: You are allowed to use any C library function, such as printf(), putchar(), etc. Your program will be a variant of the Unix echo program.
You are allowed to use any C library function, such as printf(), putchar(), etc. Your program will be a variant of the Unix echo program.
Background: Recall that when a program is run on the command line, argv[0] points to the first token of the command line (which is the name of the program itself), argv[1] points to the second token on the command line, and so on. So if you run cal 11 2019, then argv[0] points to (the start of) a string "cal", argv[1] points to a string "11", and argv[2] points to a string "2019". The total number of argument tokens on the command line is the integer argc, so the last token is argv[argc-1].
All the strings pointed to by argv[k] (0
The Unix echo program echoes back all its arguments on the command line starting from argv[1]; it skips the program name itself, argv[0]. A simple C code for the echo program could be:
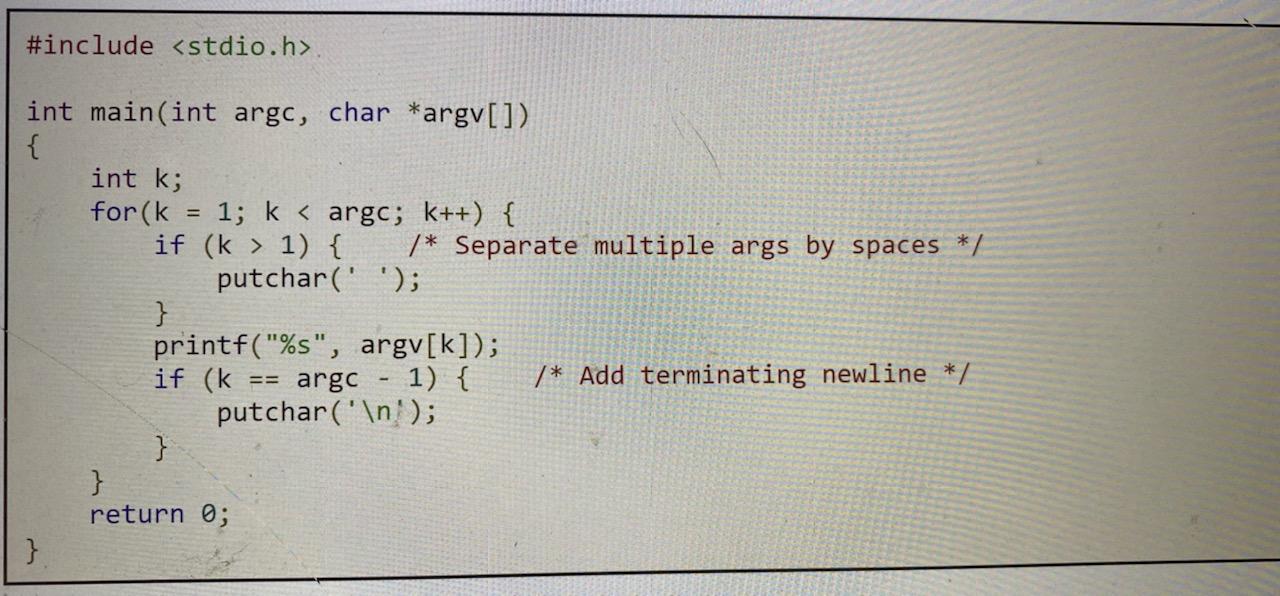
Assignment 1: Write a C program called xecho, which is like echo, but which:
- Prints the argc value first on a line by itself;
- Prints each argument on a line by itself;
- Does not skip argv[0];
- Expresses each token both as a C string and as a C array (see sample output below).
Your program should be contained in a single C source code file called xecho.c, and can make use of any C library functions using header files such as stdio.h. Compile it on the shell command line using:

#include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


