Question: You are given the following C-like code. int foo(int *p) {. *p = 1; return 2;} int bar(int *p) {*p = 3; return 4;} int
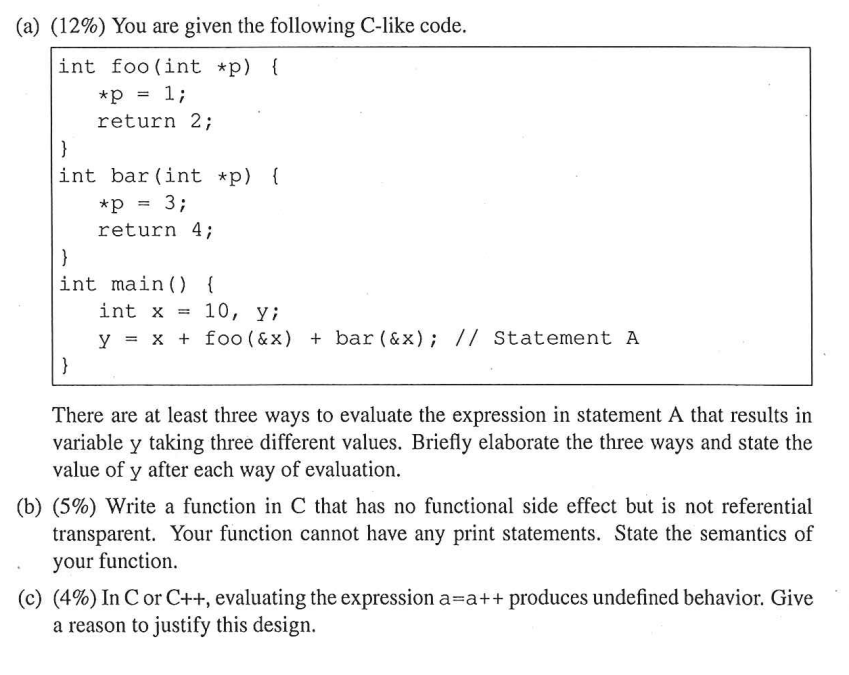
You are given the following C-like code. int foo(int *p) {. *p = 1; return 2;} int bar(int *p) {*p = 3; return 4;} int main() {int x = 10, y; y = x + foo(&x) + bar(&x);//Statement A} There are at least three ways to evaluate the expression in statement A that results in variable y taking three different values. Briefly elaborate the three ways and state the value of y after each way of evaluation. Write a function in C that has no functional side effect but is not referential transparent. Your function cannot have any print statements. State the semantics of your function. In C or C++, evaluating the expression a = a++ produces undefined behavior. Give a reason to justify this design
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


