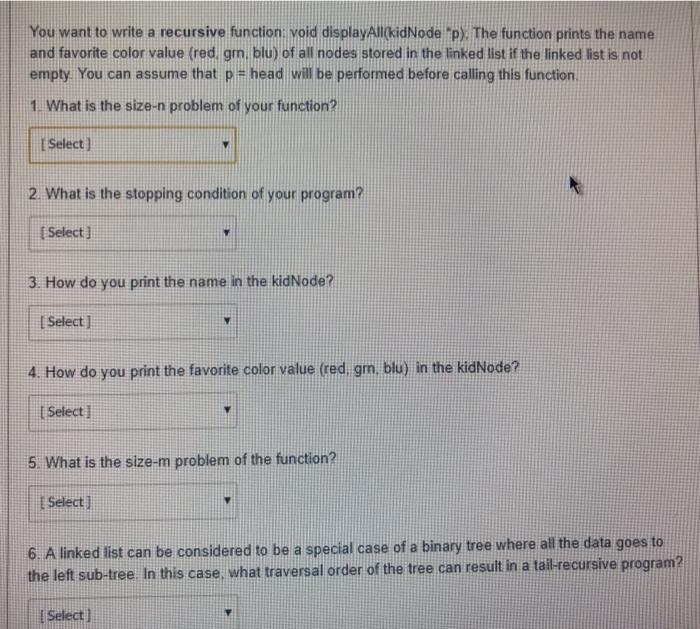
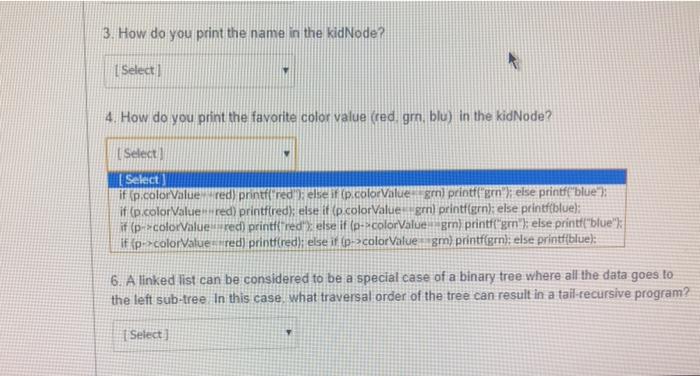
Question: You want to write a recursive function: void displayAllkidNode p). The function prints the name and favorite color value (red, gm. blu) of all nodes
![How do you print the name in the kidNode? [ Select] 4.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f31aeba6470_17166f31aeb4138b.jpg)
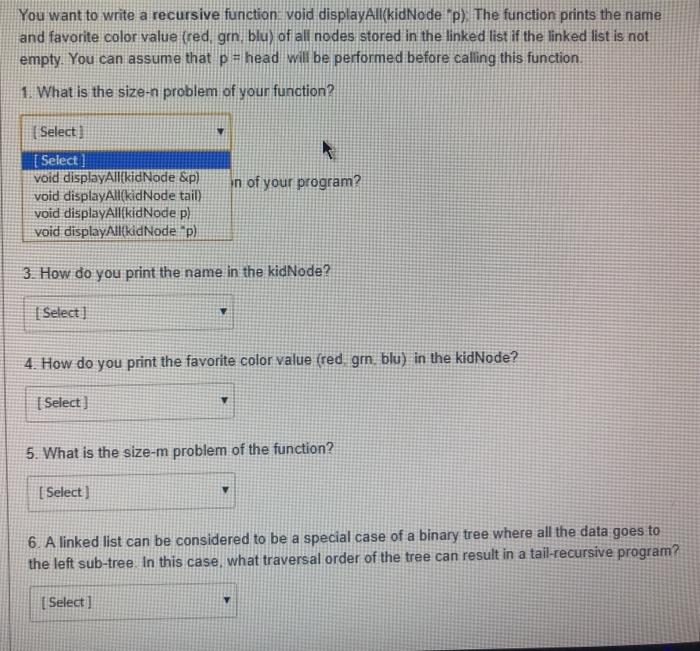
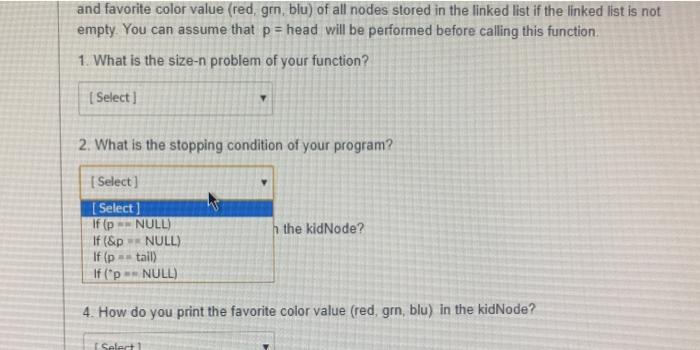
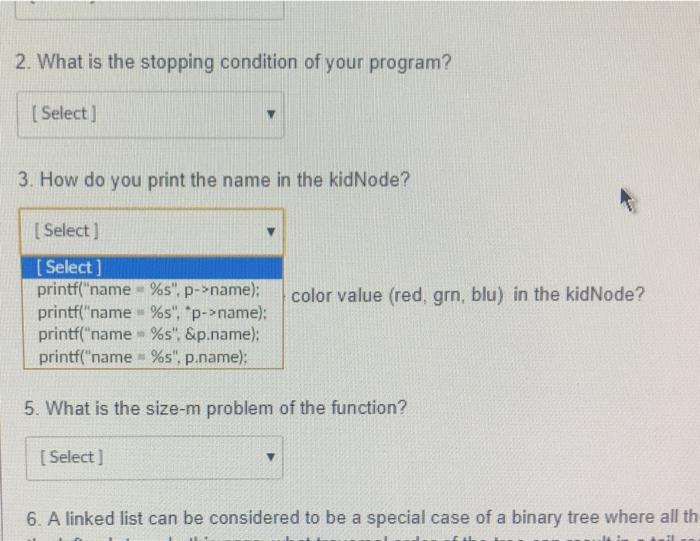
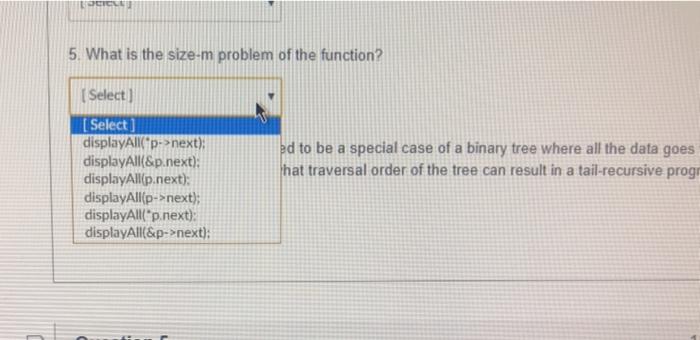
You want to write a recursive function: void displayAllkidNode p). The function prints the name and favorite color value (red, gm. blu) of all nodes stored in the linked list if the linked list is not empty. You can assume that p= head will be performed before calling this function, 1. What is the size-n problem of your function? Select) 2. What is the stopping condition of your program? Selecta 3. How do you print the name in the kidNode? [ Select] 4. How do you print the favorite color value (red, gm. blu) in the kidNode? | Select 5. What is the size-m problem of the function? Select) 6. A linked list can be considered to be a special case of a binary tree where all the data goes to the left sub-tree. In this case, what traversal order of the tree can result in a tail-recursive program? I Select] You want to write a recursive function, void displayAllkidNode 2) The function prints the name and favorite color value (red, grn, blu) of all nodes stored in the linked list if the linked list is not empty. You can assume that p = head will be performed before calling this function. 1. What is the size-n problem of your function? (Select in of your program? [ Select void displayAllkidNode &p) void displayAllkidNode tail) void displayAllkid Node pl void displayAllikid Node p 3. How do you print the name in the kidNode? [ Select] 4. How do you print the favorite color value (red grn, blu) in the kidNode? v [ Select) 5. What is the size-m problem of the function? [ Select) 6. A linked list can be considered to be a special case of a binary tree where all the data goes to the left sub-tree. In this case, what traversal order of the tree can result in a tail-recursive program? [ Select] and favorite color value (red, grn, blu) of all nodes stored in the linked list if the linked list is not empty. You can assume that p = head will be performed before calling this function 1. What is the size-n problem of your function? [ Select] 2. What is the stopping condition of your program? [Select] Select) NULL) If (&p ** NULL) If (p = tail) If (p NULL) If (p h the kidNode? 4. How do you print the favorite color value (red, grn, blu) in the kidNode? Selert 2. What is the stopping condition of your program? [ Select] 3. How do you print the name in the kidNode? [ Select] color value (red, grn, blu) in the kidNode? [ Select) printf("name %s". p->name): printf("name"%s", p->name); printf("name %s". &p.name); printf("name - %s". p.name): 5. What is the size-m problem of the function? [Select ] 6. A linked list can be considered to be a special case of a binary tree where all th 3. How do you print the name in the kidNode? Select 4. How do you print the favorite color value (red grm, blu) in the kidNode? [ Select Select if Ep.colorValue wredyprintreageer (p.colorValue gmi printfern"); ele printf("blue") if (p.color Valuered) printfired); else it (p.colorValue grn) printfern); else printf(blue) if (p-colorValue red) printfredy else if (e-colorValue, gr) printf"grn"); else printf("blue": ifp-colorValues red printf(red);else i 1-2 colorValue gm) printf(grn); else printf(blue): 6. A linked list can be considered to be a special case of a binary tree where all the data goes to the left sub-tree In this case, what traversal order of the tree can result in a tail-recursive program? Select LOCICLE 5. What is the size-m problem of the function? (Select) [ Select ] displayAll('p->next); displayAll(&p.next): displayAlip.next); displayAll{p->next); displayAll('p.next): displayAll(&p->next): ed to be a special case of a binary tree where all the data goes hat traversal order of the tree can result in a tail-recursive progn 5. What is the size-m problem of the function? [ Select] 6. A linked list can be considered to be a special case of a binary tree where all the data goes to the left sub-tree. In this case, what traversal order of the tree can result in a tail-recursive program? Select [ Select] in-order pre-order post-order All of them
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


