Question: You will be given a matrix A as a nested dictionary, the shape of the matrix as a tuple shape = (nm) and a (densely

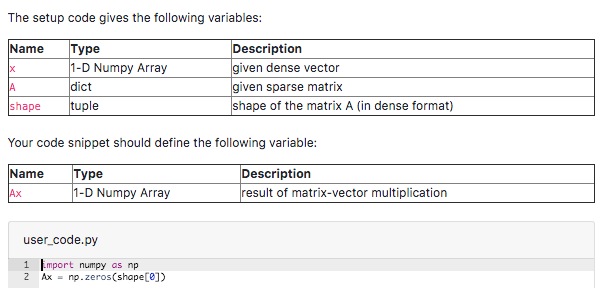
You will be given a matrix A as a nested dictionary, the shape of the matrix as a tuple shape = (nm) and a (densely stored) vector x as a numpy array. The nested dictionary storage for A works as follows: The outermost dictionary maps a row index of the matrix to another inner dictionary, representing the row. If a given row of A consists of all zeros, its row index will not be present in the dictionary. The inner dictionary maps the column index to an element of A. If an element of A is zero, the inner dictionary will not contain an entry for it. For example, the matrix TO 0 0 0 0 0 Lo 14 corresponds to the following Python data structure: 17 317 0 5 0 0 0 0] A = {0: {2: 17, 3: 31), 1: {3: 5), 3: (1: 14}} Write a code snippet that efficiently computes the matrix-vector multiplication Ax and stores the result in the the numpy array Ax. Your code should take take advantage of the sparse format of the matrix Ax. In other words, the amount of work should be proportional to the number of non-zero entries in A, and not proportional to nm, where n x m is the shape of A. You will likely get timed out if you don't take advantage of the sparsity of the given matrix The setup code gives the following variables: Name Type 1-D Numpy Array dict tuple Description given dense vector given sparse matrix shape of the matrix A (in dense format) shape Your code snippet should define the following variable: Name Type 1-D Numpy Array Description result of matrix-vector multiplication user_code.py 1 2 import numpy as np Ax = np.zeros(shape[0]) You will be given a matrix A as a nested dictionary, the shape of the matrix as a tuple shape = (nm) and a (densely stored) vector x as a numpy array. The nested dictionary storage for A works as follows: The outermost dictionary maps a row index of the matrix to another inner dictionary, representing the row. If a given row of A consists of all zeros, its row index will not be present in the dictionary. The inner dictionary maps the column index to an element of A. If an element of A is zero, the inner dictionary will not contain an entry for it. For example, the matrix TO 0 0 0 0 0 Lo 14 corresponds to the following Python data structure: 17 317 0 5 0 0 0 0] A = {0: {2: 17, 3: 31), 1: {3: 5), 3: (1: 14}} Write a code snippet that efficiently computes the matrix-vector multiplication Ax and stores the result in the the numpy array Ax. Your code should take take advantage of the sparse format of the matrix Ax. In other words, the amount of work should be proportional to the number of non-zero entries in A, and not proportional to nm, where n x m is the shape of A. You will likely get timed out if you don't take advantage of the sparsity of the given matrix The setup code gives the following variables: Name Type 1-D Numpy Array dict tuple Description given dense vector given sparse matrix shape of the matrix A (in dense format) shape Your code snippet should define the following variable: Name Type 1-D Numpy Array Description result of matrix-vector multiplication user_code.py 1 2 import numpy as np Ax = np.zeros(shape[0])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


