Question: You will implement an adjacency-list-based graph implementation where each node has a label (an integer between 1 and |V|) and a set nodes representing the
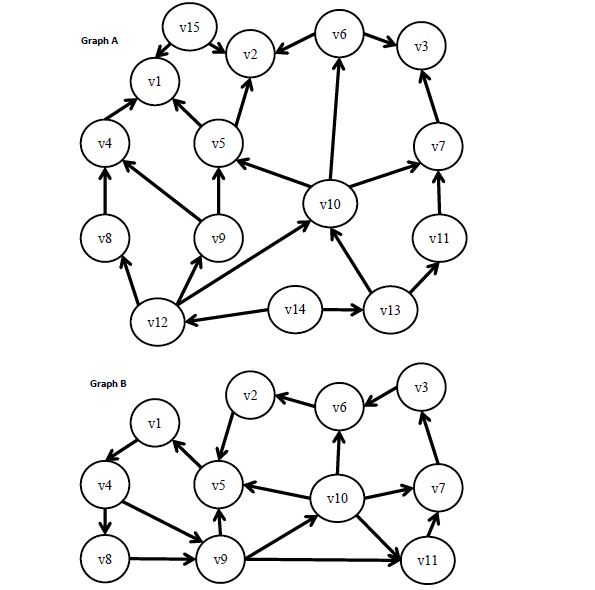
You will implement an adjacency-list-based graph implementation where each node has a label (an integer between 1 and |V|) and a set nodes representing the outgoing edges (see the last page for example). For simplicity, the nodes will store no additional values. Implement the following operations. These will be graded based on correctness and efficiency. DirectedGraph(String str) Initializes a directed graph from a string. The string representing the graph is in the following format: [v1, v2][v3, v4][v2, v3] where each [vi, vj] pair represents an edge between two vertices vi and vj. The constructor will parse the string and initialize a set of Graph Node objects. Collection getIncomingEdges(GraphNode v) In our implementation each node does not store incoming edges, only outgoing edges. This method will return the collection of nodes that have an edge directed to the given node v. boolean isDAG() Returns true if the graph is a directed acyclic graph. Collection getRoots() Returns the roots of the graph (i.e., the nodes with no incoming edges). int edgeCount() Returns the total number of edges in the graph. void printAsAdjacencyMatrix() Prints the graph as an adjacency matrix. List findCycle(GraphNode v) Returns a cycle for v, if one exists. Note that multiple cycles may exist, but this method will only return one, represented as a list of nodes. Hint: Note that many of these operations will rely on basic graph traversals (e.g., DFS, BFS). Test Cases: Initialize Graph A and Graph B. Apply isDAG, getRoots, edgeCount, and printAsAdjacencyMatrix on both graphs.
 Example Java-like code. Uncompiled, untested. class DirectedGraph { private Collection nodes; // Pick a reasonable collection (e.g., ArrayList, // std::vector, set, etc). public DirectedGraph(String str) { } public Collection getIncomingEdges(GraphNode v) { } public boolean isDAG() { } public Collection getRoots() { } public int edgeCount() { } public void printAsAdjacencyMatrix() { } public List findCycle(GraphNode v) { } } class GraphNode { private final int index; private final Collection outgoingEdges; public GraphNode(int index) { this.index = index; } }
Example Java-like code. Uncompiled, untested. class DirectedGraph { private Collection nodes; // Pick a reasonable collection (e.g., ArrayList, // std::vector, set, etc). public DirectedGraph(String str) { } public Collection getIncomingEdges(GraphNode v) { } public boolean isDAG() { } public Collection getRoots() { } public int edgeCount() { } public void printAsAdjacencyMatrix() { } public List findCycle(GraphNode v) { } } class GraphNode { private final int index; private final Collection outgoingEdges; public GraphNode(int index) { this.index = index; } }
Graph A v8 Graph B v8 v15 v6 v3 v1 v10 v11. v14. v13 v12 v3 v1 v10 v9 v11
 Example Java-like code. Uncompiled, untested. class DirectedGraph { private Collection
Example Java-like code. Uncompiled, untested. class DirectedGraph { private Collection


