Question: YS 250 - Introductory Physics I - Laboratory - Lab Form Index i Time t and Time Intervals At (s) Position x Velocity v t
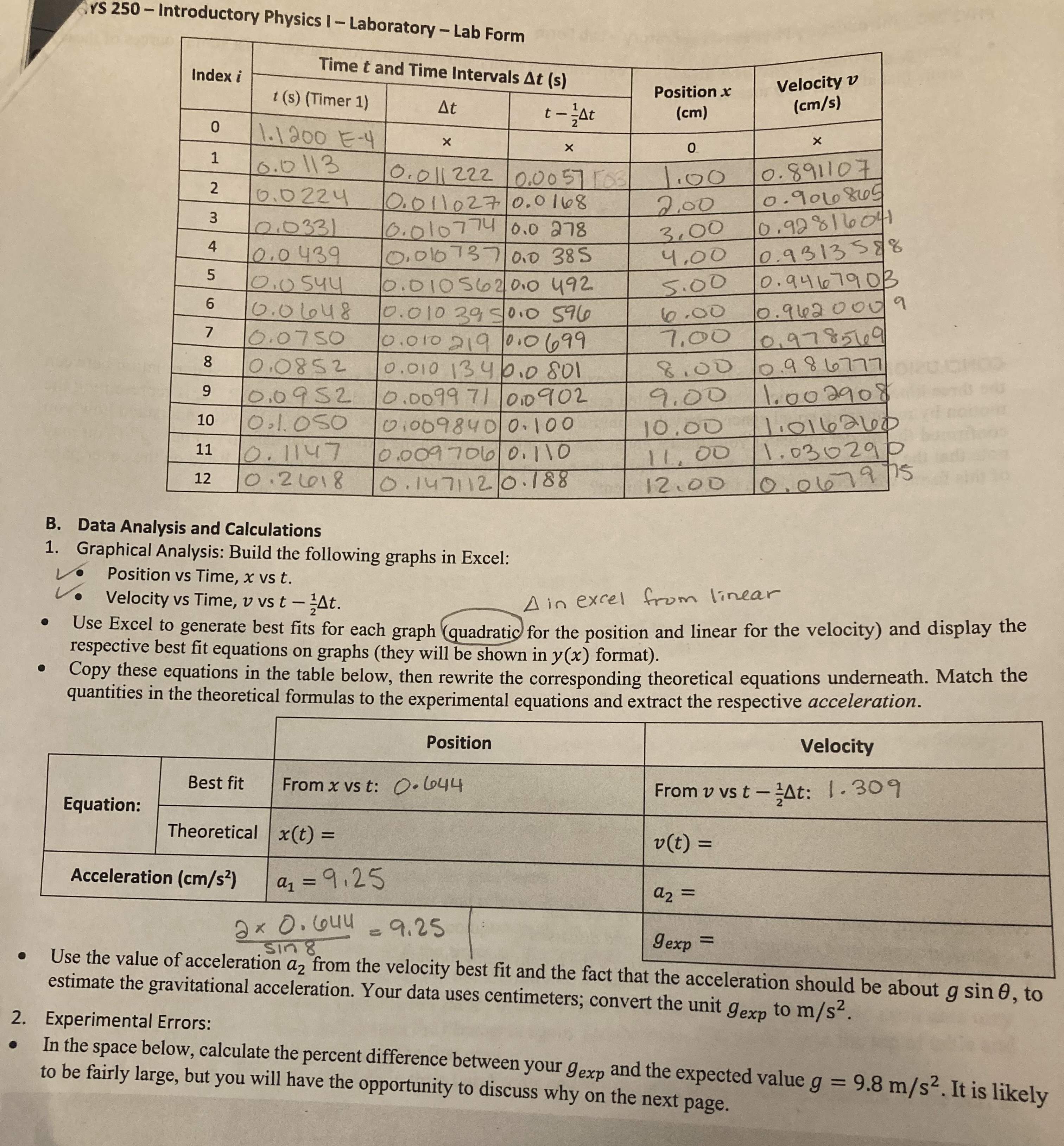
YS 250 - Introductory Physics I - Laboratory - Lab Form Index i Time t and Time Intervals At (s) Position x Velocity v t (s) (Timer 1) At t - zAt (cm) (cm/s) 0 1. 1200 E-y 1 0.0 113 2 0. 01 1 2 22 | 0. 0 057 1 1:00 0 . 891107 6.022 4 0. 0 1 1 027 0. 0168 3 2.00 0 . 906 865 2. 0331 6.010 774 0.0 278 3,00 0. 92 8 16 04 4 0. 0 439 0. 010 737 / 010 38 5 4,00 0 . 9 3 13 5 8 8 5 10.05 4 4 10. 0 10 5 6 2 / 010 492 5.00 0 . 946 79 03 6 0.06 4 8 0. 010 39 5/010 596 6.00 0. 962 0 00 / 9 7 10. 0750 0. 010 219 1010 69 9 7,00 0. 97 8 5409 8 010852 0 . 010 134 10.0 801 8.00 0. 9 8 67 7 7 9 10.09 52 0. 00 9 9 71 010 902 9.00 1.002908 10 0 . 1. 050 010098 40 0 . 100 10.00 1:0162 64 11 0. 1147 0. 009 706 0 . 110 11. 00 1. 03029 0 12 0. 24018 0 . 1471 12 0 . 188 12.00 10. 0679 B. Data Analysis and Calculations 1. Graphical Analysis: Build the following graphs in Excel: Position vs Time, x vs t. . Velocity vs Time, v vs t - 2At. A in excel from linear Use Excel to generate best fits for each graph (quadratic for the position and linear for the velocity) and display the respective best fit equations on graphs (they will be shown in y(x) format). Copy these equations in the table below, then rewrite the corresponding theoretical equations underneath. Match the quantities in the theoretical formulas to the experimental equations and extract the respective acceleration. Position Velocity Best fit From x vs t: 0. 644 From v vs t - ;At: 1 . 309 Equation: Theoretical x (t ) = v(t) = Acceleration (cm/s?) a1 = 9.25 a2 = 2 x 0. 64u = 9.25 . sin 8 Jexp = Use the value of acceleration a2 from the velocity best fit and the fact that the acceleration should be about g sin 0, to estimate the gravitational acceleration. Your data uses centimeters; convert the unit gexp to m/s2. 2 . Experimental Errors: In the space below, calculate the percent difference between your gexp and the expected value g = 9.8 m/s2. It is likely to be fairly large, but you will have the opportunity to discuss why on the next page
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


