Question: Expand Your Knowledge: Pooled Two-Sample Procedure Consider independent random samples from two populations that are normal or approximately normal, or the case in which both
Expand Your Knowledge: Pooled Two-Sample Procedure Consider independent random samples from two populations that are normal or approximately normal, or the case in which both sample sizes are at least 30.
Then, if s1 and s2 are unknown but we have reason to believe that s1 5 s2, we can pool the standard deviations. Using sample sizes n1 and n2, the sample test statistic x1 x2 has a Student’s t distribution, where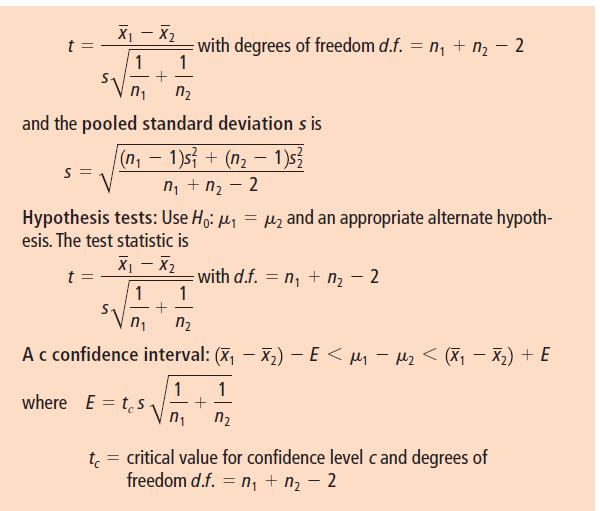
Note: With statistical software, select the pooled variance or equal variance options.
There are many situations in which we want to compare means from populations having standard deviations that are equal. This method applies even if the standard deviations are known to be only approximately equal. Consider Problem 19 regarding average incidence of fox rabies in two regions. For region I, n1 5 16, x1 5 4.75, and s1
(a) Use the method of pooled standard deviation to redo Problem 19(a).
(b) Use the method of pooled standard deviation to redo Problem 19(b).
- X1 X2 1 1 with degrees of freedom d.f. = n + n-2 and the pooled standard deviation s is (n-1)s+ (n-1)s S , - 2 Hypothesis tests: Use Ho: = and an appropriate alternate hypoth- esis. The test statistic is t X1-X2 1 1 + with d.f. nn - 2 - - A c confidence interval: (x) - E < M - M2 < ( x) + E 1 1 where E=ts + n t = critical value for confidence level c and degrees of freedom d.f. n + n - 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


