Rising atmospheric CO 2 and higher tree mortality associated with climate change have been hypothesized to drive
Question:
Rising atmospheric CO2 and higher tree mortality associated with climate change have been hypothesized to drive increases in the abundance of lianas (climbing woody vines) in tropical forests. Laurance et al. (2014) counted the number of lianas in a series of 1-ha plot sites located in primary Amazonian forest in two surveys. The first survey was conducted between 1997 and 1999 and the second survey was an average of 13.6 years later, in 2012. A plot of the results is shown. The data from 12 sites are provided in the table.
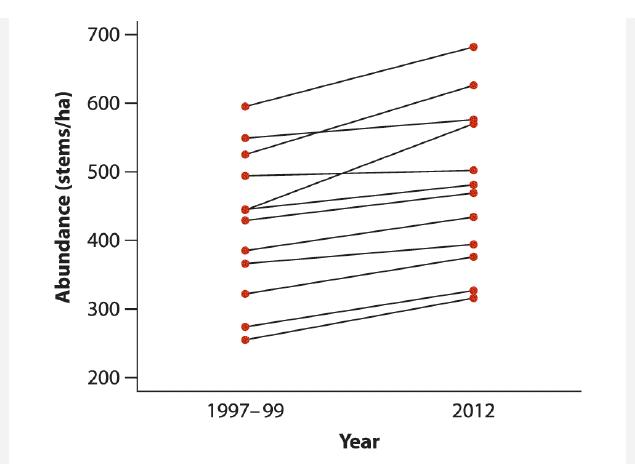
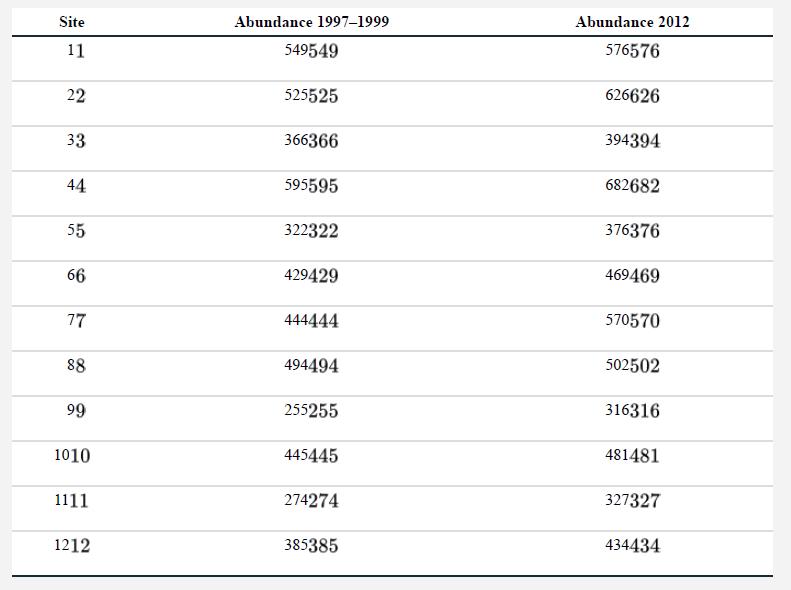
a. Compute the mean abundance of lianas on the dates of the two surveys.
b. Did the abundance of lianas change significantly between the two surveys? Carry out the appropriate test.
c. How large was the increase? To decide, calculate the 95% confidence interval for the mean change in liana abundance between the two survey dates.
Step by Step Answer:

The Analysis Of Biological Data
ISBN: 9781319226237
3rd Edition
Authors: Michael C. Whitlock, Dolph Schluter





