Question: 29. Consider a single-server queueing system in which customers arrive in accordance with a renewal process. Each customer brings in a random amount of work,
29. Consider a single-server queueing system in which customers arrive in accordance with a renewal process. Each customer brings in a random amount of work, chosen independently according to the distribution G. The server serves one customer at a time. However, the server processes work at rate i per unit time whenever there are i customers in the system. For instance, if a customer with workload 8 enters service when there are three other customers waiting in line, then if no one else arrives that customer will spend 2 units of time in service. If another customer arrives after 1 unit of time, then our customer will spend a total of 1.8 units of time in service provided no one else arrives.
LetWi denote the amount of time customer i spends in the system. Also, define E[W] by
![]()
and so E[W] is the average amount of time a customer spends in the system.
Let N denote the number of customers that arrive in a busy period.
(a) Argue that E[W] = E[W1 + · · · + WN]/E[N]
Let Li denote the amount of work customer i brings into the system; and so the Li , i 1, are independent random variables having distribution G.
(b) Argue that at any time t, the sum of the times spent in the system by all arrivals prior to t is equal to the total amount of work processed by time t.
Hint: Consider the rate at which the server processes work.
(c) Argue that
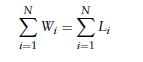
(d) Use Wald’s equation (see Exercise 13) to conclude that E[W] = μ
where μ is the mean of the distribution G. That is, the average time that customers spend in the system is equal to the average work they bring to the system.
E[W]= lim (W++ Wn)/n 11-00
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


