Air is contained in a pistoncylinder assembly at 2 MPa and 400 K (state 1). The 0.15-m-diameter
Question:
Air is contained in a piston–cylinder assembly at 2 MPa and 400 K (state 1). The 0.15-m-diameter piston is locked in place by stops at the 0.2-m position, and a 2-kg steel block sits on top of the piston, as shown in the sketch. The mass of the piston is 0.1 kg. The stops are removed and the rapidly expands until the piston comes to rest at the upper position (x = 0.4 m), while the block continues upward as shown in the sketch on the right. The temperature is 310 K (state 2). Assume that the process is so rapid that it can be considered adiabatic and that the constant-pressure specific heat is constant (cp= 1.013 kJ/ kg · K). The atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa.
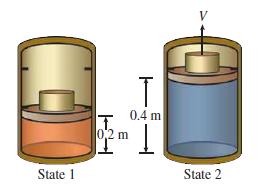
A. Considering the air, piston, cylinder, and the block to be the system, determine the work done by the system on the surroundings.
B. Determine the velocity of the steel block immediately after the piston comes to rest.
C. Neglecting drag, determine the maximum height achieved by the block measured from the bottom of the cylinder.
Step by Step Answer:

Thermodynamics Concepts And Applications
ISBN: 9781107179714
2nd Edition
Authors: Stephen R. Turns, Laura L. Pauley





