Question: Super View Companys comparative balance sheets and its current income statement are presented below. Super View Company Income Statement For the year ended December 31
Super View Company’s comparative balance sheets and its current income statement are presented below.
Super View Company
Income Statement
For the year ended December 31
Current Year
Sales……………………………………………. $ 1,875,000
Cost of Goods Sold…………………………..… 1,125,000
Gross Profit……………………………………... $ 750,000
Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses… $ 998,500
Bad Debt Expense………………………………. 65,500
Depreciation Expense…………………………… 200,000
Amortization Expense…………………………… 30,000
Total Operating Expenses……………………….. $ 1,294,000
Loss before Interest and Taxes…………………... $ (544,000)
Interest Expense…………………………………. (75,110)
Franchise Fees……………………………………. 8,950
Loss from Continuing Operations before Tax….... $ (610,160)
Income Tax Benefit (Expense)…………………… $ 244,064
Increase in Valuation Allowance…………………. (44,064)
Net Tax Benefit…………………………………… $ 200,000
Loss from Continuing Operations…………………. $ (410,160)
Discontinued Operations–net of tax……………….. 20,500
Net Loss……………………………………………. $ (389,660)
Additional Information:
1. Super View did not sell any plant or intangible assets during the current year. It acquired equipment and a new franchise during the year using cash.
2. Super View reports accounts receivable net of the allowance for bad debts.
3. The deferred-tax asset is caused by a net operating loss; Super View reported it net of a valuation allowance estimated at $ 44,064.
4. Due to its net operating loss, the company was not able to declare and pay dividends this year. 5. N o debt payments were made this year.
6. Due to the net operating loss, there are no taxes due and payable for the current year. The company did pay the amount of taxes payable from the prior year.
7. Supper View reported the income from discontinued operations net of tax and as a cash transaction.
Required
Prepare the company’s cash flow statement for the current year under the indirect method and present required disclosures.
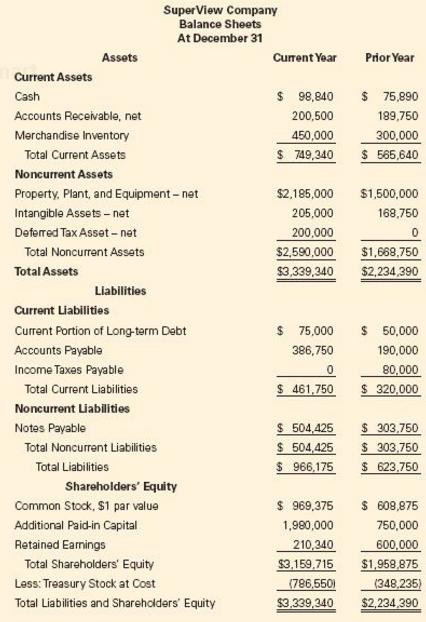
SuperView Company Balance Sheets At December 31 Assets Current Year Prior Year Current Assets $ 98,840 75,890 189.750 300,000 749,340 565,640 Accounts Receivable, net Merchandise Inventory 200,500 450,000 Total Current Assets Noncurrent Assets Property, Plant, and Equipment-net Intangible Assets -net Deferred TaxAsset net $2,185,000 $1500,000 168,750 200,000 0 $2590000 $1.668 750 $3,339,340 $2,234,390 205,000 Total Noncurrent Assets Total Assets Liabilities Current Liabilities Current Portion of Long term Debt Accounts Payable Income Taxes Payable S 75,000 386,750 50,000 190,000 80,000 Total Current Liabilities Noncurrent Liabilities Notes Payable 461.750 320,000 S 504 425 S 303750 504,425 303.750 $ 966,175 623,750 Total Noncurrent Liabilities Total Liabilities Shareholders' Equity Common Stock, $1 par value Additional Paid-in Capital Retained Earnings $ 969.375 608.875 750,000 210.340 600000 $3,159.715 $1958 875 ,980,000 Total Shareholders Equity Less: Treasury Stock at Cost Total Liabilities and Shareholders Equity (7865501348 235 3,339.340 $,234.390
Step by Step Solution
3.25 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The first step in the solution is to isolate all balance sheet changes and classify the changes as operating investing or financing Analysis of Balance Sheet Changes and Cash Flow Classification Asset... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
578-B-A-B-S-C-F (1967).docx
120 KBs Word File


