Question: Suppose that an object can be at any one of n+1 equally spaced points x 0 , x 1 . . . x n .
Suppose that an object can be at any one of n+1 equally spaced points x0, x1. . . xn. When an object is at location xi, it is equally likely to move to either xi−1 or xi+1 and cannot directly move to any other location. Consider the probabilities {Pi}ni=0 that an object starting at location xi will reach the left endpoint x0 before reaching the right endpoint xn. Clearly, P0 = 1 and Pn = 0. Since the object can move to xi only from xi−1 or xi+1 and does so with probability 1/2 for each of these locations, Pi = 1/2 Pi−1 + 1/2 Pi+1, for each i = 1, 2. . . n − 1.
a. Show that
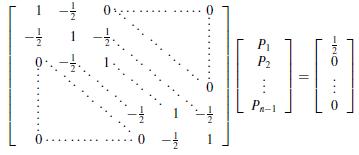
b. Solve this system using n = 10, 50, and 100.
c. Change the probabilities to α and 1 − α for movement to the left and right, respectively, and derive the linear system similar to the one in part (a).
d. Repeat part (b) with α = 1/3 .
1-2 0 0 1 1-2 12 0 0 12 1 1-2 1-2
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (185 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a We have P 0 1 so the equation P 1 12 P 0 12 P 2 gives P 1 12 P 2 12 Since P i 12 P i1 12 P i1 we h... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
731-M-N-A-N-L-A (722).docx
120 KBs Word File


