Question: The Levinson-Durbin algorithm described in section 11.3.1 solved the linear equations ? m a m? = ? ? m where the right-hand side of this
The Levinson-Durbin algorithm described in section 11.3.1 solved the linear equations
?mam?= ? ?m
where the right-hand side of this equation has elements of the autocorrelation sequence that are also elements of the matrix ?. Let us consider the more general problem of solving the linear equations
?mbm = cm
where cm is an arbitrary vector. (The vector bm is not related to the coefficients of the backward predictor.) Show that the solution to ?mbm = cm?can be obtained from a generalized Levinson-Durbin algorithm which is given recursively as
bm(m) = c(m) - ?bIm ? 1bm ? 1/Efm ? 1
bm(k) = bm ? 1(k) ? bm(m)avm ? 1(m ? k)?k = 1, 2, . . . ., m ? 1
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?? m = 1, 2. . . p ?
Where bI(1) = c(1)/?xx(0) = c(1)/Ef0?and am(k) is given by (11.3.17). Thus a second recursion is required to solve the equation ?mbm = cm.
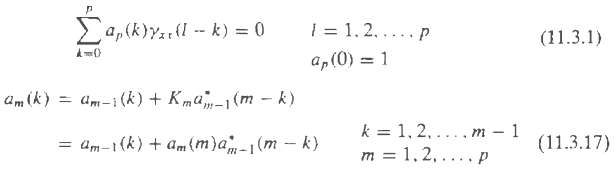
| = 1, 2. .... p La, (k)Yz:{l -- k) = 0 (11.3.1) ap(0) = 1 am (k) = am-i(k) + Kma-1 (m - k) k = 1, 2,...., m - k) = Um-1 (k) + am (m)a-1(m - (11.3.17) m = 1.2,....p
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Let Then dm1 Em bm1 8 m 246 2m tm1 mm mm Im1 21 0 bm 1 Hence Im1m1E... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
31-E-T-E-D-S-P (939).docx
120 KBs Word File


