Question: The Streeter-Phelps model can be used to compute the dissolved oxygen concentration in a river below a point discharge of sewage (Figure), o = o
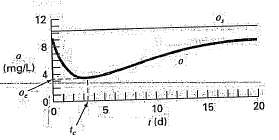
The Streeter-Phelps model can be used to compute the dissolved oxygen concentration in a river below a point discharge of sewage (Figure),
o = os?? kdLo/kd + ks ? ka (e?kat?? e?(kd + ks)t) ? Sb/ka?(1 ? e?kat)
where o = dissolved oxygen concentration [mg/L], os = oxygen saturation concentration [mg/L], t = travel time [d], Lo = biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) concentration at the mixing point [mg/L], kd = rate of decomposition of BOD [d-1], ks = rate of setting of BOD [d-1], ka = reaeration rate [d-1], and Sb = sediment oxygen demand [mg/L/d]. As indicated in Figure. Eq (P16.16) produces an oxygen ?sag? that reaches a critical minimum level oc some travel time tc below the point discharge. This point is called ?critical? because it represents the location where biota that depend on oxygen (like fish) would be the most stressed. Determine the critical travel time and concentration, given the following values:
os = 10 mg/L? ?? ? ? ? ? ??kd = 0.2 d?1? ? ??? ? ? ? ? ??ka = 0.8 d?1
?ks = 0.06 d?1 ?? ? ? ? ? ??Lo = 50 mg/L? ?? ? ? ? ? ??Sb = 1 mg/L/d
12 (mg/L) 20 15 10 5.
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
A plot of the function indicates a m... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
45-M-N-A-O (62).docx
120 KBs Word File


