Question: This exercise will lead you through a proof of Chebyshevs inequality. Let X be a continuous random variable with probability density function f (x). Suppose
This exercise will lead you through a proof of Chebyshev’s inequality. Let X be a continuous random variable with probability density function f (x). Suppose that P(X
a. Show that
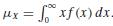
b. Let k >0 be a constant. Show that μX ≥
![]()
c. Use part (b) to show that P(X ≥ k) ≤ μX /k. This is called Markov’s inequality. It is true for discrete as well as for continuous random variables.
d. Let Y be any random variable with mean μY and variance σ2Y. Let X = (Y − μY)2. Show that μX = σ2Y.
e. Let k > 0 be a constant. Show that P(|Y −μY| ≥ kσY ) = P(X ≥ k2σ2Y).
f. Use part (e) along with Markov’s inequality to prove Chebyshev’s inequality: P(|Y − μY| ≥ kσY ) ≤ 1/k2.
Hy = 10 xf(x) dx kf(x)dx = k P (X > k).
Step by Step Solution
3.23 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b c X k kPX kk PX k d X YY 2 2 Y e PY Y k ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
944-M-S-P (8447).docx
120 KBs Word File


