Use the following differential equations to compute the velocity and position of a soccer ball that is
Question:
Use the following differential equations to compute the velocity and position of a soccer ball that is kicked straight up in the air with an initial velocity of 40 m/s:
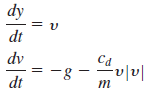
Where y = upward distance (m), t = time (s), y = upward velocity (m/s), g = gravitational constant (= 9.81 m/s2), cd = drag coefficient (kg/m), and m = mass (kg). Note that the drag coefficient is related to more fundamental parameters by
Cd = ½ pACd
Where r = air density (kg/m3), A = area (m2), and Cd = the dimensionless drag coefficient. Use the following parameter values for your calculation: d = 22 cm, m = 0.4 kg, r = 1.3 kg/m3 and Cd = 0.52.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Numerical Methods for Engineers
ISBN: 978-9352602131
7th edition
Authors: Steven C. Chapra, Raymond P. Canale
Question Posted:





