Question: (a) Determine the signal sequences y(n) generated using zero-order interpolation and linear interpolation and then compute the total harmonic distortion (THD) in each case for
(a) Determine the signal sequences y(n) generated using zero-order interpolation and linear interpolation and then compute the total harmonic distortion (THD) in each case for N = 32, 64, 128.
(b) Repeat part (a) assuming that all sample values are quantized to 8 bits.
(c) Show that the interpolated signal sequences y(n) can be obtained by the system shown in figure(b). The first module inserts one zero sample between successive samples of x(n). Determine the system H(z) and sketch its magnitude response for the zero-order interpolation and for the linear interpolation cases. Can you explain the difference in performance in terms of the frequency response function?
(d) Determine and sketch the spectra of the resulting sinusoids in each case both analytically [using the results in part (c)] and evaluating the DFT of the resulting signals.
(e) Sketch the spectra of xi(n) and y(n), if x(n) has the spectrum shown in figure(c) for both zero-order and linear interpolation. Can you suggest a better choice forH(z)?
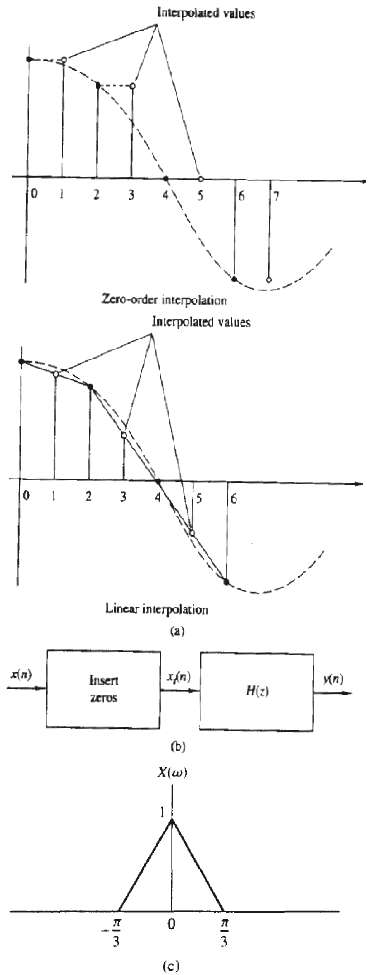
Interpolated values Zero-order interpolation Interpolated values Lincar interpolation (a) n) xfn) Kn) Insert Hz) zeros (b) X(w) (c)
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Refer to figure b Refer to ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
31-E-T-E-D-S-P (906).docx
120 KBs Word File


