Question: A liquid-liquid extraction process is conducted batchwise as shown in Figure. The process begins in vessel 1 (original), where 100 mg each of solutes A
A liquid-liquid extraction process is conducted batchwise as shown in Figure. The process begins in vessel 1 (original),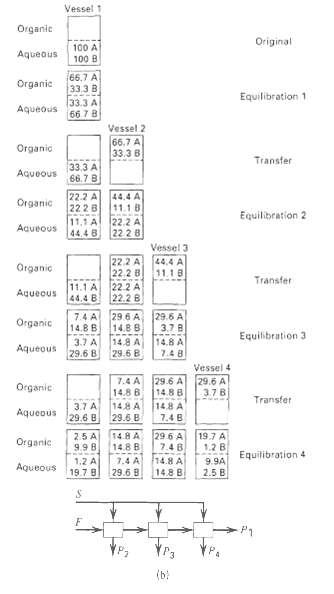 where 100 mg each of solutes A and B are dissolved in 100 ml of water. After adding 100 ml of an organic solvent that is more selective for A than B, the distribution of A and B becomes that shown for equilibration 1 with vessel 1. The organic-rich phase is transferred to vessel 2 (transfer), leaving the water-rich phase in vessel 1 (transfer). Assume that water and the organic solvent are immiscible. Next, 100 ml of water is added to vessel 2, resulting in the phase distribution shown for vessel 2 (equilibration 2). Also, 100 ml of organic solvent is added to vessel 1 to give the phase distribution shown for vessel 1 (equilibration 2). The batch process is continued by adding vessel 3 and then 4 to obtain the results shown.(a) Carefully study the process in Figure and then draw a corresponding cascade diagram, labeled in a manner similar to Figure (b).(b) Is the process of the cocurrent, countercurrent, or crosscurrent type?(c) Compare the separation achieved with that for a single-batch equilibrium step.(d) How could the process be modified to make it a countercurrent cascade.
where 100 mg each of solutes A and B are dissolved in 100 ml of water. After adding 100 ml of an organic solvent that is more selective for A than B, the distribution of A and B becomes that shown for equilibration 1 with vessel 1. The organic-rich phase is transferred to vessel 2 (transfer), leaving the water-rich phase in vessel 1 (transfer). Assume that water and the organic solvent are immiscible. Next, 100 ml of water is added to vessel 2, resulting in the phase distribution shown for vessel 2 (equilibration 2). Also, 100 ml of organic solvent is added to vessel 1 to give the phase distribution shown for vessel 1 (equilibration 2). The batch process is continued by adding vessel 3 and then 4 to obtain the results shown.(a) Carefully study the process in Figure and then draw a corresponding cascade diagram, labeled in a manner similar to Figure (b).(b) Is the process of the cocurrent, countercurrent, or crosscurrent type?(c) Compare the separation achieved with that for a single-batch equilibrium step.(d) How could the process be modified to make it a countercurrent cascade.
Vessel 1 Organie Original 100 A 100 B Aqueous 66,7 A 33.3 B Organic Equilibration 1 33.3 A 66 7 8 Aqueous Vessel 2 66,7 A 33.3 B Organic Transfer 33,3 A 66.7 B Aqueous 22.2 A 2228 11,1 A 44.4 8 Organic 11.1 Equilibration 2 22.2 A 22 2 8 Aaueous Vessel 3 44,4 A 11.18 22.2 A 22.2 8 22.2 A 22.2 B Organic Transfer 11.1 A 44.4 8 Aquecus 29.6 A 3.7 B 7.4 A 14.8 B 29.6 A 14.8 8 14.8 A 29.6 B Organic Equilibration 3 14.8 A 7.4 8 3.7 A Aqueous 29.6 8 Vessel 4 7.4 A 29.6 A 14.8 B 14.8 A 7.4 B 29.6 A 3.78 Organic 14.8 8 14,8 A 29.6 B Transfer 3.7 A 29.6 B Aqueous 25 A 9.98 14.8 A 14.8 B 29.6 A 7.4 8 19.7 A 1.2 B Organic Equilibration 4 1,2 A 7.4 A 29.6 8 14.8 A 9.9A Aqueous 19.7 8 14.8 B 2.5 B P1 (b
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a A cascade diagram representing Fig is the following b The above cascade is a twodimensional tri... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
37-E-C-E-S-P (166).docx
120 KBs Word File


