Question: Hydrogen gas is used in a process to manufacture a sheet material of 6-mm thickness. At the end of the process, H2 remains in solution
Hydrogen gas is used in a process to manufacture a sheet material of 6-mm thickness. At the end of the process, H2 remains in solution in the material with a uniform concentration of 320 k mol/m3. To remove H2 from the material, both surfaces of the sheet are exposed to an air stream at 500 K and a total pressure of 3 atm. Due to contamination, the hydrogen partial pressure is 0.1 atm in the air stream, which provides a convection mass transfer coefficient of 1.5 m1h. The mass diffusivity and solubility of hydrogen (A) in the sheet material (B) are DAB = 2.6 x 10-8 m2/s and SAB = 160k mol/m 3 ? atm, respectively.
(a) If the sheet material is left exposed to the air stream for a long time, determine the final content of hydrogen in the material (kg/m3).
(b) Identify and evaluate the parameter that can be used to determine whether the transient mass diffusion process in the sheet can be assumed to be characterized by a uniform concentration at any time during the process.
(c) Determine the time required to reduce the hydrogen mass density at the center of the sheet to twice the limiting value calculated in part (a).
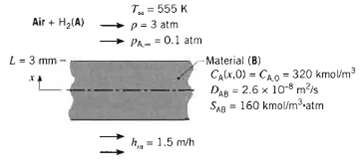
T= 555 K Air + H,(A) p-3 atm PA-=0.1 atm L- 3 mm Material (B) CAlx.O) = CAo - 320 kmolm Das = 2.6 x 10 mis SAg = 160 kmol/matm h = 1.5 m/h
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Sheet material has high uniform concentration of hydrogen at the end of a process and is then subjected to an air stream with a specified low concentration of hydrogen Mass transfer parameters s... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (1397).docx
120 KBs Word File


