In an industrial plant a shell-and-tube heat exchanger is heating pressurized dirty water at the rate of
Question:
In an industrial plant a shell-and-tube heat exchanger is heating pressurized dirty water at the rate of 38 kg/s from 60 to 110°C by means of steam condensing at 115°C on the outside of the tubes. The heat exchanger has 500 steel tubes (ID = 1.6 cm, OD = 2.1 cm) in a tube bundle which is 9 m long. The water flows through the tubes while the steam condenses in the shell. If it may be assumed that the thermal resistance of the scale on the inside pipe wall is unaltered when the mass rate of flow is increased and that changes in water properties with temperature are negligible, estimate
(a) The heat transfer coefficient on the water side and
(b) The exit temperature of the dirty water if its mass rate of flow is doubled.
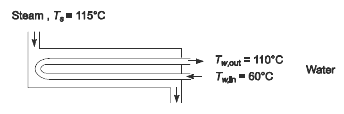
GIVEN
- Shell-and-tube heat exchanger - dirty water in steel tubes, steam condensing in shell
- Water flow rate (mw) = 38 kg/s
- Water temperatures
- Tw,in = 60°C
- Tw,out = 110°C
- Steam temperature (Ts) = 115°C
- Number of tubes (N) = 500
- Tube diameters
- Di = 1.6 cm = 0.016 m
- Do = 2.1 cm = 0.021 m
- Tube bundle length (L) = 9 m
ASSUMPTIONS
- The thermal resistance of the scale in the pipe is unaltered when the mass flow rate is increased
- Changes in water properties with temperature are negligible
- Two, or a multiple of two, passes
- The dirty water has the same thermal properties as clean water
Step by Step Answer:

Principles of heat transfer
ISBN: 978-0495667704
7th Edition
Authors: Frank Kreith, Raj M. Manglik, Mark S. Bohn





