Question: Leah Sanchez is concerned that if she orders too few calendars, customers disappointment in not finding a calendar might drive them to shop elsewhere, resulting
Leah Sanchez is concerned that if she orders too few calendars, customers’ disappointment in not finding a calendar might drive them to shop elsewhere, resulting in more of a loss over the long term than just the $9.00 of lost profit on the calendar. Modify the model in Figure11.7 by adding a row that calculates unmet demand (number of calendars not sold, but could have been if a sufficient number were ordered). Assume Leah assigns $3.00 to each unmet-demand calendar as the additional opportunity cost due to future lost sales. For example, if Leah ordered 650 calendars and 700 are demanded, 50 calendars is the unmet demand and $150 is the additional opportunity cost. Incorporate this additional cost into your model. How many calendars would you recommend that Leah order based on this new model?
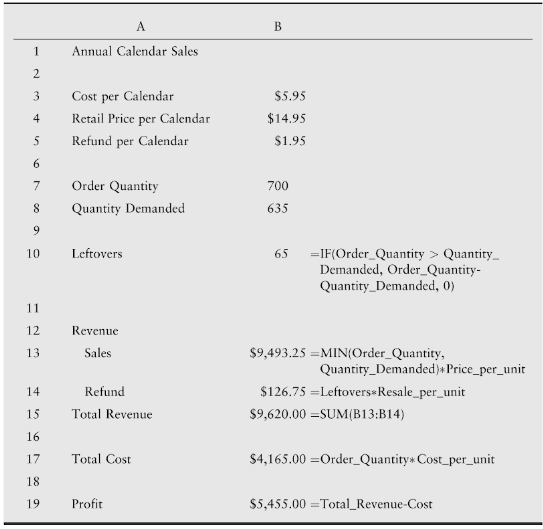
Annual Calendar Sales Cost per Calendar $5.95 Retail Price per Calendar $14.95 Refund per Calendar $1.95 Order Quantity 700 Quantity Demanded 635 Leftovers =IF(Order_Quantity > Quantity_ Demanded, Order_Quantity- Quantity_Demanded, 0) 10 65 11 12 Revenue Sales $9,493.25 =MIN(Order_Quantity, 13 Quantiry_Demanded)+ Price_per_unit $126.75 =Leftovers Resale_per_unit Refund 14 Total Revenue 15 $9,620.00 =SUM(B13:B14) 16 $4,165.00 =Order_Quantity* Cost_per_unit Total Cost 17 18 Profit $5,455.00 =Total_Revenue-Cost 19
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The new consequence measure is labeled Profit and includes the opportunity cost of missing sales due ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
668-M-S-S-M (1016).docx
120 KBs Word File


