Question: This problem involves the use of crosscorrelation to detect a signal in noise and estimate the time delay in the signal. A signal x(n) consists
This problem involves the use of crosscorrelation to detect a signal in noise and estimate the time delay in the signal. A signal x(n) consists of a pulsed sinusoid corrupted by a stationary zero-mean white noise sequence. That is,
x(n) = y(n – n0) + ω(n) 0 ≤ n ≤ N – 1
where ω(n) is the noise with variance σ2ω and the signal is
y(n) = A cosω0n, 0 ≤ n ≤ N – 1
= 0, otherwise
The frequency ω0 is known but the delay n0, which is a positive integer, is unknown, and is to be determine by crosscorrelating x(n) with y(n). Assume that N > M + n0. Let
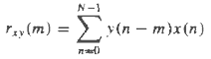
Denote the crosscorrelation sequence between x(n) and y(n). in the absence of noise this function exhibits a peak at delay m = n0. Thus n0 is determined with no error. The presence of noise can lead to errors in determining the unknown delay.
(a) For m = n0, determine E[rxy(n0)]. Also, determine the variance, var[rxy(n0)], due to the presence of the noise. In both calculations, assume that the double frequency term averages to zero. That is, M » 2π/ω0.
(b) Determine the signal-to-noise ratio, defined as
SNR = {E[rxy(n0)]}2 / var[rxy(n0)]
(c) What is the effect of the pulse duration M on the SNR?
N-1 (m) %3D - )x ()
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b c As M increase... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
31-E-T-E-D-S-P (995).docx
120 KBs Word File


